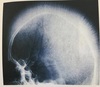
Mid semester exam Flashcards
1 - Describe the major radiographic findings.
2 - What is the name of this condition and what is its aetiology?
1 -
Loss of height of the anterior portions of the vertebrae over multiple levels.
Trapezoidal shaped vertebrae. Irregular end plates.
2 -
Scheuermann’s
Avascular necrosis of the secondary ring of the vertebral body. Could be hereditary, endocrine or osteoporosis
What is the site and age of Legg-calve-perthes?
Femoral capital epiphysis
3-12 (peak 5-7)
What is the site and age of Friebergs?
Metatarsals heads of 2nd and 3rd digits of the feet
13-18 year old girls
What is the site and age of Kienbocks?
Lunate
20-40 year olds, predominately males
What is the site and age of Kohlers?
Navicular
5 year olds, predominantley males
What is the site of osgood schlatters?
Tibial tuberosity (tibial tubercle apophysis)
What is the aetiology of osgoods?
Traction apophysitis/ tendonitis caused by trauma or repetitive microtrauma.
What are the radiological features of Osgood schlatters?
Soft tissue swelling
Patella tendon thickening
Bones appear with irregular isolated ossicles towards anterior margin of tuberosity.
Possible chondro osseous avulsion
What is the best image to view radiographic findings?
T2 or Fat sat sagittal
1 - Describe the radiographic findings?
2 - Give 3 different differentials.
3 - Choose one and outline your reasoning behind your diagnosis and radiographic findings.

1 -
Osteopaenia (widespread) enlargement of bones and epiphysis regions.
Eggshell thin cortices
Reactive sclerosis
Increased soft tissue density
Pseudocysts
Erosive changes - anteroinferior and posterosuperior calcaneus = interruption to cortices
2 -
Charcots joint
JRA
Osteogenesis imperfecta
Haemophilia
3 -
Juvenile RA - Causes enlargement of the epiphyseal regions. Also results in osteopaenia due to disuse or medications. Cortical thinning
Haemophilia - Juxtaarticular osteopaenia, haemarthrosis could cause the osteopaenia, joint disorganisation, cortical thinning, osteophytes.
What are the films in a complete ankle series?
Dorsoplantar, lateral, medial oblique
How would you go cobbs on this diagram?

:)
What are the 3 areas of the body used to determine skeletal maturity?
Non-dominant hand - distal radial epiphysis
Vertebral ring epiphysis
Iliac epiphysis (risser sign)
Provide some complications that may arise from the image seen above right
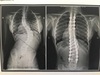
Degeneration (levels just above and below hardware), # around hardware, sensitivity to weather, infections from surgery, DJD, pain, Supp OM
What age bracket and sex do we need to be concerned about with scoliosis?
Females, 12-16, convex left
Outline the method to interpret chest films.

1 - Request details
2 - Technical
3 - Trachea
4 - Heart and mediastinum
5 - Diaphragm
6 - Pleura
7 - Lung fields
8- Hidden areas
9 - Hila
10 - Below diaphragm
11 - Soft tissue density
12 - Bone
What are the major radiographical findings?
What is the diagnosis
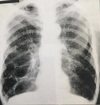
Pancake/vertical heart
Hyperlucent lung fields
Barrel chest
Depressed diaphragm
Blebs
Hyperinflated
Diagnosis = emphysema
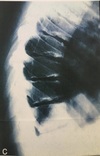
1 - What are the black arrow heads pointing at?
2 - What are 2 possible reasons for the radiographic findings?

1 - Apophysis of the calcaneus
2 - Avulsion
Normal finding
Severs
1 - What is the diagnosis?
2 - How might the patient present in the clinic?

1 - Hiatal hernia
2 - heart burn, chest pain, dysphagia, loss of weight, anorexia, reflux
- What is the diagnosis
- What is the arrow pointing at?
- What is the common age bracket for this patients condition?
- Any other radiographic findings?

- Perthes or Dwarfism
- Sagging rope sign - intertrochanteric line
- 3-12
- Buttressing of femoral head, mushroom cap deformity, coxa magna, coxa vara
- What is this congenital malformation called?
- Is it clinically significant?
3.

- Pectus carinatum
- Yes, the restriction of the ribs could alter lung capacity - low tidal volume predisposes to pneumonia
- Describe 4 radiographic findings
- What is the condition?

- Flattened pelvis (champagne glass pelvis), mushroom cap femoral head, coxa magna, enlargement of lesser trochanter, diverticuli
- Dwarfism
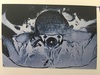
- What type of study is this?
- Outline 8 muscles attaching to the scapula

CT bone window axial and coronal
Rotator cuff
Teres major
Levator scapulae
Latissimus dorsi
Trapezius
Deltoid
Pec minor
Omohyoid
This is the L4/5 disc space
- Which nerve root is displaced?
- What reflexes would be affected
- What muscles are affected by this nerve root?
- What is A, B, C and D

- L5
- Achilles
- gluteus maximus muscle mainly S1.
- gluteus medius muscle.
- gluteus minimus muscle.
- tensor fasciae latae.
- tibialis anterior.
- tibialis posterior.
- extensor digitorum brevis.
- extensor hallucis longus.
- A = left L4 nerve root, B = right common iliac artery, C = Colon, D = facet