Observing microorganisms through a microscope Flashcards
(55 cards)
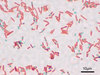
Acid fast staining of a patient’s sputum is a rapid reliable, and inexpensive method to diagnose tuberculosis. What color would bacterial cells appear if the patient has TB?

The bacteria will appear fuschia
what genera of bacteria require acid-fast staining?
- Mycobacterium
- Nocardia
How large are protozoa?
100 microns
how big are yeasts?
8 microns
What is the size range of bacteria?
0.2-1 microns wide and 2-8 microns long (some are much longer than wide)
Clymidia and mycoplasmas are 0.25 microns they are at the __________ of the resolution of a _____________ microscope.
- lower limit
- light
how big are viruses?
20-250 nm
What kind of flagellar arrangement does this bacteria have?

- monotrichous
what are microscopes used for?
to magnify small objects
why does size of a specimen matter when choosing which type of microscopy to use?
because different microscopes have different resolution ranges, the size of a microscope determines what type of microscopy is most effective in veiwing the microbe.
As light wave length decreases what happens?
resolution increases

A. Ocular lenses
B. Objective lenses
C. Condenser
D. Diaphragm
E. Illuminator
F. Coarse focusing knob
G. Fine focusing knob
Magnification
How much all the lenses magnify the specimen
(TM = Ocular x Objective)
Resolution
- The ability of lense to distinguish objects; resolving power
- 0.2 microns is the resolving power of a light microscope
Contrast
Stains change refractive index; an increase in contrast between bacteria and surrounding media allows for better visability
Refractive index
- how light appears as it passes through an object
- measures the light bending ability of a medium
why are filters used on light microscopes?
to increase resolution by decreasing the wave length of the light passing through the the side.
What does light do as it passes through substances?
it bends
what does air do to light?
it bends it
when is immersion oil used?
with a 100x objective lense or higher
why is oil used with an oil lens?
- to lessen the amount of light lost by bending in air; keep light from bending
- No oil; resolving power will be deminished greatly
- Light may bend so much that it misses the small high magnification lens
Brightfield microscopy
- simplest of all the optical microscopy illumination techniques
- Dark objects are viasble against a bright background
- light is reflected off specimen does not enter objective lenses

Darkfield microscopy
- Light objects visable against dark background
- used to enhance the contrast in unstained samples
- instrument of choice for spirochetes
- only light reflected off specimen enters the objective lense

Fluorescence Microscopy
- uses UV light; energizes fluorochromes
- Flourescent substancesabsorb UV light and emit visable light
- Cells may be stained with fluorescent chemicals called fluorochromes
- immunofluorescence; fluorochromes only stain object you want to be stained, antibodies with fluorochromes attached attach to antigens on bacteria.