Images- finished Flashcards
What is this study?
Double contrast barium of small intestines (enteroclysis)
Positive= Opaque = Barium
Negative= Dark = Air
What pathology is this?
What are the main radiographic signs?
What are other DDx?

Osteogenesis Imperfecta
Diagnosed when 2 of 4 major criteria are present:
- 1: Osteoporosis with abnormal skeletal fragility.
- 2: blue sclera (Whites of the eyes may have a blue, purple, or grey tint)
- 3: abnormal dentition
- 4: premature otosclerosis
What is this pathology?
What type of image is this?
DDX?

- *Hill Sachs lesion**
- Are a posterolateral humeral head compression fracture, typically secondary to recurrent anterior shoulder dislocations, as the humeral head comes to rest against the anteroinferior part of the glenoid.
- FAT SAT, T2 Coronal
- Bleeding uptake
- Submedullary bleed
-Bankart lesion = They result from detachment of the anterior inferior labrum from the underlying glenoid as a direct result of the anteriorly dislocated humeral head compressing against the labrum
- DDX:*
- contusion
- labral tear
- Falls
- Bankart lesion
What is this pathology?
What are the radiograph findings?

- *Osteopetrosis**
- Family hereditary condition.
- No resorption of normal primitive osteochondroid tissue; osteoclasts may not respond to parathyroid hormone; primitive calcified cartilage persists.
- Results in inhibition of medullary canal formation; absence of marrow; anaemia and extramedullary hematopoiesis.
Radiology:
- Generalised skeletal sclerosis. Homogenous increased density, absence of trabeculation, absence of medullary canal.
- Bone within a bone appearance or endobones.
- Flared elongated metaphyses on long bones.
- Spine see uniformly dense vertebrae, or sandwich vertebrae with dense bone adjacent to endplates and normal centra.
What is this view?
What is the pathology?

T2- weighted sagittal view
-Meniscal Tear
What pathology is this?
What are other DDX?

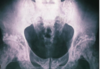
Congenital dwarfism
White balls = remnant of contrast media in the bowel
-IVP would be iodine
DDx:
- Enostosis but too bright
- Calcified lymph node
- Calculi
- Diverticulitis and contrast
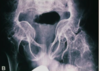
What is this pathology?
Radiological appearance?

Pneumonia:
Viral and bacterial. Many types of pneumonia commonest lobar pneumonia. Infection of the alveolar epithelium. May spread to entire lobe and 75% caused by Streptococcus pneumonia.
Radiological appearance:
- Confluent airspace opacification.
- See focal spherical consolidation (seen more commonly in children), with lobar enlargement caused by oedema
- Fissure bulge’s away from involved lobe
- Lobar pneumonia superimposed on emphysema resemble necrosing pneumonia (numerous small lucencies within consolidated area of lung)
What is this pathology?
What are other DDx?

First image:
Aortic calcification
Second image:
Pylographic intravenous - iodine
What is this pathology?

- Transverse ultrasound image through shoulder demonstrates full-thickness subscapularis tear with tendon retraction (short arrow).
- Intraarticular dislocation of long head of biceps tendon (long arrow)
What is this pathology?
Kohler’s
-Possible ischaemic necrosis (vascular deficiency), or may represent a normal growth variant in some cases, of the tarsal navicular.
Radiographical signs:
- Patchy or homogenous sclerosis of the navicular, collapse and fragmentation, joint spaces preserved.
- Bones scan helps differentiate between growth variation frown ischaemic necrosis.
What is this pathology?
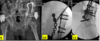
- Neck of femur fracture
- Pubis ischium
What pathology is this?

Aortic Arch Aneurysm
What is this pathology?

Haemophilia
-ankylosing
What pathology is this?
What is the major radiographical finding?
Other DDX?

Osteopetrosis
- Endobone (bone within bone)
- Widespread sclerosis
- Widespread calcification
DDX?
- Mets
- Ivory bone
What is this pathology?
- What film is this?
- What are common radiographic findings in this condition?
What other DDX?

- *Ankylosing spondylitis**
- CT soft tissue window axial
- S1 level
- Discrete areas of sclerotic reaction in bilateral ilium.
- Mets
- Other common radiographic findings:*
- Rosary beads lower 2/3 of the ilium (right side)
-STAR sign
- Marginal syndesmophytes
- Shiny corner sign
- Ghost joint
What is this pathology?

- *Thalassemia**
- Can see Hair on end radiating new bone spicules
- DDx:*
- Solid Periosteal Response:* We would not expect it cover the entire skull
What pathology is this?
What major radiographical signs can you see?
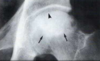
Avascular Necrosis
Radiographical signs:
-Homogenous increase in density
-Bite Sign: Curvilinear inferior border is evident. Gouged-out areas of bony destruction may be similar to small animal bites.
-Crescent Sign: subchondral fracture
What is this pathology?
What is the main radiological sign?
DDX’s?

- *Haemophilia**
- Pseudotumours (tumourlike expansion of the ilium)
DDX:
- Soap bubble apperance
- ABC (aneurysmal bone cyst)
- SBC (simple bone cyst)
- giant cell tumour
What is this pathology?
What are DDX?

Osteopoikilosis
Juxtaarticular small round or ovoid radio-opacities (pathognomonic).
Epiphyseal and metaphyseal regions affected.
Symmetric involvement: a predilection for long bones, carpal and tarsals.
Occurs: ilium, scapula, glenoid.
Rarely in skull, spine ribs or clavicles.
DDX:
-blastic metastatic
- tuberous sclerosis.
- multiple myeloma
- Charcots (neurotrophic arthropathy)
What is this pathology?

Hiatal Hernia
What is this pathology?

- Bone window
- Coronal
- *Vacuum** phenomenon: are a result of the accumulation of gas (principally nitrogen) within the crevices of the intervertebral discs or adjacent vertebrae.
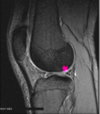
What is the arrow pointing at?

PCL
What is this pathology?
What is another DDX?

- Fracture right through the scapula
- Right on the scap (not outstretched hand)
- Straight through the clavicle
What is this pathology?

Lateral collateral tear