Midterm II: Ketogenesis + breakdown (Ben) Flashcards
What is the 1st step of ketogenesis?
(involving a β-oxidation enzyme)
Reactants?
Enzyme?
Products?
Condensation of two acetyl-CoA…

Reactants: 2x Acetyl-CoA
Enzyme: Thiolase (reverse rxn from β-oxidation)
Products: Acetoacetyl-CoA + CoA-SH
What is the 2nd step of ketogenesis, occuring after the reversal of the thiolase reaction?
Reactants?
Enzyme?
Products?
Condensation…

Reactants: Acetoacetyl-CoA + Acetyl-CoA + H2O
Enzyme: HMG-CoA Synthase
Products: HMG-CoA + CoA-SH
What is the 3rd step of ketogenesis, after condensation via HMG-CoA synthase?
Cleavage…

Reactants: HMG-CoA
Enzyme: HMG-CoA Lyase
Products: Acetoacetate + Acetyl-CoA
What are the two ketone bodies which are interconverted?
By which enzyme + coenzyme?
Acetoacetate + β-Hydroxybutyrate
via
β-Hydroxybutyrate Dehydrogenase
( and NAD in the direction using β-OH Butyrate as a reactant)

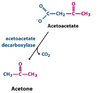
What occurs to acetoacetate produced in ketogenesis?
it undergoes spontaneous decarboxylation
via acetoacetate decarboxylase
What controls the equilibrium between the two interconvertible ketone bodies?
Redox State
- more specifically [NAD+]/[NADH] ratio
- high NAD+ favors the dehydrogenation of β-hydroxybutyrate to acetoacetate

What tissues use ketone bodies during ketosis?
- cardiac muscle
- skeletal muscle
- brain
- kidney (renal cortex)
What is the 1st step in the oxidation of ketone bodies by extrahepatic tissues?
Reactants?
Enzyme?
Product?
Activation via CoA…
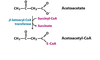
Reactants: Acetoacetate + Succinyl-CoA
Enzyme: β-Ketoacyl-CoA Transferase
Product: Acetoacetyl-CoA + Succinate
What is the second step in oxidation of ketone bodies by extrahepatic tissues?
(resulting in a citric acid cycle intermediate)
Reactant?
Enzyme?
Product?
Cleavage…

Reactant: Acetoacetyl-CoA + CoA-SH
Enzyme: Thiolase
Product: 2 Acetyl-CoA
Since ketone bodies are generated starting from acetyl-CoA and then oxidized into acetyl-CoA for later use…
what is their purpose?
the are a transport form of acetyl groups
make some regulation cards
ok


