Module 2 - Nerves Flashcards
(114 cards)
Three states of information processing in the nervous systems?
- Sensory input
- integration
- motor output
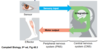
Two types of signalling?
Local vs Distance
Two types of local signalling?
Paracrine and Synaptic signalling
Three stages of cell signalling?
Reception, Transduction, Response
What is paracrine signalling?
A signalling cell acts on nearby target cells by secreting molecules of a local regulator (a growth factor, for example)
What is Synaptic signalling?
A nerve cell releases neurotransmitter molecules into a synapse, stimulating the target cell, such as a muscle or another nerve cell
What is a form of long distance signalling?
Endocrine (hormonal) signalling
What is endocrine signalling?
Specialised endocrine cells secrete hormones into body fluids, often blood. Hormones reach most body cells, but are bound by and affect only some cells.
Two main types of receptors?
Plasma membrane receptors and intracellular receptors
What is an intracellular receptor?
A steroid receptor
Three types of plasma membrane receptors?
Ion channel linked receptors:-Na+channel opened by ligand
G protein-coupled receptors: 7 TM-spanning regions- all aspects of physiology and pharmacology
Tyrosine kinase linked receptors:
Example of ion channel linked receptors
nicotinic receptors, glutamate receptors
Where would G protein-coupled receptors be found?
all aspects of physiology and pharmacology
Example of Tyrosine kinase linked receptors?
metabolism, cell growth, cell reproduction
What energy is used in G-protein receptors?
ATP (adenlyl) and GTP (g protein)
Four main proteins in a G-protein receptor?
G protein-couple receptor (GPCR)
G protein
Adenlyl cyclase
Protein kinase A
What can activate a G-protein couple receptor?
light, ions (eg. Ca2+), odourants, gustative molecules,neurotransmitters, hormones, peptides, proteins.
What do GPCRs interact with? For what cause?
Heterotrimeric G proteins to control the activity of enzymes, ion channels, and instracellular signal trasnduction pathways
What enzymes mediate transfer of phosphates in Tyrosine kinase linked receptors?
Kinases
What is a phosphate?
PO4-
What occurs during Tyrosine kinase linked receptors?
Phosphorylation cases are mediated by Kinase - these enzymes transfer phosphate and activate or inactive target proteins
Three structural vetebrate neurons?

What are cells that support nerve cells?
Glia cells
Two types of glia cells?
Astrocytes and Oligodendrocyes & Schwann Cells
















