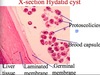
Parasitology Flashcards
American trypanosomiasis: T. cruzi
- Epidemiology: Latin Americas & Trinidad; women & children more at risk (go to sleep first)
- Vector: Kissing bugs: feed on mouth and eyes; Hemimetabolous: no pupal stage b/w larva & adu
- Features: Typicall C-shaped (see fig)
- Trypomastigote stage: characteristic of the genus Trypanosoma in the mammalian host bloodstream as well as infective metacyclic stages in the fly vector;
- Amastigote stage: inside cells of host
- Parasite stage can invade heart muscle (Cardiac)
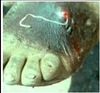
- Sx: Chagoma (Romana’s sign): unilocular conjunctivitis, lasts for several months;
Fever, progressive anemia, edema, lymphadenopathy, hepatosplenomegaly, EKG abnormalities, CNS involvement -> death or recovery - Pathology: edema, degeneration of parasitized tissue, destruction of mycoardial fibers and ganglion cells (cardiomegaly, apical aneurysms), destruction of myenteric plexus (megacolon)
- Dx: C-shaped on thin film, xenodiagnosis (let kissing bugs feed on Pt purposely and sample fecal pellet of bug; +ve test typically show 10e4 of parasites), serology Ag, DNA probes, PCR than DNA
- Rx: Benzidazole & Nifurtimox; effective against trypomastigote stage not amastigotes; screening is important as rx only effective in acute phase
- Control: ITN, screening, education, improved housing, no vaccine available

T. rangeli
- Epidemiology: Apathogenic trypanosome found in same geographical area as T. cruzi
- Features: Prominient undulating membrane long pointed posterior end
- Vector:
- Dx testing:
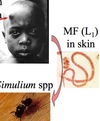
African trypanosomiasis: sleeping sickness
T. brucii gambience
T. brucii rhodesiense
- Epidemiology
- Vector: Tsetse flies, holometabolous, zoonotic
- Features:
- T. brucii gambiense
- only on stage of parasites (no amastigote stage)
- East Africa: acute disease
- West Africa: chronic disease
- Sx: Enlarged cervical lymph nodes (Winterbottoms sign), sleepiness, T.b. rhodesiense is acute, gambiense is chronic
- Dx: hx & clinical signs, demonstration of trypomastigotes on buffy coat/blood film, PCR/DNA (direct), ELISA (indirect)
- Rx: Suraman or Eflornithine (IV), removes tryps except in CNS; Melarsoprol (crosses BBB)
- Control: Biconical trap (plastic bag traps where Tze fly gets cooked in the bags during the day)

Leishmania
- Epidemiology: both old & new world
- Vector: sandfly spp Lutzomyia spp (New world); Phlebotomus (Old World)
- Features: Amastigotes in WBC (vertebrate host); Promastigote (vector in new host); after 48h amastigotes (binary fission) pack macrophage and are released when cell bursts
- cutaneous Leishmaniasis
- visceral Leishmaniasis
- Dx: spleen or bone marrow aspirate showing amastigotes is gold standard; rK39 Dipstick test used in field (detects antigen, commercially available test kits)
visceral Leishmaniasis
- L. donovani complex (Kala-azar)
- 4-6 d move to inner organs,
- Sx: early & late
- early: irregular fever, anaemia, leucopenia, diarrhoea, bleeding gums, joint pain, wt loss
- late: enlargement of lymph nodes, splenomegaly, hepatomegaly, death
- Rx: Amphoteracin B, pentavalent antimonial compounds (sodium stibogluconate - Pentostam), paramomycin, miltefosine
- Epidemiology: Africa & NE India
Cutaneous Leishmaniasis
- Sx: small red papule, wet ulcer (Leishmania major
) or dry ulcer (Leishmania tropica aka Oriental sore -> heal spontaneously) - Dx: travel Hx, clinical signs, amastigotes in aspirated fluid from ulcer (direct)
- Rx: same as L. donovani
New World Mucocutaneous
- Leishmania braziliensis complex
- Sx: small cutaneous papule, ulcer, oral and/or nasal lesions may develop after 3-20 yrs (very destructive)
- Dx: amastigotes in lesions (direct), culture/lab animals (monoclona Ab)
- Rx: same as L. donovani
- Epidemiology: males more infected than females (occupational disease), rain forest transmission zoonoses (sloths, rodents, dogs are reservoir hosts)
- Control: flea collar on dogs

Trichomoniasis: T. Vaginalis
- Dx: smear (direct) showing characteristic trophozoites, molecular test
- Sx: vaginitis, burning sensation, thick yellow discharge, vulvar and/or vaginal erythema; males often asymptomatic
- Rx: metronidazole

Giardiasis: Giardia lamblia aka G. intestinalis, G. duodenale
- Epidemiology: Mostly in developing countries, less so in N. America, Europe, and Australia, at risk include immunosuppressed (AIDS Pt), sewage workers, crowded institutions, travelers
- Reservoir/hosts: beaver and dogs
- Transmission: thru environment, fecal-oral
- Features: trophozoite not infective, fecal-oral parasites.
- Sx: pale loose stools (foul smelling; fatty), frequent, DOES NOT CAUSE FEVER, ab distention & pain, flatulence (offensive), wt. loss, sulphorous belching
- Dx: Stool microscopy (cysts/trophs in severe diarrhea), ELISA, immunofluorescent test, string test (indirect, used if other test results -ve, capsule filled w corn flour and usually get dramatic improvement)
- Rx: metronidazole
- Epi: worldwide

Cryptosporidium parvum
- Epidemiology: lake areas of the world
- Reservoir host: cows, dogs
- Vector
- Features: zoonotic, oocyst in greenish diarrhea
- thin-walled oocysts reinvade gut -> autoinfection so DO NOT slow down with anti-diarrhea meds, sporozoites innoculates host
- Sx: vary according to immunocompetent or immunosuppresed
- Immunocompetent: diarrhea (explosive, watery, greenish-brown), frequent (2 to 10/day). fever vomiting, anorexia, ab discomfort,
- Immunocompromised: large vol. diarrhea (5 L/day), malabsorption, wt loss, villous atrophy
- Dx: modified Ziehl-Neelsen stain for oocysts in stool, ELISA, immunoflourescent test (IFAT)
- Rx: none except supportive therapy
- Control:

Amoebiasis: Entamoeba histolytica
- Epidemiology
- Vector: lives free form in water?
- Features: Trophozoites (RBC’s invasive form)
- Sx: varies depending on Intestinal or Invasive type
- Intestinal: 95% aymptomatic, diarrhea inconsistent w gradual onset, no fever, no flatulence, ab pain, frequency
- Invasive: bloody diarrhoea, pathogenic invasive strains, may form amoebic abscesses in: liver (majority), brain, skin, lungs, orbit, spleeb, and genitals, Amoebic Liver Abscesses (ALA; fever, tender liver, epigastric pain, hepatomegaly),
- Dx: cysts in stool (smear or float), ELISA, direct aspiration of abscess, US, X-Ray, CT, MRI (indirect)
- Rx: vary depending on Intestinal or Amoebic Abscesses
- Intestinal: Metronidazole followed by Paromomycin
- Amoebic Abscesses: chemo, metro for small cycsts, US-guided drainage for large
- Control: Hygience, boiling or filtering water, cooking veggies, proper sanitation, safe pipes, no night soil fertilisation


Toxoplasmosis: T. gondii
- Epidemiology: world-wide, at risk include undercooked meat eaters, cat owners, butchers, vets, children who eat soil or unwashed veggies
- Host: definitive hosts are cats however b/c they produce the oocysts, but also pigs, goats, chickens, goat, sheep, pigeons,
- Features: Zoonotic, vertical transmission
- Bradyzoites: clusters enclosed by an irregular crescent-shaped wall, slow-growing, no inflammatory changes
- Oocysts
- Tachyzoites: motile forms of coccidians that form tissue cysts, infect leucocytes, infection predilection sites are Brain & Eye (fetus)
- Sx:
- immunocompetent individuals: asymptomatic
- fetal infection: hydrocephalus, chorioretinitis
- Dx: imaging (CT, MRI), biopsy
- Rx: ventriculoperitoneal shunt
- Control: test cats of pregnant owners for T. gondi Ab (infection), maternal testing & spiramycin (prophylactic)


Malaria: plasmodium falciparum
- Epidemiology: at risk include pregnant women (more attractive to mosquitoes), vertical transmission
- Host
- Vector: anopheles mosquito; sporozoites innoculated by mosquito -> mosquito bite -> Mature liver schizont release merozoites -> tropnozoite (in RBC; clinical stage)
- Features:
- numerous fine ring forms
- banana shaped
- double chromatin dots
- marginal forms
- RBC not enlarged
- Sx: anemia, hepatosplenomegaly, elevated fever, renal failure, jaundice & fever, pulm edema, vomitting, diarrhea, delirium, stupor, disorientation, cerebral malaria (coma, convulsions, abnormal posturing, dysconjuage gaze, retinal hemorrhages)
- Dx
- Rx: artemether/lumefantrine (most effective), ACT combination therapy; chloroquine, sulfadoxine/pyramethamine, meflaquine, Quinine/IV Quanadine (reserve)
- Prophylactics: Mefloquine, doxycycline, chloroquine, atovaquone & proguanil (Malarone)
- Control: ITN (anopheles are nocturnal), vector controls (egg, larva, and pupa in water so fill in swamps or add fish)


P. malariaie
- Epidemiology
- Host
- Vector: anopheles mosquito
- Features
- Sx: fever at every 72h
- Dx
- Rx: chloroquine
- Control


P. ovale
- Epidemiology
- Host
- Vector: anopheles mosquito
- Features: hypnozites in liver (sleeping/resting zoites causing relapse of disease, need to treat this); enlarged RBC
- Sx: fever every 48 h
- Dx
- Rx: chloroquine + primaquine (hypnozoites)
- Control

P. vivax
- Epidemiology
- Host
- Vector: anopheles mosquito
- Features: hypnozites in liver (sleeping/resting zoites causing relapse of disease, need to treat this)
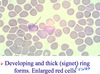
- developing and thick (signet) ring forms
- enlarged RBC
- Sx: fever every 48 h
- Dx: chloroquine + primaquine (hypnozoites)
- Rx
- Control

Slide y Questions y (and z)
A:
B:
C:
D:
E:
Which are transmitted by nocturnal vector and in fecal pellets? Which w 72 h fever?
Which Amphoteric B to treat?
Which Malasoprol?
Slide y Questions y (and z)
A: Falciparum
B: Malariae
C: Leishmania (wbc w/ amastigotes)
D:T.brucii
E:T.cruzii
Which are transmitted by nocturnal vector and in fecal pellets? E Which w 72 h fever? B
Which Amphoteric B to treat? C
Which Malasoprol? D

Schistosoma haematobium
- Epidemiology: Africa
- Intermediate Host: snail
- Host:
- vector:
- features: terminal spine
- Sx: swimmer’s itch, schistosomular pneumonitis, inflammation from trapped eggs of bladder and ureter -> polyps & bladder cancer (squamous cell metaplasia), hydronephrosis, hematuria
- Dx: eggs in urine (direct),
- indirect: serology, haematuria, imaging
- Hx of water contact
- Rx
*

Schistosoma mansoni
- Epidemiology: Caribbean, Africa, S. America
- Host: snail intermediate
- Intermediate host: snails
- Host: buffalo,
- vector:
- features: sub-terminal spine
- Sx: Symmer’s pipe-stem fibrosis, eggs get into mesenteric veins, wimmer’s itch, schistosomular pneumonitis, inflammation from trapped eggs in walls of mesenteric veins, ova trapped in portal v. and br., periovular granuloma, fibrosis, portal hypertension, varices, hematemesis, melena/anemia
- Dx: detection of eggs in stool or rectal biopsy (direct)
- Hx of water contact
- Rx: Praziquantal
- Control