Movement Disorders Flashcards
(22 cards)
Normal movement
- Intact cortex -> NMJ
- Fine tuned by cerebellum and basal ganglia for fluid movement
- Intact CNS: think soemthing-> pass medsage sthorugh pyramidla trac to muscles and have action

**Difficulties with movement
- Can arise anywhere from Cortx -> nMJ
- Stroke, multiple scleroisis, tumour, motor neurone disease, myaesthenia, metsbolic issues etc.
**Movement disorders
- Uusally refers to problems with fluid movement - cerebellum, basal ganglia, metabolic
- Too little movement - hypokinesia (eg, parkinosim)
- Too much movement - hyperkinesia
Basal ganglia
- Pathways that tell you to go and stop need to be in balance
- Structures deep within brain

How the basal ganglia works
Pathway tells you to goa nd pathway telling you to stop

DIrect pathway (go pathwya) of the basal ganglia
- Cortex stimualtory structure and tells striatum it wants to go
- STriatum is inhibitory structure and wants to fine tune the movement
- globus pallidus interna is also inhibitory - turned down by straitum so thalamus which is go structure goes up and get more go.
- Direct pathway = MORE GO

Normal basal ganglia function - INDIRECT pathway
- Cortex is stimulatory
- STraitum inhibitory and inhibits globus pallidus externa
- Globus pallifus externa inhibitory so inhibits subthalamic nucleus which is stimulatory structure and stimulate globus pallidus intern which turns down thslaamus more.
- Indirect pathway = mORE STOP LESS GO
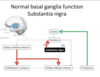
Substantia nigra function in normal basal ganglia
- lubricates process - promotes go
- Through D1 receptors it stimulates go pathway and inhibits through D2 receptors the stop pathway so
- iNhibits stop pathway through S2 receptors
- Substantia more go, direct pathway more go and indirect pathwya more stop and its about balance
Hypokinesia - Parkinsonism
- Must have bradykinesia ( slow and decrmeental movement)
- and 1 of:
- Rigidity
- Rest tremor (4-6Hz)
- Postural instability

Parkinsonism neuroanatomy
Damage to substantia nigra, results in too much stop not enough go.

Causes parkinsonism
- Idiopathic Parkinsons disease
- Vascular parkinsonism
- Medications that block dopamine
- Rarer causdes - Dementia with lewy bodues, parkinsons plus sundromes (PSP, MSA)
Hyperkinesia (too much movement) disorders
- Tremor
- Chorea
- Dystonia
- Myoclonus
- Tics
Describe Tremors - define
- Rhythmical, sinusoidal, alternating movement
- Shaking
- Type of tremor often leads you to diagnosi.

Chorea
- Chorea = random
- “Dance like”, unpredicatble, flowing movements moving from one area to another
- Ballism- chorea that affects proximal joints so movements are large and flinging
- Hemi-chorea/hemi-ballismus : affecting half the body
Affecting indirect pathway, straitum damage so loss of inhibition of the indirect pathway so too much go

Causes of Chorea
- Any structural lesion of striatum: stroke, tumour etc
- Neurodegenerative/ genetic: Huntington’s chorea, Wilson’s disease
- Immune mediated - sydenham’s chorea (in response to Group A strep infection)
- Drug induced - levodopa induced dyskinesia in parkinson’s disease
*
Dystonia
- Sustained or intermittent muscle ocntraction resulting in abnormla postural movement
- Can be repepitive, can be taask specific (writers cramp)
- Can be painful
- Geste antagoniste
- Botox is sometimes option
Causes of Dystonia
- Idiopathic? (“overuse?”)
- Genetic
- Part of other conditions (eg, PD)
- Structural lesions (trauma, tumour, stroke) - brain, spinal cord or peripherl nerve
- Immune mediated
- Post infectious
- Drugs (antipsychotics, antiemetics)
Myoclonus
- Jerky, shock like movements
- Lots of causes
- Normal -> medications-> epilepsy -> dementia
- Can be picked up by EMG
Tivs
- Uusally brief, often sterotyped
- Can be movement or osund
- Can be simple or complex
- Can be suppressed for short periods of time
- Tourettes syndrome most common cause
(tics can usually be surpressed but myoclonus usually isnt)
Wilsons disease
- Can present with parkinsonism, choream dystonia, psychiatric issues, liver disease
- Important not to miss as further brain/ liver damage can be prevented
- Wilson’s disease is a rare inherited disorder that causes copper to accumulate in your liver, brain and other vital organs.
- They have mix movement disorders.

Functional movement Disorders
- Abnormal movement due to the Nervous system not working properly without an underlying neurological disease
- Can cause - Gait abnormalities, tremor, jerking movements, mimic dystonia etc..
Hypo VS Hyperkinetic movement sdisorders
- Classification of movement disorders:
- Hypokinetic = too much stopm, lesion may be substantia nigra, systemic (Parkinsonism/ Akinetic-Rigid syndrome
- Hyperkinetic = too much go, lesion may be cerebellar, striatal, systemic (Tremor, chorea (ballism, hemi-ballism), dystonia, myoclonus, tics


