Neuroradiology Pics Flashcards
Describe appearance of blood on T1 imaging in days 1-120 of IPH
Blood on T1: starts off isointense
Day 1: isointense bleed but can see mass effect and interventricular shfit
Day 21: subacute bleed is hyperintense on T1
Then chronic (120 days) is hypointense again

Hyperdense vs. hyperintense
(a) Enhacing
Density = CT
Intensity = MRI
(a) Enhancing = breakdown of BBB, lights up when given contrast (on either CT or T1 MRI)
- enhancing on MRI = hypointense on pre-contrast image, hyperintense on post-contrast T1
(a) Type of image
(b) Findings

(a) Axial FLAIR
(b) Extensive white matter disease, mainly left temporal and b/l ocipital lobes
Dx = amyloid beta related angiitis
(a) Dx
(b) Plane of section

(a) Right putamen hemorrhage
(b) Axial plane
(a) Locate the hemorhhage
(b) Type of image

(a) Hemorrhage in the right putamen
(b) Axial and sagittal FLAIR
- white matter dark, grey matter light, CSF blacked out
54 yo F develops HA and collapses at home, unconscious on exam
(a) Dx
(b) What is the red arrow indicating?
(c) Highest risk factor for this?

(a) Left basal ganglia hemorrhage (IPH = intraparenchymal hemorrhage) w/ intraventricular extension
(b) Red arrow showing extension of hemorrhage into the 4th ventricle
(c) chronic HTN
MRI findings of amyloid angiopathy
White matter hyperintensities (usually asymmetric) and micro-bleeds in multiple lobes of the brain
-lesions shrink w/ improvement in symptoms (or successful tx w/ immunosuppressants) and enlarge w/ recurrences

Stroke of which arteries?

(1) Superior cerebellar artery
(2) Anterior inferior cerebellar artery
(3) Posterior inferior cerebellar artery
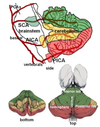
Name the type of bleed

(1) Epidural
- doesn’t cross suture lines
(2) Subdural
- crescent shaped
(3) Subarachnoid
- into the circle of willis, dooming ‘star’ sign
What is a STIR sequence?
Sequence used on MRI of the spine- T2 image (white matter dark, grey matter white) where fat signal is supressed
-image is in the sagittal plane

Features of FLAIR MRI
(a) Color of brain matters
(b) Color of CSF
(c) Color of BVs
FLAIR MRI = T2 image w/ the CSF blacked out
- often the most helpful
(a) White matter dark, grey matter white
(b) CSF dark
(c) BVs dark

75 yo M w/ sudden onset HA and left homonomyous hemianopsia
Locate the lesion
Lesion = right occipital lobe
-lobar hemorrhage (lobe adjacent to cortex, not deep structure like basal ganglia)
Most likely etiology = amyloid

Locate the lobar hemorrhage

(e) frontal
(f) temporal
(g) pareital
(h) occipital
Features of head CT
(a) Color of brain matter
(b) Color of bone
(c) Color of acute clot/hematoma

Head CT:
(a) Gray matter (medial) is darker than white matter (lighter)
(b) Bone is white
(c) Acute clot/hematoma = white

Name the type of image

(1) On the left = T1
- white matter white, gray matter gray, CSF dark
(2) On the right = FLAIR
- white matter dark, grey matter light, CSF dark
Name the two circled physiologically calcified structures

Yellow = pineal gland
Red = choriod plexus
63 yo F p/w sudden onset sever HA w/ confusion and blurry vision
-b/l abducens nerve palsies
Dx

Dx = pituitary apoplexy = bleeding in pituitary fossa
Vasogenic vs. Cytotoxic edema
(a) Where is the fluid
(b) Etiology
(c) Appearance on CT
Cytotoxic edema
(a) Fluid is in the intracellular space
(b) Ischemia, cell membrance injury (NaK pump dysfunction) causes accumulation of intracellular fluid
(c) Loss of grey/white jxn
Vasogenic edema
(a) Fluid pushed into the interstitial space => tends to accumulate where there is more interestitial space (white matter b/c grey matter is too packed w/ cell bodies)
(b) Etiology = local insult- tumor, toxo, Tb, abscess
(c) On CT: see preservation of grey-white jxn b/c increased extracellular fluid makes the white matter appear even less dense

Features of T1 MRI
(a) Color of the matters and CSF
T1 MRI- great for seeing normal anatomy
(a) White matter is white, grey matter is grey, CSF Is dark

(a) Describe what is meant by restricted diffusion
(b) Examples
Restricted diffusion = bright on DWI (diffusion weight image) b/c water molecules are stuck in the area (slow diffusion)
- while dark on ACD
(b) Restricted diffusion seen most classically in ischemic stroke - can also be seen in some tumors, active MS lesions, and abscesses

(a) Locate the hemorrhage
(b) Prognosis

(a) Pontine hemorrhage
- from branches of the basilar artery that penetrate into the pons
(b) Very poor prognosis- immediately quadraplegic, decerebrate posturing, comatose, very minimal meaningful recovery (if any)
Features of T2 MRI
(a) Color of brain matter
(b) Color of CSF
(c) Color of blood vessels
T2 MRI
- T1 vs. T2 has to do w/ the relaxation of the particles
(a) White matter is dark, grey matter is light
(b) CSF is bright white
(c) BVs are dark

Locate the lesion of
(a) Unilateral homonymous hemianopsia
(b) Bitemporal hemianopsia
(a) Unilateral homonymous hemianopsia 2/2 lesion of the optic tract
- or if macular sparing (hard to determine on exam), lesion localizes to the occipital lobe
(b) Bitemporal hemianopsia 2/2 lesion of the optic chiasm





