Natural Hazards Flashcards
(11 cards)
name 3 natural hazards at plate boundaries
- earthquakes
- volcanoes
- tsunamis
name this plate boundary

conservative plate boundary
describe a conservative plate boundary

two parallel plates move alongside each other

- in opposite directions
- in the same direction at slightly different speeds
- causing friction until they suddenly slip past and the rock snaps
- causing shockwaves (seismic waves) to shake the ground
- producing an EARTHQUAKE
- example: San Andreas Fault near Los Angeles
name this plate boundary

destructive plate boundary

what happens at a destructive plate boundary

an oceanic plate and a continental plate move towards each other and collide

- the heavier oceanic plate is forced underneath the lighter continental plate
- the friction causes the heavier oceanic plate to melt and become magma
- creating EARTHQUAKES (collsion) AND VOLCANOES (magma escaping) = TOTALLY DESTRUCTIVE!
name this plate boundary

constructive plate boundary
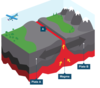
what happens at a constructive plate boundary

two plates move apart in opposite directions

- convection currents cause plates to move apart
- magma rises to fill the new gap
- on the surface, the ‘lava’ hardens to form new mountains/islands and VOLCANOES
- example: mid-Atlantic Ridge
name this zone

collision zone

what happens at a collision zone

two continental plates collide

- as both plates are the same weight, neither plate is forced under the other
- instead both plates are forced up to form fold mountains
- example: Himalayas (Asia), Andes (South America), Alps (Europe)
where are earthquakes likely to happen?
conservative (sliding parallel)
&
destructive (sliding under)
plate boundaries

where are volcanoes likely to happen?
at constructive** & destructive plate boundaries**

where there’s magma


