Misc Animals (GPs, Rabbits, Reptiles, etc.) Flashcards
How long do you leave skin sutures in for reptiles? What type of suture should you avoid? SO what would be ideal?
Leave the sutures in for 4-6 weeks, take longer to heal
** ensure no inverting sutures because of ecdysis– do not want skin inverted to have further sheds and therefore build up of abnormal sheds internally from inverted suturing
** Horizontal mattress sutures to slightly evert
Parts of the reptile eye? Glands?
scleral ossicles- hold the structure of the globe
Conus papillarus- irridescent

Chelonians vision? Drainage?
* NL gland for salt regulation– no nasolacrimal duct– tears will NORMALLY overflow and are lost via evaporation
** colour vision, third eyelid
Lizard eyes
* colour vision, eyelids (not present in geckos), Third eyelid
* some have fused eyelides (spectacle) as per snake


Snake eyes


Typical problem with dysecdysis often husbandry problem e.g. humidity, something to rub against




Cut a wedge in the spectacle and drain the fluid
** can have retained spectacles from shedding

What is the picture? Other common eye problems of reptiles?




Reptile Skin

What are the 3 layers of the epidermis in a reptile? What fuses to form the shell in chelonians? What are osteoderms?
* Dermis fuses to form the shell in chelonians
* Osteoderms- bony plates in some species



One method of speciating chelonians

What is the problem when humidity is too low with ecdysis? What is endysis?
* Lymph dries out and therefore dysecdysis

Main causes of dysecdysis? Treatment?
* Getting rid of the shed- warm water baths, patience
* Correct underlying issues

What is the most common reptile mite?

Reptile mite diagnosis

Mite treatment

General principles with treating reptiles
** don’t put straight back into its enclosure can cause toxicity if allowed to build up

Common causes of skin infections in reptiles? Treatment?



Treatment?





* histopath evidence of intralesional hyphae
* culture difficult
* contagious
* Poor husbandry- pre-existing wounds
* Treatment often unrewarding- itraconazole, surgical debridement

Petechial haemorrhages in the inguinal or shoulder area?
Septicaemia
Rabbit eyes

GP eyes

Rat eyes
* Poor nocturnal vision
* Large Harderian gland
* Secrete lipids and red porphyrin- chromodacryorrhea= red tears (this does mean we have a stressed rat)
Ferret eyes
* well developed nictitating membrane
* adapted for nocturnal life
* cataracts common in aged ferrets
Rabbit eye conditions
* Conjunctivitis
* dental disease as a contributing factor
* Nasolacrimal duct
* Encephalitozoon cuniculi


Nasolacrimal system in a rabbit
Chronic dental problems, the inflammation, can block the NLD

What is this in a rabbit?

Dacryocystitis
If you see mucopurulent discharge, tx?
* irrigation of NLD and dental workup

With sudden head tilt, what is it likely? Diagnosis and treatment?

* many will become infected in utero
* may rupture the lens
** Diagnosis and Tx: test for EC, surgical removal of lens, Fenbendazole (can be toxic, but some still use as a preventive measure in some clinics)…if the eye is not painful may not do anything… could remove the eye if severe… ophthamologist can use ultrasound, break it down, and suck it out
** DDX without head tilt– abscess, uveitis from other causes

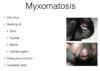
Common rabbit eye problems
* myxomatosis- swollen eyelids (chemosis- swelling of the conjunctiva)

GP common eye problems
Dermoid cyst- can just shave it off

Ferret common eye problems
* Cataract- common
* retinal degeneration

Chromodacryorrhoea in a rodent
Considerations with enucleation in rabbits
* close to the eyelids in the rabbit- venous plexus/ sinus…. just a bit of pressure, rabbit blood clots rapidly

Normal moult in a rabbit (particularly wild rabbit)

* barbering- cage mate will groom, dominance

Two kinds of mites on rabbits? What do they often mean?
Cheyletiella parasitovorax
= main culprit
•
Leporacus gibbus
may also be present:
•
usually asymptomatic.
•
clings to hair shaft
•
May be commensals?
•
Look for underlying cause/illness



Tx and control?

* Selamectin, Ivermectin, Pain relief (Meloxicam), Avoid ear solutions/ cleaning until inflammation/ pain settled, hygiene and quarantine
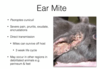
Concern with fleas on rabbits? Tx?
* Selamectin (Revolution), Imidacloprid (Advantage)
** Do not use Fipronil (Frontline) - toxic to rabbits
* Environmental cleaning, treat all animals in the household


* look for underlying cause (e.g. inadequate fiber intake)
* Supportive care, clean/clip fur (sedate)
* Analgesia, AMs
** Avoid cortisone based creams (immune system crash)

What can occur with Cylap? How do you avoid?




Physiological hair loss in GPs



GP presenting with enlarged lymph nodes
Remove LNs affected

Why do we recommend desexing female GPs?
* can look potbellied

In a GP


Lice on GPs indicates what?
Poor husbandry

In a GP

* might think the GP is epileptic, but it could be pruritis
** think of commensal?? Old GP
** Or introduction/ purchase of new pet
** Consider vitamin C status
** TX: Selamectin, Shampoos, Pain relief? AMs?


Sedate and bathe, selamectin, ivermectin, pain relief, AMs

Common ferret lumps


Should you remove anal glands in ferrets?
No just desex

What would you see with Distemper or Adrenal Gland disease in ferrets?



Common neoplasms in rats and mice?
* Mammary tumours
** Desex!! ovariectomy
* Tx: do nothing, wait for ulceration/ self trauma, surgery- rats

Other than mammary tumours, other skin masses in rats and mice?



