Pelvis and Perineum I Practice Questions Flashcards
Describe the bones and joints of the pelvis
Anterior View


Describe the bones and joints of the pelvis
Posterior


Joints of the Pelvic Girdle


Differentiate between male and female pelvis
- Narrow arch in male
- Wider arch in female pelvis

Identify the muscles of the pelvic walls

- Piriformis (covers posterior wall of the pelvis)
- Obturator internus (covers lateral walls)

Identify the muscles of the pelvic floor

- Levator ani (Puborectalis + Pubococcygeus +Iliococcygeus)
- Coccygeus

Explain the function of the pelvic diaphragm
Pelvic diaphragm = levator ani and coccygeus muscles.
– (Innervated by pudendal nerve: S2, 3, 4)
– Supports pelvic viscera
– Resists increases in intra-abdominal pressure.
– Controls the openings of the rectum, urethra, and vagina
– On contraction, raises the entire pelvic floor.
Describe the perineum
Diamond-shaped area between thighs.
Located inferior to the pelvic diaphragm (levator ani).
Divided into urogenital triangle and anal triangle.
Contains structures that support pelvic organs that play a vital role in urination, defecation, sexual intercourse and childbirth.
Describe the Urogenital triangle of the Perineum
– Area between ischiopubic rami and a line joining ischial tuberosities.
– Contains external genitalia and urethra
– Roots of the external genitalia
– In women, the openings of the urethra and the vagina.
– In men, the distal part of the urethra is enclosed by
erectile tissue and opens at the end of the penis
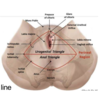
Describe the Anal triangle of the Perineum
– Area between coccyx, sacrotuberous ligaments and a line joining ischial tuberosities.
– Contains anus (anal orifice and external anal sphincter), & ischioanal fossa
Fat-filled area surrounding the anal canal.
Anal aperture
– The opening of the anus.
External anal sphincter muscle
– Voluntary muscle responsible for opening and closing the anus.
Two ischioanal fossae
– Wedge-shaped spaces filled with fat and connective tissue.
– Located laterally to the anus.

Rectal–Anal Inhibitory Reflex (RAIR)
hint: “sampling reflex”
when the rectum becomes distended, the internal sphincter relaxes and the external sphincter contracts and allows for “sampling” of rectal content by the nerve endings of the anal canal; can differentiate between liquid, solid, and gas
RAIR lost in Hirschsprung disease
Explain the importance of the perineal body
Perineal Body
(Central Tendon of the Perineum)

A fibromuscular mass
• Located in the center of the perineum between the anal canal and vagina (or bulb of the penis).
Functions:
Support and attachment point for muscles of perineum and levator ani.
In women, acts as a tear resistant body between the vagina and the external anal sphincter.
A 3D CT scan of the pelvis shows an abnormality due to trauma sustained in a car accident.
What is the name of the joint (indicated by the dashed line) that is dislocated?

Pubic symphysis
A urologist is questioning medical students during clinical rotation about the anatomy of the urogenital triangle. After the skin and subcutaneous tissue, the urologist wants to know how the other layers are ordered in general from superficial to deep. The correct answer is which of the following?
A. Fascia, fascia, pouch, pouch
B. Fascia, pouch, fascia, pouch
C. Fascia, pouch, pouch, skin
D. Pouch, fascia, pouch, fascia
E. Pouch, pouch, fascia, fascia
B
A 29-year-old woman is in the hospital going through labor and delivery of her first baby.
The baby’s head is very large as it emerges through the vaginal opening and begins to tear the pelvic diaphragm. Which of the following muscles will most likely be affected?
A. Piriformis
B. Detrusor
C. Obturator internus
D. Ischiocavernosus
E. Levator ani
Levator ani
An obstetrician has determined that a 33-year-old pregnant woman’s obstetrical conjugate measures 9.5 cm. Which of the following is the correct assumption based on this fact?
A. This woman can have a normal, easy delivery.
B. The obstetrical conjugate has no clinical significance.
C. 9.5 cm obstetrical conjugate is less than it normally should be in any woman.
D. An obstetrical conjugate should normally be 9 cm so 9.5 cm in this woman is ok.
C
Which of the following structures is used as a boundary to demarcate the pelvic outlet?
A. Sacral promontory
B. Margin of ala
C. Anterior inferior iliac spine
D. Ischiopubic ramus
E. Iliac crest
D
A 49-year-old woman complains of fecal incontinence.
The most likely contributing factor to such a problem is atrophy, paralysis, or dysfunction of which of the following structures?
A.Puborectalis muscle
B. Perineal membrane
C. Iliococcygeus muscle
D. Urethra
E. Piriformis
A
If medically necessary, a physician will perform a/an _____________ on a woman who is giving birth to prevent uncontrolled tearing of the perineal body.
A. Hysterectomy
B. Diagonal conjugate measurement
C. Episiotomy
D. Obstetric conjugate measurement
C
Erectile tissue in the male is considered to be a content of the ischioanal fossa but the erectile tissue of a female is different than a male so it is located in the deep perineal pouch.
Is the statement
TRUE or FALSE ?
TRUE
Which of the following is the platypelloid pelvis shape?

B
A medical assistant is prepping a male patient for surgery within the perineal region. Which of the following is an optimal position that the patient most likely will be placed in on the operating table for this surgery to occur?
A. Prone, lower limbs abducted
B. Supine, lower limbs adducted
C. Supine, knees and hips flexed, thighs adducted
D. Laying on left side of body in fetal position
E. Sitting up at end of table, knees and hips flexed
F. Supine, knees and hips flexed, thighs abducted
F
Which of the following structures is located within the anal triangle?
A. Bartholin’s glands
B. Labia majora
C. Pudendal nerve
D. Penis
E. Urethra
C
What ligament stabilizes the joint outlined in the image below?

Anterior sacroiliac ligament


