MSK Upper Limb 2 Flashcards
(64 cards)
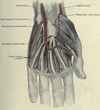
Label the superficial & intetermidiate muscles of the anterior forearm


Where do the superficial forarm flexors attach
Medial epicondyl of the ulnar via the common flexor tendon

State the order of the superficial forearm flexors of the forearm from medial to lateral

What is the action of pronator teres?
Pronation of forearm
Apart from flexing the wrist, which superficial muscle is involved in abduction (radial deviation) of the wrist joint
Flexor carpi radialis
Apart from flexing the wrist, which superficial muscle is involved in adduction (ulnar deviation) of the wrist joint
Flexor carpi ulnaris
What nerve supplies the superficial muscles of the anterior compartment of the forearm
Median Nerve:
Flexor Carpi Radialis
Flexor Digitorum superficialis
Pronator Teres
Ulnar Nerve:
Flexor Carpi Ulnaris
Where is the flexor digitum located
Lies immediately deep to the superficial group of flexors in the forearm and is seen as the only muscle on the intermediate group of the forearm
Origin
Insertion of FDS
Action
Origin:
Humeroulnar head: Medial epicondyle of humerus, coronoid process of ulna
Radial head: Proximal half of anterior border of radius
Insertion:
All fingers except thumb at the middle phalanx
Action:
Metacarpophalangeal and proximal interphalangeal joints 2-5: Finger flexion
State the bone names of the hand

Name the carpel bones

What is special about the brachioradialis
Only muscle in the anterior forearm which is not a flexor
Label the Deep Group of Muscles in the anterior compartment of the forearm


Flexor Digitorum Profundus
Action:
Innervation:
Action:
Flexion of hand and both intephalangeal joints
Innervation:
Medial side (Ring and pinky) :
Ulnar Nerve
Lateral side:
Median Nerve
Flexor Pollicis Longus (FPL) Innervation
Action
Innervation
Action:
Flexes thumb
Innervation
Median Nerve
Pronator Quadratus
Action
Innervation
Action:
Pronator at both the proximal and distal radioulnar joints.
Innervation:
Median Nerve


Fill in the blanks:
The median nerve enters the forearm to the brachial artery.
It then heads under the muscle and passes down the forearm between the FDS and FDP.
It enters the carpal tunnel the flexor retinaculum.
The median nerve enters the forearm medial to the brachial artery. It then heads under the pronator teres muscle and passes down the forearm between the FDS and FDP.
It enters the carpal tunnel under the flexor retinaculum
Which muscle(s) does the median nerve not supply in the anterior forearm?
Flexor carpi ulnaris and medial half of flexor digitorum profundus
Fill in the blanks:
After passing posterior to the of the humerus the ulnar nerve enters the forearm by passing between the heads of
Both the ulnar nerve and ulnar artery descend close to each other down the medial aspect of the forearm
The ulnar nerve lies to the ulnar artery at the level of the wrist
After passing posterior to the medial epicondyle of the humerus the ulnar nerve enters the forearm by passing between the heads of flexor carpi ulnaris muscle. Both the ulnar nerve and ulnar artery descend close to each other down the medial aspect of the forearm
The ulnar nerve lies medial to the ulnar artery at the level of the wrist
What two muscles anchor the fibrous flexor reticulum?
The scaphoid and the trapezium on the lateral side
The pisiform and hamate bone on the medial side.

Contents of Carpal Tunnel
4 tendons of flexor digitorum superficialis
4 tendons of flexor digitorum profundus
1 tendon of pollicis longus
median Nerve
State the 5 compartments of the hand
1) Thenar compartment
2) Hypothenar compartment
3) Lumbricals and long flexor tendons – central compartment
4) Adductor compartment
5) Interosseous compartmen
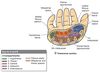
State the thenar muscles
· Abductor pollicis brevis (APB)
· Flexor pollicis brevis (FPB)
· Opponens pollicis (OP)