Parkinsons and Huntingtons Flashcards
How common is Parkinsons?
Parkinsons is common

Huntington’s Chorea
- How it presents
- WHta it is
- Chorea, Tics, Psychiatric symptoms
- Autosomal dominant disease
- CAG repeat of the hUntingtin Gene (chromsome 4p)
- normal number of repeats is 28, diseease occurs at >/40
- ABnormal Huntingtin protein aggregates in cell and is assoicated with cell death
- The more repeats, the earlier and more severe the disease
- Anticipations
Diagnosis Huntingtins chorea
- Genetic testing - Genetic counselling prior to diagnostic test, issues around confidentiality
- Differential diagnosis - any other cause of chorea/ tics- always think about Wilson’s disease (autosomal recessive)
Treatment Hungtintons
- Maintaining nutrition - associated with improves outcome and need to keep intake as burn lots more with constant movements
- Physiotherapist
- Drug-SYmptomatic treatments: First line VMAT2 inhibitors eg, tetrabenazine (reduce dopamine in presynaptic neuron) or atypical antipsychotic (block dopamine receptors) like lanzopine
- Drugs on horizon - Gene therapy (Deleting excess gene)

Normal basal ganglia function - Substnatia nigra

Parkinsons disease
Must have bradykinesia and 1 of:
- Rigidity
- Rest tremor (4-6hZ)
- Posutral instability

Parkinsons disease pathology - idiopathic
- Misfolding of alpha-synuclein associated with Lewy Bodies and neuronal cell death
- Likely (complex) interplay between genetic and environmental factors
- Neuroinflammation, problems clearing things out of cells (autopahgy), mitochondrial dysfunction etc
PD and genetics
- Parents of children with Gaucher’s disease are mor elikely to get PD (GBA homozygous)
- Genetic PD is exception not the rule:
- Autosomal dominant - PARK8 (AKA LRRK2) and SNCA (Park 1/4), mutation in alpha-synuclein (first described but rate)
- Autosomal recessive - PARK 2 (AKA parkin), problem with clearing toxic proteins.
Clinical Diagnosis Parkinson’s disease
UK Brain bank Criteria
ABout diagnosis it, excluding everything else and supportive criteria

Premotor features of Parkinsons
- (Loose neurones before get Parkinsons)
Subtle symptoms you can get before getting Parkinsons
- Anosmia
- REM sleep behavior disorder- acting out dreams overnight
- Constipation - changes to nerves in the gut
- (Mood changes)- not that helpful as common in population, same with coxnstipation
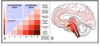
Non motor symptoms Parkinsons
People really struggle with concentration issues, hallucinations etc

The main differential diagnoses Parkinsons
- Essential tremor - refer back to diagnosis parkinsonism on brain bank criteria
- Vascular parkinsonism - repeated strokes and strictly unilateral features after 3y might suggest (on UK brain bank criteria for exlusion criteria).
- Parkinson’s plus syndromes - PSP, MSA, CBS (In pbl) circled below
- Dementia with lewy bodies- some pathological process as PD but the different course of the disease. The onset of cognitive Sx<1year from Parkinsonism or before.
Refer back to the criteria.

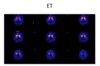
Essential tremor on DAT scan
This shows in brain, beautiful comma shape
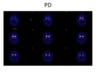
Parkinsons disease on DAT scan
Full stops - (comma is Essential trmeor)
Levodopa for PD
Need to dopa decarboxylase inhibitor add it to stop dopamine breakign down so can cross BBB to synapse where can go and have downstream effect for lots of Go.
These are the Co-Beneldopa and Co-careldopa

Dopamine Agonist for PD
Bind to post synaptic dopamine receptor
Few more side effects but very effective
Can cause impulse contorl disorder with things like gambling

Monoamine Oxidase B inhibitors for PD
Prevent breakfdown dopamine by MAOb
Can have intersctiosn with some antidepressants

Essential tremor vs PD on dat scan
ET - comma shape
PD - full stop shape

Catechol-O-methyltransferase (CONT) inhibitors for PD
Can’t be given alone have to be with levodopa

Advanced therapies for PD
- Deep brain stimulation - turn of subthalamic nucleus to reduce stop. One of best treatments for tremor.
- Apomorphine - Dopamine agonist give under skin subcutaneously for when people have fluctuations but respond well to medications
- Duodopa - through cut in tummy wall into stomach with tube into jejunum and continuous drip into bowl
Ecpensive and need to fit right criteria
Person with PD
Non-drug treatments and ways to support people.

Summary Pathology of huntingtons chorea and parkinsons disease and diagnostic process

Important DDx for Huntingtons Chorea and PD and treatments

Summary of Hungtintons chorea - pathology, diagnosis, DDx, and treamtnets
- Pathology - Neurodegenerative disease caused by CAG repeat in Huntingtin Gene
- Diagnosis - Clinical suspicion confirmed by genetics
- Important DDx - Lots, FH will guide youm WIlsons disease is good to rule out
- Treatment - supportive focusing on non drug treatment
- Must be patient centred
Summary of parkinsons disease - pathology, diagnosis, DDx, and treamtnets
- Pathology - IPD is neurodegenerative disease caused by?? resulting in aggregation of alpha syneuclein and lewy Bodies
- Diagnosis - CLinical diagnosis using uK brain bank critera supported by biomarkers and exclusion of other causes
- Important DDx - ET for tremor, several for Pdism- use brain bank critera to guide you (Vascular, Parkinsons plus, Dementia with Lewy bodies )
- Treatments - supportive bUT very effective and good quality of life for many for many yesrs, both drug and non drug treatment important
- Most be patient centred


