Peripheral Arterial and Venous Disease Flashcards
What is the role of the deep fascia in the leg?
The deep fascia surounds the calf muscle. This means that when the muscles contract, the pressure rises which allows venous flow to go up.
What are the key deep veins in the leg?
- External iliac vein
- Femoral vein
- Popliteal vein

What are the key superficial veins in the leg?
Long saphenous vein (drains into femoral triangle)
Short saphenous vein (drains into popliteal fossa)
Where is the long saphenous vein?
This is the one constant vein.
ALWAYS infront of the medial malleolus.
It is important as can use it to get fluid into venous system.
What are the roles of valves?
Prevent backflow.
How is venous blood returned to heart?
Blood flows from superficial to deep.
Deep via calf muscle pump pushes blood back to the heart
What are varicose veins?
Varicose veins are tortuous, twisted or lengthened veins.
Where are common sites of varicose veins?
Long saphenous
Short saphenous
What causes varicose veins?
The vein wall is inherently weak in varicose veins,
which leads to dilatation and separation of valve
cusps**so that they become**incompetent
What are the symptoms of varicose veins?
- Heaviness
- Tenson
- Aching
- Itching
Only attribute it if along the vein itself.
What are the complications if a patient has venous hypertension in the lower limb?
From the vein itself
- Haemorrhage
- Thrombophlebitis
From venous hypertension
- Oedema
- Skin pigmentation
- Varicose eczema
- Lipodermatosclerosis
- Venous ulceration
How do you stop bleeding from varicose veins?
Lie the patient down and elivate the leg.
(Bleeding from varicose veins usually occurs in the shows as the patient is standing (gravity) and hot (venodilation)
What is thrombophlebitis?
Low blood velosity which results in thrombosis.
Venous thrombosis produces an inflammatory response, including PAIN (bad pain)
What is haemosiderin staining?
Oxidising iron in blood from ferrous to ferric.
So, see rust under the skin.
Varicose eczema
- Lower limb
- Very itchy
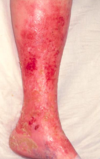
What is Lipodermatosclerosis?
Thickening of the fat in the skin,
Can lead to venous ulceration

Venous ulceration
It is venous hypertension that leads to venous ulceration.
Venous hypertension is a result of calf muscle pump failure.
What are the causes of calf muscle pump failure?
- ‘Failure; of calf muscle contraction - immobility, obesity, reduced hip, knee and/or ankle movement
- Deep vein incompetence
- Volume overload - superficial vein incompetence (as blood goes through the valve the wrong way and into calf muscle pump. So, overfilling of calf muscle pump)
What is Virchow’s triad?
Thrombosis occurs when there is:
- Changes in the lining of the vessel wall
- Changes in the flow of blood
- Changes in the constituents of blood
What is the most common cause of arterial thrombosis?
Changing in the lining of the vessel wall
What is the most common cause of venous thrombosis?
Changes in blood flow - Stasis leads to venous thrombosis
Why does stasis lead to venous thrombosis?
In reality it is usually stasis plus another ‘provocateur’ – surgery
(trauma), oral contraceptive pill, dehydration, cancer.
Arterial thrombosis in response to bleeding involves platelets, extrinsic and then intrinsic pathways. Arterial thrombi are platelet rich
Venous bleeding
Venous thrombosis does not involve platelets in
a major way, initially the intrinsic pathway is
involved and then the extrinsic. Venous thrombi
are fibrin rich.
Low flow initiates Venous thrombosis
What does DVT produce?
Most commonly begins in the deep calf veins.
Produced an inflammatory response.
- Calor
- Dolor
- Functio laesa
- Rubor
- Tumor




