Orthodontics- upper removable appliances Flashcards
How does an upper removable appliance work?
It applies pressure to move the teeth through tipping and tilting movements.
Discuss the advantages and disadvantages of an upper removable appliance.
Adv-
Excellent anchorage
easier to maintain oral hygiene
Non-destructive to tooth surfaces.
Disadv-
Patient can remove it
Can only move 2 teeth at once
Rotations are difficult to correct.
Less precise control of movement.
What are the components of stainless steel?
72% Iron
18% Chronium
8% nickel
- 7% Titanium
- 3 % carbon
What does ARAB stand for ?
Active component
Retentive components.
Achorage
Baseplate/
What is the active component?
The part that is moving the teeth through the application of force.
what type of stainless steel wire is used in orthodontic appliances?
Hard circular stainless steel wire.
Name this active component.
Give :
its function.
Its location
the characteristics of the wire.
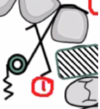
Finger Spring and guard.
Moves teeth backwards.
Palatally.
0.5mm HSSW.
Name this active component
Give :
its function.
Its location
the characteristics of the wire.

Z spring.
Pushes teeth straight forward
Palatally.
0.5mm HSSW
Name this active component
Give its position
Characteristics of the wire.

Flapper spring.
Palatally
0.5 HSSW
Name this active component
Give :
Its position
The characteristics of the wire.

T spring.
Buccal movement of the teeth.
Palatally.
0.5mm HSSW
Name this active component.
Give :
its function.
Its location
the characteristics of the wire.

Buccal canine retractor
Retract teeth backwards and inwards.
Buccal.
0.5mm HSSW and 0.5mm internal diameterTubing
Name this active component
Give :
its function.
Its location
the characteristics of the wire.

Robert’s retractor
It moves teeth backwards and provides retention.
Buccal
0.5mm HSSW with 0.5mm of internal tubing.
Why do we use tubing?
To give strengtht to the buccally placed active components as the wire is commonly distorted on the buccal side.
Name the 5 intra-oral displacement forces.
Tongue
Gravity
Chewing through mastication
Talking
Active component.
Name this retentive factor.
What is its function.
Discuss the wire characteristic.

Adam’s clasp
Provides posterior retention. (goes into the undercut of the 6s)
0.7mm HSSW.
Name this retentive factor.
What is its function.
Discuss the wire characteristic.

This is the southend clasp.
Provides anterior retention
0.7mm HSSW
Name this retentive factor.

This is the labial bow.
Which posterior teeth do we choose to clasp and why?
6s and the 4s.
6s- they have the biggest roots .
4s-to prevent wire overlapping (which would happen if we chose the 5s and the 6s)
What is anchorage?
This is to ensure that only the teeth that we want to move, move.
What is the function of the baseplate?
- Join the components together
- Helps with achorage
- Helps for retention/adhesion and cohesion.
What material do we make baseplates in and why?
Self cure acrylic as it is finished in 20minutes
Discuss passive components?
This is the stop, which prevents the tooth moving back into their old position (closing the new gap)
It is made of 0.7mm flattened HSSW.
They are positioned on the side of the tooth in the gap.

How do we deal with anterior crowding?
We extract teeth to make space, and move teeth into the space.
How do we treat an overbite?
We use a flat anteiror bite plane to prop open the lower teeth. This causes a posterior open bite resulting in the continued eruption of the posterior teeth.
When the bite plane is removed, the anterior teeth are proped open. This leaves space anteriorly to move the lower teeth back and then the upper.







