Neoplasia I- Histology and Cytology Flashcards
Neoplasia
new growth
Cancer
Latin for crab
tend to adhere to any part that they seize on in an obstinate manner
Oncology
Study of tumors or neoplasms
Tumor parenchyma
= neoplastic cells
Reactive stroma
connective tissue, includes fibrous tissue, blood vessels, and inflammatory cells
in many malignant tumors connective tissue contains abundant and is firm: desmoplasia (desmoplastic stroma)
Desmoplasia
in many malignant tumors connective tissue contains abundant collagen and is firm
Nomenclature of benign mesenchymal neoplasms
cell of origin + oma
Benign mesenchymal tumor of fibrous tissue
fibroma
Benign mesenchymal tumor of adipose tissue (lipid)
lipoma
Benign mesenchymal tumor of cartilage
chondroma
Benign mesenchymal tumor of bone
osteoma
Benign mesenchymal tumor of blood vessels
hemangioma
Benign mesenchymal tumor of lymph vessels
lymphangioma
Benign mesenchymal tumor of smooth muscle
leiomyoma
Greek for smooth
leio
Benign mesenchymal tumor of striated muscle
rhabomyoma
Greek for rod
rhabdo

Lipoma
Cells on slide are regular size = benign

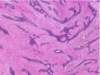
Leiomyoma
Spindle cells resemble smooth muscle
same size and shape and color = benign
Nomenclature of malignant mesenchymal neoplasms
cell of origin + ~sarcoma
sar =fleshy (greek)
Malignant mesenchymal tumor of fibrous tissue
fibrosarcoma
Malignant mesenchymal tumor of adipose tissue
liposarcoma
Malignant mesenchymal tumor of cartilage
chondrosarcoma
Malignant mesenchymal tumor of bone
osteosarcoma