Paper1/2-SC5/SC6/SC7 Flashcards
Why do metals conduct electricity?
When a potential difference is applied between two points on a piece of metal, the electrons will flow to the positive side and will form an electrical current.
What is an electric current?
Flow of charged particles.
What is valency?
The number of covalent bonds formed by atoms of different elements.
Explain diamond.

Explain giant covalent.

What are anions?
Atoms that have gained electrons.
What are monomers?
Small simple molecules that can be joined in a chain to form a polymer.
Explain the pros and cons of a metallic lattice drawing?
Shows the metal ions held in a lattice but does not show the ions will be vibrating at all times.
Explain graphene.

What are some of the allotropes of carbon?
Fullerenes, graphene, graphite and diamond.
What are covalent bonds?
Shared pair of electrons between two non metals.
What are ionic bonds?
Formed between metals and non metals and there is electrostatic attraction between the anion and cation.
What is metallic bonding?
Electrostatic attraction between the positive metal ions and the negative delocalised electrons. This attraction is really strong so metals have high melting and boiling points.
Explain graphite.

What are bonds?
Forces of attraction that hold atoms together. When bonds form between atoms, energy is released from the atoms making them more stable(less reactive).
What are electrostatic forces?
Forces of attraction between all positively and negatively charged objects.
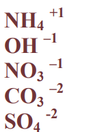
What are the 5 poly atomic ions you need to know?
Ammonium, hydroxide, nitrate, carbonate and sulfate.
Explain ionic.

Why are metals malleable?
When they are hit the layers of ions slide over eeachother and the sea of electrons golds the ions together so the metal changes shape instead of breaking.
What increases the electrical conductivity in metals?
Increases as the number of delocalised electrons increases.
What is a molecular formula?
The number of atoms of each element bonded together in a simple molecule.
What does the term malleable mean?
They can be hammered or rolled into shape without shattering.
Explain the pros and cons of the 3D ball and stick models.
It shows which atoms are joined together and shows the shape of the structure but shows the atoms too far apart and are not really sticks holding the atoms together.





