Paper1-SC10/SC11/SC12/SC13 Flashcards
(69 cards)
Explainendothermic reactions.
Take in energy so get colder.
Explainexothermic reactions.
Give out energy so get hot.
What are stainless steels?
Contain chromium which reacts with oxygen in the air. These resist rustinf. The layer is thick enough to stop air and water reacting with the metal.
What is brass made of?
Copper and zinc.
Why is the haber process heated not cooled down?
As when a cold temp is used, although more amonia will be produced, it will be produced slower so 450C is the right balance. It is like getting 5 pound a day instead of 10 pound a week.
What is electroplating?
Coating the surface of one metal with a thin layer of another metal. Silver and gold are attractive transition metals but they are expensive. Silver or gold can be electroplated onto cheaper ‘base metals’ such as copper or nickel. This produces attractive jewellery that is cheaper than solid or gold.
What is an alloy?
A mixture of a metal element with one or more other elements that are usually metals.
What are some of the chemical properties of transition metals?
They form coloured compounds.
Often used as catalysts.
When are inert(unreactive)electrodes(usually graphite or platinum)used?
When doing the electrolysis of molten or dissolved ionic salts. When a molten salt is electrolysed ions are discharged as atoms or molecules.
What is sacrificial protection?
Method of rust prevention that does not rely on keeping air or water away, instead a piece of magnesium or zinc is attached to the iron or steel object. Magnesium and zinc oxidise easier so they react with them instead of the steel or iron. This can run out though.
What are alloy steels?
Made by deliberately adding other elements to iron.
What is the electrolyte?
An ionic substance with freely moving ions that can conduct electricity.
What is corrosion?
Whne a metal reacts with oxygen making the metal weaker over time, the metal gains oxygen so is oxidised. The corrosion of iron requires water as well as oxygen and is known as rusting.
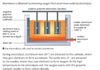
What is galvanising?
When iron and steel objects are protected from rusting by coating them with zinc.
How is copper purified using electrolysis?
Copper electrodes can be used. The copper atoms in the anode lose electrons to become copper ions. These dissolve in the solution and migrate to the cathode where they are deposited as pure copper. Inpurities from the anode do not form ions and collect below the anode as a ‘sludge’.
What happens when metals react with oxygen in the air?
They oxidise.
What ores are found in their native state(un combined elements)?
gold and platinum as they are very unreactive.
How do displacement reactions work?
More react metal will replace less reactive one.
What are transition metals used for?
Construction, vehicles, electrical wiring,, jewellery and other everyday uses.
How do conditions affect the position of equilibrium?

What is the equilibrium position?
The ratio of the products:reactants in a system that has made equilibrium.
What else can electroplating be used for?
To improve a metal objects ability to resist corrosion.
What is oxidation?
The loss of electrons.