opthalmology Flashcards
Differentials for conjunctivitis
- acute glaucoma (SEVERE pain, blurry, corneal clouding, dilated pupil)
- episcleritis
- uveitis
- keratitis (cloudy vision, severe pain)
- corneal ulcer

define diabetic retinopathy and types of it.
- microvascular complication of diabetes which affects your eye
- major cause of visual loss + blindness
- Early symptoms = asymptomatic SCREENING NEEDED (retinal imaging)
Types:
- Background
- Pre-proliferative
- Proliferative
- Maculopathy
Pathophysiology of retinopathy
- Hyperglycemia => activation of different pathways (high glucose delivered to retina by retinal arteries)
- Affects endothelial function => retinal ischemia
- Produces factors that increase permeability of blood vessels => factors leak into surrounding vessels => macula oedema
- Erythropoietin factor=> retinal neurovascularisation
examination findings of diabetic retinopathy
FUNDOSCOPY
background
- hard exudate- cholesterol
- microaneurysms (dots)
- blot haemorrhages
pre-proliferative
- cotton wool spots (ischaemia)
proliferative
- little thin new vessels developing from optic disc (problems => tears can lead to bleeding in vitrious=> BLIND)
Maculopathy
- affects direct vision
- blots/dots (microaneurysms)
- hard exudates

Treatment for retinopathy
- Background => improve blood glucose control (don’t need glasses change as diabetes is causing changes lens shape) + WARN PATIENT ABOUT DIABETES
- Pre-proliferative/proliferative => refer to eye doctor => PAN retinal photocoagulation (laser off ischaemic areas)
- Maculopathy => Anti-VEGF injections , Grid photocoagulation
complications of retinopathy
- vitreous haemorrhages- new vessels leaking
- glaucoma- new vessels affect fluid flow => increase pressure in eye => damage optic nerve
- retina detachment - new scar tissue growth pushes eye forwards
- BLINDNESS
define uveitis
inflammation of the uvea (iris, ciliary body, choroid)
- anterior uveitis (most common)
- intermediate uveitis (vitreous inflammed)
- posterior uveitis (retina/choroid inflammaed)
causes of uveitis
- IDIOPATHIC (40%)
- systemic inflammatory disorders (ankylosing spondylosis-young men, juvenile arthritis-women, MS, sarcoidosis, IBD, SLE, Behcet’s)
- infection (TB, HSV, HZV)
- trauma
- neoplasia
symptoms + signs of uveitis

symptoms:
- cloudy/blurred vision
- red around the limbus (cornea-sclera border)
- moderate painful eye
- photophobia
- watery eye
signs:
- pupil irregular/constricted
- flashes and flares (leakage of proteins) - inflammatory cells in anterior chamber
- keratic precipitate in cornea
management for uveitis
- refer to opthamologist
- medical: (only given by opthamologist)
- non-infectious => topical corticosteroids + cyclopentolate (paralyses cilliary body - relieves pain)
- infectious => antimicrobial + corticosteroids + cyclopentolate
- chronic/ SEVERE => immunosuppressants, TNF inhibitors, laser phototherapy, cryotherapy
prognosis + complications of uveitis
- most resolve after treatment
- some become chronic=> visual impairment, ocular complications, blindness
COMPLICATIONS:
- cystoid macular oedema
- secondary cataract
- secondary glaucoma.

define thyroid eye disease
autoimmune disease usually caused by hyperthyroidism (Grave’s) leading to eye inflammation (eye muscles, eyelids, tear glands, fatty tissue behind eye)
- active
- stable phase
symptoms of thyroid eye disease
- red painful eye
- diplopia (restricted ocular mobility)
- dry/watery eyes
- bulging/STARE eyes
- PROPTOSIS (exopthalmos) not always present
- lid retraction/ lid lag
- difficulty closing eyes
- reduced visiual acuity (more severe)
FHx, more common in females/40-60s

investigations for thyroid eye disease
- TFTs (T4/TSH levels)
- anti-TSH/TPO/thyroglobulin antibodies (not very specific/sensitive)
- CT/MRI orbital area
- thyroid uptake scan
Management for thyroid eye disease
- Mild (dry eye/diplopia) => conservative (drops)
Moderate
- corticosteroids (intravenous)
- orbital radiotherapy
- Surgical decompression
Severe (vision loss)
- IV corticosteroids + urgent orbital decompression
Systemic disease:
- anti-thyroid drugs (propylthiouracil, carbimazole)
what is conjunctivitis
inflammation of conjunctiva caused by infection or allergies usually affecting both eyes
causes of conjunctivitis
- viral (most common) - adenovirus
- bacterial - strep. pyogenes, staph. aureaus, H. influenza
- allergic
- chemical/ contact lens associated
- reactive arthritis
symptoms of conjunctivitis
- eye redness (starts in one eye spreads to other)
- eye discomfort - gritty, foreign body, burning
- watery eyes/ discharge => temporary vision blurring
Bacterial => rapid redness, pus discharge with crusted eye lids
Viral => pink eye, watery discharge, previous URTI
Allergic => watery discharge, sneezing/runny/blocked nose, eyelid swelling

signs of conjunctivitis
Inner upper eyelid
- papillae- raised inflammtion with central vessel (Allergy/bacterial)
- follicles- raised lymphocytes (yellow)- CVT/ chlamydia, toxic, viral
lesions on upper eyelid => HSV
Huthinson’s sign (lesions on nose) => HZV
Conjuctival membrane (yellow fibrin layer above conjuctiva) - severe infection

investigations for conjuctivitis
- usually none
- if not resolved with treatment => swab => viral PCR for HSV/adenovirus or bacterial culture
management for conjuctivits
Viral
- self-limiting (7 days)
- eye care - cool compress, saline-wash eye lids, lubricating eye drops
- CONTAGIOUS so avoid contact with others + hygiene
Bacterial
- delayed use of topical antibiotics (chloramphenicol)
- eye care
- avoid contact with others
Contact lens associated
- stop using contact lens
- eye care
When to refer to opthamology (for red eye)
Red flag symptoms
- reduced visual acuity
- headache/photophobia - meningitis
- recent trauma/ eye surgery
- copious mucus discharge => gonnorrhea
- worried about contact lens associated problems (keratitis)
Symptoms persist 7 days after treatment
define scleritis
- inflammation of sclera (white part of eye)
- usually due to underlying systemic inflammation
- anterior uveitis (90%)- diffuse, nodular, necrotising
- posterior uveitis
symptoms of scleritis

- painful red eye
- pain radiates to forehead, brow, jaw
- pain worse on movement
- watery eyes/ photophobia
- associated with systemic inflammation
- +/- gradual loss of vision
Posterior scleritis
- worse symptoms but quiet, white eye
- associated signs - proptosis, lid oedema, optic disc swelling, retinal detachment

conditions associated with scleritis
connective tissue disorders
- rhematoid arthritis (most common)
- SLE
- GPA (granulomatosis with polyangitis)
- reactive arthritis
- ankylosing spondylitis
gout
Syphillis
IBD
Investigations for scleritis
Bloods:
- FBC
- ESR/CRP - inflammation
- RA screen - Rheumatoid factors/ anti-CCP (specific)
- Syphillis screen - rapid plasma reagin (antibodies to syphillis bacteria)
Imaging:
- X-rays (chest/sacro-illiac joints)
- CT/MRI of sinus/orbit

management of scleritis
- SUSPECTED scleritis => refer to OPTHAMOLOGIST
- Treat cause (inflammation)
- Oral NSAIDs- ibuprofen
- Oral prednisilone
- Immunosuppressant drugs (methotrexate/azathioprine)
- Biologics - infliximab
- Surgery for complications
Complications of scleritis
- scleral thinning
- raised IOP
- uveitis
- retinal detachment (posterior)
- cataracts
define optic neuritis
inflammation of optic nerve
causes of optic neuritis
- multiple sclerosis (autoimmune)
- infections - lyme disease, measles,mumps, herpes
- sarcoidosis
- Behcet’s
- drugs - methanol (antifreeze), ethambutol (treat TB)
symptoms + signs of optic neuritis
- reduced visual acuity
- reduced colour vision
- eye pain (worse on movement)
- flashing lights
- visual field loss
- Uthoff’s sign - symptoms worse in hotter temp
Signs:
- decreased pupilary light reaction/ RAPD
- scotoma
investigations for optic neuritis
- usually clinical (visual acuity, visual field, colour vision)
- if aypical:
- FBC, ESR, TFTs, autoantibodies, syphillis serology
- CXR- check for sarcoidosis/TB/malignancy
- MRI- check for MS risk
management of optic neuritis
- refer to opthamology/neurology
- Corticosteroids - methylprednisilone , speeds up visual recovery
complications for optic neuritis
- optic nerve damage
- permanenet visual loss
- steroid side effects => prone to infection, mood changes, weight gain
types of visual field defects
- monocular blindness
- bitemporal hemianopia
- homonymous hemianopia (same side + half)
- homonymous quadrantopia (same side + quarter)

retinal causes of visual field loss
- retinal detachment (flasher, floaters, curtains)
- retinal artery/vein occlusion
- age-related macular degeneration
- drugs
- chloroquine
- vigabatrine (treat epilepsy)
pre-chiasmal causes of visual field defects
- one eye only, ipsilateral
- optic neuritis
- amaurosis fugax - temporary vision loss in both eyes
- optic atrophy
- retrobulbar optic neuropathy
- trauma
- glaucoma
chiasmal causes of visual field defects (bitemporal hemianopia)
- pituitary adenoma
- suprasellar aneurysm
post chiasmal causes of visual field defects (contralateral eye, homonymous hemianopia)
- stroke
- tumour
- trauma
causes of cranial nerve palsy
- CN III
- CN IV
- CN VI
Oculomotor
- vasculitis
- aneurysms (posterior communicating artery)
Trochlear
- congenital
- trauma
- vascular tumour
Abducen’s
- cranial pressure
- vascular tumour
symptoms of oculomotor nerve palsy
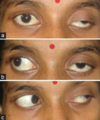
- ptosis
- eye down and out
- mydriasis (dilated pupil), unreactive to light

symptoms of
- CN IV palsy (superior oblique)
- CN VI palsy (lateral rectus)
CN IV palsy
- prevents moving inwards and down
- some diplopia
CN VI palsy
- prevents eye moving outwards
- diplopia

investigations for visual field defects
- visual field testing
- Amsler grid - checks damage to macula/optic nerve
- Full neurological examination
- Special tests: static perimetry, kinetic perimetry
management of visual field defects
- treat cause (glaucoma => laser)
- increasing head movements + scanning exercises
- prisms
- coloured markers l line guides to help with reading


