Neuroradiology Flashcards
Computed Tomography
–Ionizing radiation (x-rays)
–Measuresattenuation of radiation by tissues
–Revolutionized the practice of modern medicine
What are the risk of a CT scan?
- Cancer induction
- Contrast nephropathy
What are the color densities of CT scan?
–CSF
•Dark
–Grey matter
•Light grey
–White matter
•Dark grey
–Bone (Skull)
Bright (white)
Density of blood depends on age. What is the difference between acute bleed and chronic bleed?
Acute Bleed - Bright
Chronic - Dark
Epidural hematoma: acute bleed (Left picture)
Subdural hematoma: Chronic bleed (right picture)

Intravenous Contrast is used for CT scans. It is Iodinated, causes high attenuation of x-rays. How does it appear?
Appears bright
What Intravenous Contrast not used for?
Not used for head trauma
- Acute hemorrhage and contrast both appear bright
- Want to avoid confusing one for the other
What is Intravenous Contrast helpful for?
Intracranial infection or tumor
- Inflammation from infection and tumor disrupts the blood-brain barrier
- Contrastenters into diseased areas of brain and causes them to become brighter and easier to detect
What is the difference between these two images?
Images of Abscess

Left image = Without contrast
Right image - With contrast
CT scan
This is an image of?

Glioblastoma Multiforme
CT scan w/ contrast
Magnetic Resonance Imaging
–Uses large magnetic field
–No known increased cancer risk
–Complex physics; measures radiofrequency signal from protons
What are the imaging sequences of an MRI?
–T1weighted
•Fatis bright, water is dark (fat has lots of H1)
–T2weighted
•Wateris bright (think H2O)
–Diffusion weighted imaging (DWI)
•Acute stroke is bright
–Susceptibility weighted imaging (SWI)
•Blood is very dark
What are the strengths of T1 compared T2?
–T1weighted
- Anatomy
- Bone marrowpathology (such as tumor)
–T2 weighted
- Pathology
- Edema (increased water content) - bright
Infection, tumor, inflammation (good for detecting this)
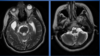
Which image was done with T1 weighed and which one is done with T2 weighed?

Left image = T1 (Cerebrospinal fluid is dark)
Right image = T2 (Cerbrospinal fluid is bright)
What type of MRI was this image obtained from?

T1
Bright fatty bone marrow of the skull
How does blood appear on MRI?
– Appearance depends on ageand composition of blood products
–SWI sequence
•Very dark in most stages of blood

IV contrast w/ MRI
•Intravenous contrast
–Gadolinium; large radiofrequency signals
–Appears very bright
Using IV contrast w/ MRI is helpful for?
–intracranial infection or tumor
- Inflammation from infection and tumor disrupts the blood-brain barrier
- Contrastenters into diseased areas of brain and causes them to become brighter and easier to detect
This radiographic test was used to obtain this image?

MRI w/ contrast
Image of Abscess
This is an image of ?

Glioblastoma Multiforme
Done with MRI w/ contrast
CT vs MRI
Which is which?

LEft
CT: Bone bright, scalp fat dark
Right
MRI: Bone bright + dark, scalp fat bright
What are the two different type of stroke a person could have?
•Hemorrhagic stroke
–Bleeding in the brain
–Usually due to hypertension
•Ischemic stroke
–Lack of blood flow to the brain
–Usually due to clot
Acute Ischemic Stroke
Timing?
Physiology?
•Timing
–Less than 2 weeks old (including acute and subacutestages)
•Physiology
–Cytotoxic edema
•Increased intracellular fluid
Decreased extracellular fluid
On CT scan, How does Acute Ischemic Stroke appear?
–Increased water in brain tissue
–Affected tissue becomes darker with time
–Very early stroke is difficult to detect
If 6 past after an Acute Ischemic Stroke, how does that affect the CT scan?
– At 6 hours, 60% of patients will have CT abnormality
–At 24 hours, all patient will have CT abnormality