Neonatal rashes Flashcards
(38 cards)
When do you develop the following embryologically?
- Nails
- Hair
- All layers of epidermis
- Epidermal barrier
- Nails: 8-9 wks
- Hair: 17-19 wks
- All layers of epidermis: 24 wks
- Epidermal barrier: 35 weeks
When is erythema toxicum first noted?
What is a key feature of it?
What type of cells are seen?
What does it resolve?
24-48h post delivery
Spares palms/soles
Eosinophilic
Lesions last <1 day, settles within a week
Name this rash

Erythema toxicum neonatorum
When is transient neonatal pustular melanosis first noted?
When do they resolve?
What cells are seen in the pustule?
At birth (5% darker skins, <1% white)
Weeks to months
Neutrophils
Name this rash

Transient neonatal pustular melanosis
Name this rash
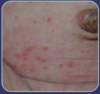
Miliaria rubra
What layer of skin does miliaria crystallina occur?
What layer of skin does miliaria rubra occur?
Eccrine sweat ducts
Spinous layer
Name this rash

Neonatal cephalic pustulosis
When is neonatal cephalic pustulosis typically seen?
When does it disappear?
2-3 weeks of life
By 3 months
Name this rash

Congenital candidiasis
When do lesions present for congenital candidiasis?
What does the rash look like?
Which population is at high risk of disseminated disease?
What is the mortality rate of disseminated systemic candidiasis?
How long do you treat with fluconazole?
At birth or first few days of life
widespread vesiculopustular eruption with fine scale
Premature/low birth weight infants
20%
21 days after microbiological clearance
Name this rash

Neonatal Candidiasis
When do lesions present for neonatal candidiasis?
Describe the appearance of lesions.
Where do the lesions tend to be located?
How are they treated?
1 week
Erythematous patches, satellite papules/pustules
Flexures and diaper area
Topical antifungal (imidazole = cannestan)
List 3 features of congenital HSV?
Which pregnancies are at highest risk?
What type of infection carries a 2% risk?
When are lesions noted with congenital HSV?
- Aplasia cutus
- Microcephaly
- Temporal lobe encephalitis
- Chorioretinitis
Primary infection during pregnancy (57%)
Recurrent infection
Birth or within 48h
What are the 3 types of neonatal HSV?
What is the incubation period for HSV?
What is the recommended treatment?
- Mucocutaneous
- Disseminated
- CNS
4-21 days
IV Acyclovir 14-21 days, prophylaxis x 6 months
Name this rash

Neonatal lupus
List 3 complications of neonatal lupus
What type of antibodies are seen with this disorder?
- Thrombocytopenia
- Hepatosplenomegaly
- Congenital heart block
Maternal anti-Ro and anti-La
List 3 physical causes of blistering in a neonate
- Iatrogenic
- Sucking blister
- Electrodes from fetal scalp monitoring
- Instrumental delivery
- Iodine/alcohol burn
List 2 inflammatory causes of blistering in a neonate
- Bullous mastocytosis
- Urticaria pigmentosis
List 3 autoimmune causes of blistering in a neonate
- Bullous pemphigoid
- Chronic bullous dermatosis of childhood
- Maternal bullous disease
List 3 genetic causes of blistering in a neonate
- Epidermolysis bullosa
- Incontinentia pigmenti
- Epidermolytic ichthyosis
Name this skin disorder

Staphylococcal scalded skin syndrome
Name the location the exfoliative toxin attacks in SSSS
Desmoglein-1
Name this rash
What is the deficiency?
List the triad

Acrodermatitis enteropathica
Zinc deficiency
- Alopecia
- Diarrhea
- Periorificial rash/diaper rash





