OBJ - Amino Acids in Proteins Flashcards
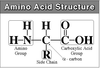
Draw the general structural plan of amino acid molecules and identify the α-carbon, the carboxylic carbon, the amino nitrogen and the position of the side chain
@ physiological pH COOH -> COO- NH2 -> NH3+ becomes zwitterion
Ionization state of SIDE CHAIN determines its chemical nature
how the protein will fold, bind & interact with its environment
Classify amino acids based on the physicochemical properties of their side chains into nonpolar, aromatic, polar positively charged, polar negatively charged, and polar uncharged
Nonpolar Aliphatic (7 - VIMPGAL)
Nonpolar Ar (3 - PTT)
Polar Uncharged (5)
Polar Charged - Neg (2 - E,R)
Polar Charged - Pos (3 - HAL)
Recognize the sulfur-containing amino acid side chains, and explain formation of disulfide bond between two cysteine residues
Methionine
Cysteine (R = S-H)
- Disulfide bond: oxidation of 2 Cysteine side chains -> 2 H+ & R-S-S-R
- weaker than C-C; vulnerable to Nu attach; weak link in a molecule -disulfide bonds shape tertiary structure of proteins in folding -disulfide bonds: prefer hydrophobic environment
- Cysteine residues = hydrophilic Makes a huge change in protein folding

Recognize potential hydrogen bond donors and acceptors in amino acids side chains
anything with OH, NH
Tyrosine
Tryptophan
Serine
Threonine
Asparagine
Glutamine
Arginine
Lysine
Histadine
**Tyrosine, cysteine, serine, Histidine, Lysine, aspartate present in some enzyme active sites
** 2 OH groups that have pKa’s too hight (Serine/Threonine), but still can H bond
List the amino acid side chains with dissociable groups, and identify their ionized and deionized states
AA with Ionizable Side Chains:
- **Tyrosine = OH
- **Cysteine = SH
- Polar Neg
- Aspartate = COO-
- Glutamate = COO-
- Polar +
- Histidine = N=C
- Arginine = C=NH2+
- Lysine = NH3+ PIC
Explain how the pKa of dissociation for a particular side chain dictates the ionization status of its dissociable group at a given pH
PIC

**Peptide bond
Amide linkage; bond between COOH & Amide group with the loss of H2O picture

**3 letter abbreviations for 20 Amino Acids

picture

**Properties of side chains
- determines how the protein is going to be folded
- what molecule it will bind to how it will interact with its enviornment
**Sickle Cell Anemia
-mutation of 1 AA in beta subunit of Hb causes proteins to aggregate with each other & RBC sickles -AA mutates from Polar Neg -> aliphatic

**Osteogenesis Imperfecta (Type II)
-mutation of Gly-> Asparate @ any of 6 positions causes collagen deformation & perinatal lethality -AA mutates from Aliphatic -> Polar Neg changes/ruins the collagen triple helix -> why cartilage/bone matrix, tendons, cornea can’t form

**Testicular feminization
substitute 1 AA at either of 2 positions -> Angrogen Receptor (AR) protein
AR have 2 DNA binding Zinc fingers, but mutation can’t coordinate with Zinc -> unable to interact with DNA preventing transcription activation of many genes
- males develop female secondary sexual characterisitics
- AA mutates from Sulfur containing/disulfide forming Polar uncharged -> Ar



