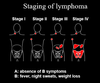
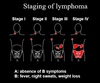
Lymphomas - Hodgkin's Lymphoma Flashcards
What is the definition of lymphoma?
Malignancies of the lymphoid system and hence may arise at any site where lymphoid tissue is present, including:
- Lymphadenopathy
- Extranodal
- Bone marrow
What are the main types of lymphoma?
- Hodgkin’s lymphoma
- Non-hodgkin’s lymphoma
What age group does Hodgkin’s Lymphoma normally occur in?
Bimodal age curve (Between ages 16 and 65):
- 15-35y - first peak
- 2nd peak later in life
What are the main lymphoid tissues?
- Lymph glands
- Adenoids
- Palatine tonsils
- Thymus
- Spleen
- Liver
What does Hodgkin’s lymphoma have an asscoiation with?
EBV - up to 40% have increased EBV antibody titres at the time of diagnosis and EBV DNA has been demonstrated in tissue from patients with HL
What are the subclassifications of Hodgkin’s Lymphoma?
- Classical Hodgkin’s lymphoma (cHL) - 90-95% of cases
- Nodular lymphocyte predominant HL (NLPHL)
What are the characteristic cells found in classical Hodgkin’s Lymphoma?
Reed-Sternberg Cells
What are the characteristic cells found in Nodular lymphocyte predominant HL?
Popcorn Cells
What are the following?

Reed-Sternberg Cells - malignant binucleate cells
What are the main groups of causes of cervical lymphadenopathy?
- Infection
- Autoimmune disease
- Drug reactions
- Primary malignancy
- Secondary Malignancy
- Miscellaneous
Why can Hodgkin’s Lymphoma produce an inflammatory picture on FBC?
Reed-Sternberg cells produce cytokines, which attracts inflammatory cells and creates an inflammatory environment
What are acute infections which can cause cervical lymphadenopathy?
- Pyogenic infections
- EBV
- CMV
- Cat Scratch fever
- Infected Eczema
What are chronic infections that can cause cervical lymphadenopathy?
- TB
- Syphilis
- HIV
What are autoimmune causes of cervical lymphadenopathy?
- Rheumatoid Arthritis
- Sarcoidosis
What can increase the risk of someone developing Hodgkin’s Lymphoma?
- Affected sibling
- EBV
- SLE
- Post-transplantation
- Obesity
What drug reactions can cause cervical lymphadenopathy?
Phenytoin
What primary malignancies can cause cervical lymphadenopathy?
- Hodgkin’s Lymphoma
- Non-Hodgkin’s Lymphoma
- CLL
- ALL
What secondary malignancies can cause cervical lymphadenopathy?
- Thyoid
- Laryngeal
- Lung
- Melanoma
- Breast
- Stomach
- Nasopharyngeal/Oropharyngeal
What mnemonic can you use to help you remember groups of causes for lymphadenopathy in general?
- Malignancy
- Infection
- Autoimmune
- Miscellaneous
- Iatrogenic
What are miscellaneous causes of cervical lymphadenopathy?
- Kawasaki disease
- Sarcoidosis
What are symptoms of Hodgkin’s Lymphoma?
- Swellings
- Fever
- Weight loss
- Night Sweats
- Pruritis
- Lethargy
What is characteristic of the swellings seen in Hodgkin’s Lymphoma?
- Painless
- Non-Tender
- Rubbery
- Superficial
Where does lymphadenopathy most commonly occur in Hodgkin’s Lymphoma?
- Cervical
- Axilla
- Inguinal nodes
What are signs of Hodgkin’s Lymphoma?
- Lymphadenopathy
- Cachexia
- Anaemia
- Splenomegaly
- Hepatomegaly