Oral Patho Flashcards
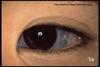
Osteogenesis Imperfecta, blue sclera

Pulp chamber oblitereated, severe wear, violet colored teeth. may occur with osteogenesis imperfecta


Osteopetrosis- excessive hardening of bone
spongiosis is obliterated
eyes wide set
teeth poorly calcified
teeth on xrays excessively opaque
paranasal sinus may be obliterated
bone is homogeneously radiopaque

Cleft palate. 1 in 2000 births have
lack of nutrients for kids
obturator- clear acrylic mouth piece produces vacuum to suck
bifid uvula is least significant manifestation

Cleidocranial dysostosis
family disease, autosomal dominant
large head, bulging forehead
open frontales throughtout life
hypoplasia or complete absence of clavicles
poorly DEVELOPED MAXILLA
SHEDDING OF PRIMARY TEETH ANDERUPTION OF PERMANENT
SUPERNUMERARY TEETH IN BOTH JAWS
DELAYED ERUPTION
Common in people with cleidocranial dysostosis?

Gemination
Developing teeth splits into two teeth
Common in people with cleidocranial dysostosis

union of two normally seperated teeth


Concresence: a condition where the CEMENTUM overlying the roots of at least two teeth join together.
Common in people with cleidocranial dysplasia

Etiology is unknown- maybe has something to do with circulatory malformation.
Bone is excessively Vascular.
manifest at middle life or later
thickening of bones
increase in hat size and dentures get too tight
only affects maxilla and above.

result of an inflamatory process produced by an organism. May be CHRONIC OR ACUTE
area of involved bone becomes necrotic and pus is often formed. As healing occurs, the necrotic bone is sequestered.
Mandible is more likely to get infrection. Mandible has less WBCs to fight infection. Infection of bone is cured by antibiotics.
Condensing osteitis
result of low grade infection around root of tooth
EXTRA BONE AROUND ROOT
radiopaque area extending from the area of the tooth apex.
Often in lower premolar and molar area
Associated with teeth with large restorations of carious teeth.

Osteoradionecrosis
aftermath of therapeutic radiation.
BONE DEATH DUE TO RADIATION.
most often the mandible
irradiated bone is always weakened.
massive areas of necrotic bone and infection occur if bone is infected.


Osteoma
benign tumor of bone
new growth from the periosteum
Single or multiple
composed of compact bone or compact bone with spongey center.
attached by broad base or pedicle.
Surgically removed
frequently on outer surface of mandble in premolar area and angle of mndible


Exostosis
benign outgrowth of normal bone often in maxilla buccle side only.
High reoccurence rate if removed


Torus
possibly due to trauma irregular occlusion, hereditary
single, unilateral, multiple,spindle shaped nodlar
difficult for denture making
20% of population has this on palate
mandibular - 7-20 %


Central Giant Cell Granuloma (CENTRAL IN BONE)
will keep expanding until removed surgically
As a result of trauma, cells overrepair. Usually from trauma such as tooth loss
loosening of teeth occurs
BIG CELL MULTIPLE NUCLEI

Peripheral Giant Cell Granuloma
Caused by trauma but manifests in tissues

Eosininophilic Granuloma
Etiology is unknown
overexpression due to allergic reaction
Rapid increase of large mononuclear cells of reticuloendothelial
teeth loosen
eosinophil proliferation

Fibrosarcoma ( cancer of mesoderm)
unknown etiology.
Rare
teeth are loose for no apparent reason is often first sign
rapid and invasive with considerable destruction
xray diffuse radiolucent area without distinct borders
treatment is surgical removal
resistant to radiation
Chondrosarcoma: Cancer of cartilage
very rare in oral cavity because there is not much cartilage
arises from endosteal fibrous connective tissue in areas of endochondral ossification
Trauma is important secondary cause
not as invasive and mestatic as when found in long bones.
most often at angle of mandible.
Most common in men
Treatment is surgery, no radiation

Osteosarcoma
Malignant tumor of bone
Etiology: trauma trigger and pagets disease
in young individuals
pain and paraesthesia
sunray appearance on xray
treatment is to remove entire bone

Multipe myeloma : Soft tissue or bone
etiology is from plasma cell or any cell the marrow cells
very aggressive angle, ascending ramus, molar area
loosening of teeth
metastasis common
punched out raiolucent areas
no increase in thickness of skull

Osteomalacia
AKA RICKETS
calcium deficiency often from vitamin d deficiency
often normal bone xrays
pathological fracture seen
delayed tooth eruption

Globulomaxillary cyst
radiolucent area between roots of maxillary lateral and canine. ALWAYS
often pear shaped
doesnt affect teeth







