Multiple Myeloma and Bone Pain Flashcards
What is multiple myeloma?
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ghvoKhpAc64
Myeloma is a malignant disease of bone marrow plasma cells. There is a clonal expansion of abnormal, proliferating plasma cells producing a monoclonal paraprotein, mainly IgG or IgA, and rarely IgM and IgD.
The paraproteinaemia may be associated with excretion of light chains in the urine (Bence Jones protein), which are either kappa or lambda.
What age group does multiple myeloma normally affect?
Elderly
What is the peak age at which MM presents?
70 years
Who is it more common in; Africans or Caucasians?
Africans - 2:1
What cells are affected by neoplastic changes in multiple myeloma?
Plasma cells
What do neoplastic myeloma cells produce?
Monoclonal paraproteins
What proportion of multiple myeloma cases have IgG paraproteins?
60%
What proportion of multiple myeloma cases have IgA paraproteins?
20%
Why does osteolysis occur in multiple myeloma?

The osteolytic destruction of the axial skeleton (sites of haemopoiesis in adults) results from malignant plasma cells stimulating osteoclasts to erode bone.
For some time it has been recognised that chemical messengers (cytokines) produced from the interaction of malignant plasma cells with their microenvironment stimulate the osteoclast activity. Such cytokines were known as osteoclast activating factors (OAFs) and are now known to include interleukin-1 and -6.
What may bee seen on blood film in multiple myeloma?
Rouleaux formation - as a consequence of the paraprotein and circulating plasma cells in the aggressive plasma cell leukaemia variant of myeloma.
What type of anaemia occurs in multiple myeloma?
Normocytic normochromic
What can be found in the urine in someone with multiple myeloma?
Bence-Jones Proteins
What are the following?
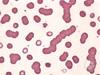
Roleaux formations
Why are bence jones proteins found in the urine?
Found in urine as a result of decreased kidney filtration capabilities due to renal failure, sometimes induced by hypercalcemia from the calcium released as the bones are destroyed or from the light chains themselves
What are the most commonly affected bones in multiple myeloma?
- Spine
- Skull
- Long bones
- Ribs
What does adhesion of bone marrow stromal cells to myeloma cells result in?
Produces cytokines, which:
-
Stimulates the production of RANKL, IL-6 and also VEGF -> angiogenesis
- RANKL -> stimulates osteoclastic osteolysis.
- OPG levels reduced -> reduced inhibition of osteoclastic activity
- Paracrine secretion of endothelin 1 and PTH-rp -> increases osteoclastic activity.

What are symptoms of multiple myeloma?
- Bone pain
- Symptoms of anaemia
- Recurrent infections
- Symptoms of renal failure
- Symptoms of hypercalcaemia
- Symptoms of hyperviscosity and bleeding - rare
- Weight loss
What is the most common type of bone pain?
Backache
What are symptoms of hypercalcaemia?
Bones, stones, groans, thrones (plenty pish but nae shite) and psychiatric overtones:
- Abdominal pain
- Vomiting
- Constipation
- Polyuria
- Polydipsia
- Depression
- Anorexia
- Weight loss
- Tiredness
- Weakness
- Hypertension
- Confusion
- Pyrexia
- Renal stones
- Renal failure
- Cardiac arrest
Why does bone pain occur in MM?
Malignancy, whether primary or metastatic, changes the osteoblastic/osteoclastic balance. This results in either lytic lesions or abnormally weakened bone that is subject to microfractures.
Increased bone turnover can also produce pain, similar to the ‘growing pains’ of rapid growth in adolescence.
If someone presented with bone pain/tenderness, what would consider as part of your differential diagnosis?
- Trauma/fracture
- Myeloma/Primary malignancy
- Metastases
- Osteonecrosis
- Osteomyelitis/periostitis
- Hydatid cyst
- Ostesclerosis
- Paget’s disease
- Sickle cell disease
- Renal osteodystrophy
- CREST syndrome/Sjogren’s
- Hyperparathyroidism
If someone presented with bone pain, what initial investigations would you do?
- FBC, U+E’s, LFTs
- PSA
- ESR
- Ca2+
- LFTs
- Electrophoresis
Why can someone with MM get recurrent infections?
Due to immunoparesis and neutropenia, plus chemotherapy
Why does renal impairment occur in MM?
Due to paraprotein deposition, which bind with Tamm-Horsfall proteins in distal loop of henle. Monoclonal antibodies also cause changes in glomeruli.
Metastatic calcification, changes of pyelonephritis and AL amyloid may also be present in the kidneys. Systemic amyloidosis is present in 10% of cases, particularly in the tongue, heart and peripheral nerves, as well as the kidneys
When does hyperviscosity and bleeding occur in multiple myeloma?
When there is bone infiltration by plasma cells
What investigations would you do in someone who you suspected had multiple myeloma?
- Bloods - FBC, ESR, U+E’s, LFTs, Ca2+, Alk phos, PSA, LDH, Blood film
- Imaging - Skeletal survey - X-rays
- Specific - Myeloma screen - Serum and urine electrophoresis, Immunoglobulins
What might you see on FBC in someone with MM?
- Hb - normal, or normochromic, normocytic anaemia
- WCC - normal or neutropenic
- Platelets - normal or low
What might you see on U+E’s in someone with MM?
Signs of Renal Failure
What might you see on serum Ca2+ investigation in MM?
Hypercalcaemia
What might you see on investigation of Alk phosphate in MM?
Ususally normal - unless there is a healing fracture
What might you see on X-ray in someone with MM?
Lytic ‘punched out’ lesions
- Pepper pot skull
- Vertebral collapse
- Fractures

What might you see on serum protein electrophoresis?
Monoclonal bands and immune paresis

What might you find on 24-hr urine collection electrophoresis?
Bence-Jones proteins

What might you see on bone marrow aspirate in someone with MM?
Hypercellularity - many plasma cells with abnormal forms
What diagnostic criteria are used to diagnose myeloma?
- Monoclonal protein band in serum or urine electrophoresis
- Plasma cells increased in BM biopsy
- Evidence of end organ damage from myeloma - Hypercalcaemia, Renal failure, anaemia
- Bone lesions - skeletal survey
What areas would you check as part of a skeletal survey?
- Chest
- All spine
- Skull
- Pelvis
What are complications of myeloma?
- Hypercalcaemia
- Spinal cord compression
- Hyperviscosity
- AKI
What are features of hyperviscosity in MM?
- Reduced cognition
- Distrurbed vision
- Bleeding
How would you manage hyperviscosity in MM?
Plasmapheresis
How would you manage an AKI in someone with MM?
- Rehydration - 3L/day fluid intake
- Consider urgent dialysis
How would you manage someone with spinal cord compression in MM?
- Consider decompression
- Dexamethasone 8mg BD
- Ranitidine/PPI
- Emergency radiotherapy to mass
How would you manage someone with MM?
- Analgesia - for bone pain
- Bisphosphonates
- Local radiotherapy
- Chemotherapy
- Surgery
- Autologous stem cell transplant - consolidation
How would you manage infections in someone with MM?
- Blood cultures
- Broad spectrum antibiotics
- IVIG if needed
What chemotherapeutic treatments could you use in MM?
- Cyclophosphamide
- Thalidomide
- Dexamethasone
- Proteasome ihibitors
- IMiDs
- Monoclonal antibodies
What are bisphosphonates used for in MM?
- Bone pain
- Reduce fracture rate
Why can boney pain present in metastatic cancers?
Cause alterations in the pain pathway, which lower pain threshold and increase the likelihood a pain impulse will be triggered. Alterations include:
- Reorganisation of dorsal horn and sensitisation of pain afferents to substance P (which stimulates pain pathways)
- Astrocyte hypertrophy and decreased glutamate reuptake transporters, causing increased glutamate and excitotoxicity
- Increased glial proteins in the spinal cord -> increase pain transmission
- Acidic environment produced by osteoclasts can stimulate pain receptors
- Increase in the receptive field for neurons and a change in ratio of types of neurons present in dorsal horn -> increased neuronal response to low-level stimuli
It is believed that these changes, among others, contribute to pain directly as well as to hyperexcitability of neurons to stimuli
What is Monoclonal gammaglobulin of unknown significance?
Pre-malignant clonal disorder of plasma cells, which has low level paraprotein or Bence Jones protein. It is very common in older populations.
This has a small risk of progressing to myeloma (1% per year)
Why would you do a PSA in someone with lower back pain?
Rule out prostatic cancer as the cause
Why does myeloma cause renal damage?
- Light chain deposition (cast nephropathy)
- NSAID use
- Infection
- Hypercalcaemia
- Amyloid
- Tubular damage - renal Fanconi syndrome
What mnemonic can you use to help remember the main features of myeloma?
- Calcium - due to bone damage
- Renal damage
- Anaemia
- Bone lesions
- Infection

If someone had MGUS, what conditions would you want to exclude?
- Myeloma
- Low grade lymphoma
- AL Amyloidosis
- POEMS syndrome
- Light/heavy chain deposition disease


