Lecture Images Flashcards

Note: no sensory distribution for C1

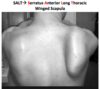
Winged scapula
(a) Muslce involved
(b) Nerve injured
Winged scapula due to injury to (b) Long thoracic causing loss of innervation to the (a) serratus anterior
SALT = serratus anterior, long thoracic
Nerve controlling
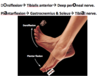
(a) Foot dorsiflexion
(b) Foot plantar flexion
(a) Dorsiflexion by the deep peroneal nerve
(b) Plantar flexion by the tibial nerve

What malignancy should be screened for in a pt w/ distal peripheral neuropathy w/o diabetes?
Screen for multiple myeloma
-also chronic alcoholism can cause stocking-and-glove distribution peripheral neuropathy
What are the two main branches fo the sciatic nerve?
Before going thru the popliteal fossa the sciatic nerve splits into the common peroneal/fibular nerve and the tibial nerve

The belt might cause injury to what nerve? How would this present?

Injury to lateral femoral cutaneous nerve
-tingling/numbness/burning in outer thigh
2/2 tight clothing, obesity/wt gain, pregnancy
Purpose of tPA
Save the penumbra- tissue that is ischemic but not yet infarcted
-takes 90 minutes on average to set up the IR suite => give tPA in the mean time to save penumbra

Baby pulled out of birth canal by arm is at risk for what?
Klumpke’s palsy (claw hand deformity) 2/2 damage to C8-T1

Name the 4 most common locations for white matter lesions in MS
- Periventricular
- look like Dawson’s fingers on sagittal view - Juxtacortical
- Infratentorial (posterior fossa)
- brainstem and cerebellum - spinal cord

Where may jaw pain radiate? Why?
Jaw pain sometimes radiates to the ear b/c both are of the C2 dermatome

Dx

Left ACA stroke

2 findings on MRI
Dx

Dx = neuromyelitis optica = Devic’s disease = simultaneous inflammation and demyelination of the optic nerve and spinal cord
- on a spectrum w/ MS
- inflammatory disease that presents w/ pathology of the optic nerve/chiasm
What nerve innervates the
(a) Quadriceps
(b) Hamstring
(c) Gluteus maximus
(a) Femoral nerve innervates the quadricep
(b) Sciatic nerve innervates the hamstring
(c) Inferior gluteal nerve innervates the gluteus maximus
Precentral vs. postcentral gyrus
Precental = primary motor cortex
Postcentral = primary sensory cortex

(a) Finding
(b) Dx

(a) Finding = juxtacortical lesion
(b) MS
48 yo POD1 from bifrontal meningioma removal, uncomplicated postop but now somnolent
(a) Dx
(b) Mgmt

(a) Dx = bitemporal tension pneumocephalus (air in the head)
(b) Mgmt = bed flat
- 100% oxygen to diffuse out the nitrogenous air
- needle decompression
- consider bifrontal craniectomy if need to
Name the two reflexes tested in the lower extremity
(a) What nerve roots innervate these reflexse?
- achilles innervated by S1/S2
- patellar reflex innervated by L3/L4

Pt cannot extend his leg at the knee- which nerve is injured?
Can’t extend knee = inability to control quadricep muscle = injury to femoral nerve
Baby pulled out of birth canal by head is at risk for what?
Erb’s palsy (waiter’s tip deformity) due to damage to C5-C6

Dermatomal landmarks
(a) Bellybutton
(b) Nipple line
(c) Thumb
(a) Bellybutton = T10
(b) Nipple line = T4
(c) Thumb = C6 (thumb’s up)
Injury to what nerve causes wrist drop
Injury to radial nerve which innervates the muscles that extend the wrist (extensor carpi ulnaris and radialis)
- ‘man falls asleep w/ arm under partner’
- ‘falls asleep w/ arm slung over the back of a chair’

Dx

Dx = MS plaque
-tissue showing discoloration in the white matter, indicating large area/amount of demyelination
(a) Dx
(b) Next step

(a) Dx = subarachnoid hemorrhage
- the dread star sign = blood in the circle of Willis
(b) Next step = CTA to find the aneurysm
What nerve innervates the
(a) Pec major
(b) Rhomboids
(a) Medial and lateral pectoral nerves innervate the pectoralis major
(b) Dorsal scapular nerve (Don’t Shoot Rhinos)