Module 1 – Customer Demand: Foundations Flashcards
(33 cards)
A certain product has a negative income elasticity of demand. What might this product be?
- Speedboat
- Rice
- Clothing
- Books
Speedboat
It’s likely that a consumer would buy more speedboats or be more likely to buy a single speedboat as their income went up. This implies a positive income elasticity.
Rice
A negative income elasticity of demand implies that a consumer will buy less of a good as his or her income increases. This could be the case for cheaper foods such as rice. A consumer with a higher income might be able to afford more expensive foods and switch to, say, quinoa, fish or steak instead.
Clothing
It’s likely that a consumer would buy more clothes as their income went up. This implies a positive income elasticity.
Books
It’s likely that a consumer would buy more books as their income went up. This implies a positive income elasticity.
Which of the following statements regarding price elasticity of demand is true? Select all that apply.
- Price elasticity of demand is a better measure of price sensitivity than slope.
- Price elasticity of demand tends to increase as price increases.
- Price elasticity of demand for a particular product will tend to increase as more substitute goods become available.
- Price elasticity of demand tends to decrease over time.
- Price elasticity of demand is necessarily equal to one halfway down a demand curve.
Price elasticity of demand is a better measure of price sensitivity than slope.
This is true because slope measures absolute changes in quantity and is sensitive to the units of measurement; in contrast, elasticity is not.
Price elasticity of demand tends to increase as price increases.
This is generally true. The higher the price, the less willing consumers will be to put up with increases in price for a particular product. For example, consumers might be willing to put up with a 100% price increase for a $1 candy bar, but not for a $20,000 car.
Price elasticity of demand for a particular product will tend to increase as more substitute goods become available.
The more available are substitute goods, the less willing consumers will be to put up with increases in price for a particular product.
Price elasticity of demand tends to decrease over time.
This is generally false. The longer the time horizon, the greater the chance of competition in a market and/or the greater chance consumers have to switch away to a substitute good. All else equal (for example, accounting for brand loyalty, consumer habits and other factors), this would make consumers more sensitive to changes in price over time.
Price elasticity of demand is necessarily equal to one halfway down a demand curve.
False. This is only true for linear demand curves.
Which of the following scenarios illustrates the concept of diminishing marginal returns?
- Nate is willing to pay $3 for a bottle of soda pop, but Max is only willing to pay $2.50.
- Alexis would pay $3 for a cup of coffee, but would only pay $4 total for two cups.
- Abe is only willing to pay $30 for a ticket to his alma mater’s hockey game because he lives out of state and travel costs are high.
- Even though Miranda would gladly pay $25 to stream music via Spotify each month, her subscription costs only $8.
Nate is willing to pay $3 for a bottle of soda pop, but Max is only willing to pay $2.50.
This illustrates how WTP varies among consumers.
Alexis would pay $3 for a cup of coffee, but would only pay $4 total for two cups.
This scenario illustrates the concept of diminishing marginal returns. The first cup is worth more to Alexis than the second cup, so she is not willing to pay as much for the second cup.
Abe is only willing to pay $30 for a ticket to his alma mater’s hockey game because he lives out of state and travel costs are high.
This statement merely indicates how WTP can be affected by external factors.
Even though Miranda would gladly pay $25 to stream music via Spotify each month, her subscription costs only $8.
This is simply an example of price being lower than a customer’s WTP.
Suppose that Alex, Maria, and Raj are the only 3 buyers of chocolate ice cream in the market. Based on the chart below showing each buyer’s willingness to pay for each additional cone, what is the price elasticity of demand for a change in price from $3 to $4 dollars?
- 6/5
- 1
- 3/4
- Impossible to determine with the information provided

6/5
Based on the WTP chart above, 6/5 is higher than the price elasticity for a price change from $3 to $4 dollars. See correct answer for explanation.
1
The elasticity would be 1 only if the percentage change in quantity was equal to the percentage change in price. See correct answer for explanation.
3/4
We can determine the total market demand at $3 by adding together the total number of cones at which Alex, Maria, and Raj’s WTP is $3 or higher. We can see that Alex will buy 3 cones at $3 or higher, Maria will also buy 3, and Raj will buy 2, which adds up to a total of 8 cones demanded at $3. Repeating the same process for $4 (or higher), we get 2 cones for Alex, 2 cones for Maria, and 2 cones for Raj, which adds up to a total of 6 cones demanded at $4. Once we have these quantities for demand at the new and old prices, we can plug them into the equation for price elasticity of demand = absolute value of [(6-8)/8]/[(4-3)/3] = 3/4.
Impossible to determine with the information provided
In order to calculate price elasticity of demand, we only need know the old and new price ($3 and $4, respectively) and market demand at the old and new prices. We know that Alex, Maria, and Raj are the only buyers in the market for chocolate ice cream cones and thus we are able to determine the entire market demand at any given price determining the total number of cones they will buy at that price or higher.
A budding tech startup has created a unique compression algorithm that consumers can use to reduce the size of their computer files. The company was previously charging $40 a month for their “unlimited plan” that allows users to compress as many files as they want. The company decides that it is not making enough revenue, however, and increases the price for their “unlimited plan” from $40 to $60. They notice that the amount of users that subscribe to the unlimited plan decreases from 5,000 to 4,500 once the price change comes into effect.
Based on this information, which of the following must be true? (Note: This question is based on one submitted by a previous HBS Online graduate)
- At the original price the demand is relatively inelastic
- At the original price demand is relatively elastic.
- At the original price the demand curve has an elasticity of 1.
- None of the above.
At the original price the demand is relatively inelastic
The price elasticity of demand at the original price point would be equal to the absolute value of [((4500-5000)/(5000)) / ((60-40)/(40))] = 0.2, relatively inelastic. The company can make more revenue by charging a higher price.
At the original price demand is relatively elastic.
From calculating the price elasticity of demand, we see that it is equal to 0.2. This means that our demand must be relatively inelastic.
At the original price the demand curve has an elasticity of 1.
See correct answer for explanation.
None of the above.
See correct answer for explanation.
The share price of a company is $20 at the beginning of the month, and $10 at the end of the month. Assuming that the company did not issue new stock during the month, which of the following statements is true? (Select all that apply)
- The WTP for the company’s stock fell by an average of 50% amongst all interested buyers.
- The WTP for the stock fell by an average of 100% amongst all interested buyers.
- Just because the price of the stock changed does not mean investor WTP for the stock has changed.
- The overall valuation of the company fell over the course of the month.
- Some investors may be willing to pay more than $10 for the stock.
The WTP for the company’s stock fell by an average of 50% amongst all interested buyers.
True. The company is now valued at 50% of what it was originally, meaning that the average investor’s WTP for the company is 50% lower as well.
The WTP for the stock fell by an average of 100% amongst all interested buyers.
The average investor is willing to pay $10 for a share, so average WTP fell by 50%, not 100%.
Just because the price of the stock changed does not mean investor WTP for the stock has changed.
Assuming that no new shares were issued, the price of a stock represents a market’s overall valuation of a company. Valuation and average WTP are then synonymous.
The overall valuation of the company fell over the course of the month.
True, since in this situation valuation and average WTP are synonymous.
Some investors may be willing to pay more than $10 for the stock.
True. The $10 valuation represents the average investor valuation of the company’s stock. However, some investors may still be willing to pay more than $10 for the stock.
Below is the demand curve for laptops for another set of incoming undergraduates. Note that this demand curve depicts how many students would be willing to purchase a laptop at any given price, not just price increments of $500.
Around what price should the producer charge in order to maximize its revenue from laptop sales?
- $1000
- $1500
- $2000
- Over $2000

$1000
If the producer charged $1000 per laptop, he would make ($1000)*(1175) = $1,175,000.00 in revenue. Based on the demand curve, the producer could make more by selling fewer laptops and charging more.
$1500
If the producer charged $1500 per laptop, he would make ($1500)*(875) = $1,312,500.00 in revenue. Based on the demand curve, the producer should charge at some price close to $1500 to maximize revenue. Remember that revenue can be calculated as price charged* quantity sold and is equivalent to the rectangular area under the demand curve.
$2000
If the producer charged $2000 per laptop, he would make ($2000)*(525) =$1,050,000.00 in revenue. Based on the demand curve, the producer could make more by selling more laptops and charging less.
Over $2000
Based on the demand curve, the producer could make more by selling more laptops and charging less.
The table below shows one consumer‘s demand for pizza slices:
Which of the following can be concluded from the information above?
- Peter cannot eat more than 1 pizza (8 slices)
- Peter is willing to pay at most $12 for 1 pizza
- Peter will not pay more than $4 for a slice of pizza
- Peter’s willingness to pay for a 5th slice is between $2.00 and $2.50

Peter cannot eat more than 1 pizza (8 slices)
This does not necessarily follow from the table. Peter might be willing to order more than 8 slices if the price fell low enough. (Whether Peter should consume more than a whole pizza is another story).
Peter is willing to pay at most $12 for 1 pizza
This does not necessarily follow from the table: if the price per slice were $1.75, for example, Peter may still order a full pizza.
Peter will not pay more than $4 for a slice of pizza
This may or may not be true. Given the demand schedule above, we cannot be sure.
Peter’s willingness to pay for a 5th slice is between $2.00 and $2.50
This is definitely true. Since Peter demands 4 slices when the price is $2.50 and 6 slices when the price is $2.00, his demand for 5 slices must be at a price somewhere in between.
Which of the following events would, all else equal, cause a rightward shift of the demand curve for yachts? Select all that apply.
- A decrease in the price of yachts
- An increase in household income
- The elimination of a regulation, which had prevented boats from sailing on a particular series of lakes
- The introduction of a wealth tax
- A decrease in the popularity of nautical activities
A decrease in the price of yachts
A change in the price of yachts would not shift the demand curve for yachts. Price changes only affect quantity demanded, not overall demand.
An increase in household income
An increase in income would allow more households to be able to afford yachts, shifting the overall demand for yachts at any given price to the right.
The elimination of a regulation, which had prevented boats from sailing on a particular series of lakes
The elimination of a regulation on boats would increase the demand for yachts to sail in previously forbidden waters.
The introduction of a wealth tax
A tax on wealth would cause a reduction in disposable income, shifting the demand curve for yachts to the left.
A decrease in the popularity of nautical activities
A change in preferences away from boating would decrease the demand for yachts, represented as a leftward shift of the demand curve.
Below are the results of a poll asking incoming undergraduates their WTP for a laptop:
Which of the following represents the demand curve for the computer in this poll?

This demand curve shows how many people would purchase a laptop at each of the prices displayed in the histogram.

Suppose that your WTP for one stick of deodorant is normally $5. The price of deodorant is also typically $5. However, this week your local store is having a buy one, get one (“BOGO”) free sale on your favorite brand. What is your WTP for one stick of deodorant now?
- $2.50
- $5
- $7.50
- There’s no way to tell given the information provided.
$2.50
With the buy one, get one (“BOGO”) free sale, the average price you pay for one stick is cut in half, but your original WTP for one stick has not changed.
$5
Even with the buy one, get one (“BOGO”) free sale, your WTP remains at $5. This is because price does not affect your WTP.
$7.50
See correct answer for explanation.
There’s no way to tell given the information provided.
See correct answer for explanation.
In honor of National Coffee Day, Starbucks runs a promotion giving away a free grande coffee to all customers that come into the store that day. As a result, Starbucks sees its number of patrons double. What conclusion can Starbucks draw from this promotion?
- Customer WTP for coffee has increased by an unknown amount.
- Customer WTP for coffee is $0.
- With a price of $0, customer WTP for coffee doubled.
- The number of customers that bought coffee all had a WTP greater than $0.
Customer WTP for coffee has increased by an unknown amount.
Just because the price of coffee fell to $0, does not mean that WTP for coffee increased. Price and WTP are different.
Customer WTP for coffee is $0.
WTP does not equal price. The increase in patrons could come from consumers with a WTP above $0 but below the original price.
With a price of $0, customer WTP for coffee doubled.
While it’s true that the price was $0 and number of customers doubled, it’s not true that WTP doubled because a change in price, by itself, does not affect willingness to pay.
The number of customers that bought coffee all had a WTP greater than $0.
This is the only plausible conclusion that the company can draw. Based on this one promotion, it cannot infer anything about customer WTP (other than people really enjoy free things).
Just as perceptions of fairness can impact customer WTP, a customer’s perception of the reputation of the seller of a product or service can have an impact on his or her purchasing decisions. Based on what you know about factors that determine WTP, which of the following is plausible?
- Despite higher prices, shoppers in a local town prefer to shop at Joe’s Groceries over chain supermarkets in order to support small businesses.
- After reports of child labor in its factories abroad, a clothes manufacturer sees a decline in quarterly sales of 10%.
- The stock price of BIG Inc., a large company, rises after its CEO decides to forgo a salary and increase the minimum company wage.
- All of the above.
Despite higher prices, shoppers in a local town prefer to shop at Joe’s Groceries over chain supermarkets in order to support small businesses.
Shoppers’ preferences to buy from local stores rather than international conglomerates can impact their WTP. But this is not the only plausible scenario.
After reports of child labor in its factories abroad, a clothes manufacturer sees a decline in quarterly sales of 10%.
Consumers’ WTP for products offered by companies with questionable labor practices is likely to be lower. But this is not the only plausible scenario.
The stock price of BIG Inc., a large company, rises after its CEO decides to forgo a salary and increase the minimum company wage.
Consumer and investor perceptions of a company’s leader can impact WTP for not only products and services, but also the company’s stock.
Fred and Frank are vacationing dog owners. Each owns two dogs which he would like to leave behind at the Pampered Pets Resort while he travels. The graphs below depict their individual demand curves for dog babysitting services.
Which of the following graphs depicts the total demand for Pampered Pets Resort’s services by Fred and Frank?

Graph 4
To obtain the total demand from the two customers, simply sum the two demand curves horizontally.

A jewelry store has a discount for customers who purchase multiple pairs of earrings: after paying full price for one pair of earrings, the second pair is 15% off. John goes to the store and finds a pair of earrings he likes that is sold for $40 per pair, so he purchases two pairs for a total cost of $74. Which of the following MUST be true?
- John’s willingness to pay for the first pair is no more than $74.
- John’s willingness to pay for the second pair is at least $34.
- John’s willingness to pay for the two pairs of earrings is at least $74.
- John’s willingness to pay for the second pair is lower than his willingness to pay for the first pair.
John’s willingness to pay for the first pair is no more than $74.
None of the information available puts an upper limit on John’s willingness to pay for the first or second pair of earrings.
John’s willingness to pay for the second pair is at least $34.
The information available does not suggest this. For example, John may have had a high WTP for the first pair and a low WTP for the second pair.
John’s willingness to pay for the two pairs of earrings is at least $74.
Since John purchased the earrings for $74, he must have been willing to pay that much for them.
John’s willingness to pay for the second pair is lower than his willingness to pay for the first pair.
This is likely but not necessarily true: John’s WTP for the second pair could also be equal to his WTP for the first.
Which of the following statements is true?
- If for some reason the price of a good changes, then the whole demand curve for the good shifts.
- The idea of diminishing marginal returns implies that different people assign different values to the same good.
- To obtain the demand curve for the whole market, one can simply sum horizontally all individual demand curves.
- All of the above.
If for some reason the price of a good changes, then the whole demand curve for the good shifts.
If the price of a good changes, the quantity demanded will change in response. We move along the existing demand curve, but the demand curve does not shift.
The idea of diminishing marginal returns implies that different people assign different values to the same good.
The law of diminishing returns says that people value consecutive units of the same good less and less.
To obtain the demand curve for the whole market, one can simply sum horizontally all individual demand curves.
Market demand is the sum of individual demand.
All of the above.
See explanations above.
Refer to the figure below showing the market demand for organic milk in Massachusetts. The arrow is consistent with which of the following events?
- As a result of lower incomes, people are switching from organic milk to lower-cost substitutes.
- The government has increased the value-added tax on organic milk, leading to higher prices. This has reduced demand.
- Due to higher demand for milk products in emerging economies, milk prices in the United States have increased, thus lowering demand.
- The arrow is consistent with all of these events.

As a result of lower incomes, people are switching from organic milk to lower-cost substitutes.
The diagram depicts a shift in the demand curve that reduces the quantity demanded at any given price. Only option A (lower incomes) results in a shift of the demand curve.
The government has increased the value-added tax on organic milk, leading to higher prices. This has reduced demand.
The diagram shows a shift in the demand curve to the left. Changes in the price of organic milk will affect the quantity demanded, but cannot result in a shift in its demand curve.
Due to higher demand for milk products in emerging economies, milk prices in the United States have increased, thus lowering demand.
The diagram shows a shift in the demand curve to the left. Changes in the price of organic milk will affect the quantity demanded, but cannot result in a shift in its demand curve.
The arrow is consistent with all of these events.
The diagram shows a shift in the demand curve to the left. Changes in the price of organic milk cannot result in a shift in its demand curve.
Which of the following statements is true?
- The demand curve is an upward-sloping line which relates price and quantity demanded.
- If a company that faces a downward-sloping demand curve charges the same price to all its customers, there are usually some customers who are paying less than their willingness to pay.
- The quantity that corresponds to a particular price on the demand curve tells us the number of people who have that price as their willingness to pay.
- All of the above.
The demand curve is an upward-sloping line which relates price and quantity demanded.
The demand curve is a downward sloping line, which relates price and quantity demanded. The negative slope results from the inverse relationship between price and quantity demanded—as one goes up, the other goes down.
If a company that faces a downward-sloping demand curve charges the same price to all its customers, there are usually some customers who are paying less than their willingness to pay.
Unless the company sells only one unit to the customer with the highest WTP, at any price it charges there will always be people who were willing to pay even more and are paying less than their WTP at the given price.
The quantity that corresponds to a particular price on the demand curve tells us the number of people who have that price as their willingness to pay.
The quantity that corresponds to a particular price tells us the number of people who have that price or higher as their WTP.
All of the above.
See explanations above.
Below are the results of a poll in which participants were asked their willingness to pay for a kayak rental.
Which of the following best represents the demand curve that could be constructed from this data?

Graph 4
This graph plots price on the vertical axis against quantity on the horizontal axis, which is correct. At a price of $75, 50 consumers would rent a kayak, and as you follow the curve down you can match other points to the histogram as well.

A product has a price elasticity of demand of 0.6, which means that:
- Total revenue falls when the price increases.
- Revenue is unaffected by price changes.
- Total revenue increases when the price increases.
- Net profit falls when the price rises.
Total revenue falls when the price increases.
Revenue would decrease in response to a increase in price only if demand for the product were price elastic.
Revenue is unaffected by price changes.
Revenue is only unaffected by price changes if the price elasticity of demand is 1.
Total revenue increases when the price increases.
The price elasticity is less than 1, which shows that the percentage change in quantity demanded will be less than the percentage change in price.
Net profit falls when the price rises.
We do not have enough information to determine net profit, since the question gives no information on cost.
Suppose that the table below shows the daily demand amongst vacationers and commuters for train tickets from Boston to New York. As the price increases from $50 to $100, who has the higher price elasticity of demand? Why might this group’s demand be more elastic?
- The vacationers. They are likely to have more flexible travel plans and therefore more elastic demand.
- The commuters. Their lower quantity demanded translates into a more elastic demand.
- The vacationers. A higher quantity demanded always implies a more elastic demand.
- The commuters. They are likely to have less flexible travel plans and therefore more elastic demand.
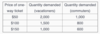
The vacationers. They are likely to have more flexible travel plans and therefore more elastic demand.
The vacationers have a price elasticity of demand equal to 0.25, compared to 0.2 for commuters. This more elastic demand could be due to vacationers’ more flexible travel schedules—the flexibility to travel at different times essentially gives the vacationers more substitutes.
The commuters. Their lower quantity demanded translates into a more elastic demand.
The vacationers have a price elasticity of demand equal to 0.25, compared to 0.2 for commuters.
The vacationers. A higher quantity demanded always implies a more elastic demand.
The vacationers have a price elasticity of demand equal to 0.25, compared to 0.2 for commuters, but a higher quantity demanded does not necessarily equate a more elastic demand.
The commuters. They are likely to have less flexible travel plans and therefore more elastic demand.
The students have a price elasticity of demand equal to 0.25, compared to 0.2 for business travelers.
Which of the following statements is true?
- If demand is linear, slope will vary across different points on the demand curve whereas the elasticity will be the same at all points on the curve.
- Elasticity does not depend on units whereas slope does.
- The data needed to know the demand curve’s entire slope are more likely to be available than the data needed to calculate elasticity at a given price.
- Price elasticity of demand and slope are two names for the same concept.
If demand is linear, slope will vary across different points on the demand curve whereas the elasticity will be the same at all points on the curve.
A linear demand curve has a constant slope, but each point on the curve has a different elasticity.
Elasticity does not depend on units whereas slope does.
A demand curve’s slope might change if the unit’s demand is measured in change.
The data needed to know the demand curve’s entire slope are more likely to be available than the data needed to calculate elasticity at a given price.
Elasticity at a point on the demand curve can be approximated if you know how quantity demanded changes with a small price change.
Price elasticity of demand and slope are two names for the same concept.
Slope measures how much quantity changes as price changes, but elasticity gives a unit-less measure of how significant that change is.
The graph below demonstrates the demand for an unknown product. We can conclude that this product:
- Has many substitutes
- Has no substitutes
- Is a luxury good
- Is being sold at too high a price

Has many substitutes
The graph shows a perfectly inelastic demand curve where changes in price have no effect on the quantity demanded. If the product had many substitutes, customers would start purchasing the substitutes instead of the original product as the price increased.
Has no substitutes
The graph shows a perfectly inelastic demand curve where changes in price have no effect on the quantity demanded. Thus, it shows that the product has no substitutes.
Is a luxury good
The graph shows a perfectly inelastic demand curve where changes in price have no effect on the quantity demanded. Thus, the product is probably a necessity rather than a luxury.
Is being sold at too high a price
The graph shows a perfectly inelastic demand curve where changes in price have no effect on the quantity demanded. We have no information on price, but whatever price is charged could not be “too high” from the profit-maximizing viewpoint.
A bakery sells individual cupcakes for $3, and boxes of 12 cupcakes for $30. A customer enters the bakery and purchases 4 cupcakes. Which of the following statements must be true of the customer’s willingness to pay?
- The customer’s willingness to pay for 6 cupcakes is less than $15.
- The customer’s willingness to pay for 5 cupcakes is less than $15.
- The customer’s willingness to pay for a 5th cupcake is $0.
- The customer’s willingness to pay for 12 cupcakes is at least $36.
The customer’s willingness to pay for 6 cupcakes is less than $15.
The customer’s willingness to pay for 6 cupcakes must be less than $18, but it could be more than $15.
The customer’s willingness to pay for 5 cupcakes is less than $15.
The customer had the option to purchase 5 individual cupcakes for $15. Since the 5th cupcake was not purchased, the customer’s willingness to pay for 5 cupcakes must be less than $15.
The customer’s willingness to pay for a 5th cupcake is $0.
The customer’s willingness to pay for the 5th cupcake must be less than $3, but could be more than $0.
The customer’s willingness to pay for 12 cupcakes is at least $36.
If the customer were willing to pay $36 or more for a dozen cupcakes, the customer would have purchased a box of 12 cupcakes for $30.




