Midterm II: Fatty Acid Oxidation (Ben) Flashcards
(40 cards)
What are longer free fatty acids bound to for transport in the blood?
How many FAs per unit of this transport molecule?
Albumin
- 10 FAs per albumin monomer
How does transport of shorter chain fatty acids differ from longer?
SCFAs are more water-soluble and exist in unionized or anion forms
What is the first step of catabolism of a free fatty acid?
What is special about this step energetically?
Fatty Acid Activation
- with CoA and ATP via acyl-CoA synthetase
- it is the ONLY step of FA oxidation which uses ATP
What is the enzyme which “activates” fatty acids for oxidation and where is it found (4 locations)?
Acyl-CoA Synthetase
Found:
- in the ER
- in peroxisomes
- in mitochondria
- on mitochondrial outer membrane
What is the overal reaction of FFA activation?
Include the enzyme.
FFA + CoA + ATP
—- acyl-CoA synthetase —->
acyl-CoA + PPi + AMP
What happens to the PPi formed from cleaved ATP during fatty acid activation and why?
it is hydrolyzed by inorganic pyrophosphatase
- to ensure that the reaction is carried out fully and is irreversible in vivo
What is the site of fatty acid activation?
the outer mitochondrial membrane
(where acyl-CoA synthetase is found)

What happens to acyl-CoA in the intermembrane space?
(before it can enter the mitochondrial matrix)
Carnitine Palmitoyltransferase-I
(or Carnitine Acyltransferase-I)
- catalyzes transfer of acyl group from CoA to carnitine to form acylcarnitine

How does acylcarnitine penetrate the inner mitochondrial membrane?
via Carnitine-Acylcarnitine Translocase
- exchanges carnitine for acylcarnitine across the membrane
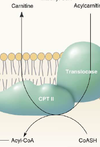
What happens to acylcarnitine once it is inside the mitochondrial matrix?
Start with the enzyme, then describe the process.
Carnitine Palmitoyltransferase-II
(or Carnitine Acyltransferase-II)
- transfers acyl group to CoA reforming Acyl-CoA and liberating carnitine

Where is Carnitine Palmitoyltransferase-I located?
across the outer mitochondrial membrane

Where is Carnitine-AcylCarnitine Translocase located?
across the inner mitochondrial membrane

Where is Carnitine Palmitoyltransferase-II located?
on the inside of the inner mitochondrial membrane

Why is β-oxidation called β-oxidation?
because it is a cycle of successive cleavages of Acyl-CoA molecules at…
the C-C bond between the α(2) and β(3) carbons
(2nd and 3rd Cs from the -COOH end)
What is the collective name for the enzymes which perform β-oxidation?
And where are they found?
Fatty Acid Oxidase
- found in the mitochondrial matrix and inner mitochondrial membrane
(adjacent to to the respiratory chain)
Energetically, what are the important products (3) of β-oxidation?
How are they used?
- FADH2 - oxidative phosphorylation > ATP
- NADH - oxidative phosphorylation > ATP
- Acetyl-CoA - citric acid cycle > ATP + NADH + FADH2
What is the first step of β-oxidation?
Substrates/reactants?
Enzyme?
Products?
Removal of one hydrogen each from α and β carbons…

Reactants: Acyl-CoA + FAD
Enzyme: Acyl-CoA Dehydrogenase
Products: Δ2-trans-Enoyl-CoA + FADH2
What is the 2nd step of β-oxidation?
Substrates/reactants?
Enzyme?
Products?
Water is added to saturate the double bond…

Reactants: Δ2-trans-Enoyl-CoA + H2O
Enzyme: Δ2-Enoyl-CoA Hydratase
Products: L-β-Hydroxy-acyl-CoA
What is the 3rd step of β-oxidation?
Substrates/reactants?
Enzyme?
Products?
What is special about the enzyme?
Further dehydrogenation of the 3-carbon…

Reactants: L-β-Hydroxyacyl-CoA + NAD+
Enzyme: β-Hydroxacyl-CoA Dehydrogenase
Product: β-Ketoacyl-CoA + NADH + H+
The enzyme is stereospecific for the L-isomer.
What is the 4th step of β-oxidation?
Substrates/reactants?
Enzyme (2 names)?
Products?
How is one of the end products different from what entered β-oxidation?
Cleavage at the 2,3 position…

Reactants: β-Ketoacyl-CoA + CoA-SH
Enzyme: Thiolase (or Acyl-CoA Acetyltransferase)
Products: Acetyl-CoA + Acyl-CoA
Acyl-CoA product here is 2 carbons shorter than acyl-CoA which entered the cycle.
How does a fatty acid chain’s length affect how it is transported into the mitochondria?
- > 12C - with carnitine
- < 12 C - without carnitine, activated in mitoch.
Which β-oxidation enzyme has 3 different isoforms?
What for?
What are they?
Which one is frequently deficient?
Acyl-CoA Dehydrogenase (the 1st step)
- for different lengths of fatty acids
- LCFAs (C 12-18)
- MCFAs (C 4-14) - frequently deficient (MCAD)
- SCFAs (C 4-8)
How many ATP are ultimately formed per NADH produced in β-oxidation?
Per FADH2?
NADH - 2.5 ATP
FADH2 - 1.5 ATP
Where are > 12 C FAs oxidized?
And < 12 C?
> 12 C - on the inner mitochondrial membrane
< 12 C - via soluble enzymes in the mitochondrial matrix




