Met SAQs Flashcards
Which of the following is a glycogenolytic enzyme?
A.ACC
B.Phosphorylase kinase
C.PFK-1
D.PDH phosphatase
Which of the following is a glycogenolytic enzyme?
A.ACC
B.Phosphorylase kinase
C.PFK-1
D.PDH phosphatase
how do high levels of acetyl co-a influence gluconeogenesis? [2]
high levels of Acetyl Co-A:
activates pyruvate carboxylase (used in step 1 of malate cycle: drives gluconeogenesis from pyruuvate -> PEP & eventually glucose)
inhibits: pyruvate dehydrogenase complex (prevents pyruvate being turned into acteyl co A & sparing it, leaving for gluconeogenesis)
insulin causes glucose to be taken up by which GLUT receptor?
GLUT1
GLUT2
GLUT3
GLUT4
GLUT5
insulin causes glucose to be taken up by which GLUT receptor?
GLUT1
GLUT2
GLUT3
GLUT4
GLUT5
alcohol metabolism produces increased what? (2)
NADH & Acetyl coA
which of the following lipoproteins has apo protein B48?
chylomicron
very low density lipo
intermediate DL
LDL
HDL
which of the following lipoproteins has apo protein B48?
chylomicron
very low density lipo
intermediate DL
LDL
HDL
During the course of a radical gastrectomy the surgeons detach the omentum and ligate the right gastro-epiploic artery. From which vessel does it originate?
SMA
IMA
Coeliac axis
Common hepatic artery
Gastroduodenal artery
During the course of a radical gastrectomy the surgeons detach the omentum and ligate the right gastro-epiploic artery. From which vessel does it originate?
SMA
IMA
Coeliac axis
Common hepatic artery
Gastroduodenal artery
which of the following cover cover lymphoid nodules
- enterocytes
- goblet cells
- paneth cells
- enteroendocrine cells
- m cells
which of the following cover cover lymphoid nodules
- enterocytes
- goblet cells
- paneth cells
- enteroendocrine cells
- *- m cells**
Which one of the peritoneal ligaments contains the right and left gastric artery?
Splenorenal ligament
Falciform ligament
Hepatogastric ligament
Hepatoduodenal ligament
Gastrosplenic ligament
Gastrocolic ligament
Which one of the peritoneal ligaments contains the right and left gastric artery?
Splenorenal ligament
Falciform ligament
Hepatogastric ligament
Hepatoduodenal ligament
Gastrosplenic ligament
Gastrocolic ligament
While on placement on a gastro ward one of your patients develops profuse diarrhoea. Where in the gastrointestinal tract is the majority of water absorbed?
Jejunum
Colon
Ileum
Duodenum
Rectum
While on placement on a gastro ward one of your patients develops profuse diarrhoea. Where in the gastrointestinal tract is the majority of water absorbed?
Jejunum
Colon
Ileum
Duodenum
Rectum
where is the endocrine function of pancreas located? [1]
islet of langerhans
Where is the majority of norepinephrine secreted from?
D cells in the pancreas & stomach
Parafollicular cells of the thyroid
Zona reticularis of adrenal cortex
Posterior pituitary
Adrenal medulla
Zona glomerulosa of adrenal cortex
Where is the majority of norepinephrine secreted from?
D cells in the pancreas & stomach
Parafollicular cells of the thyroid
Zona reticularis of adrenal cortex
Posterior pituitary
Adrenal medulla
Zona glomerulosa of adrenal cortex
Why does excessive alcohol consumption impair the TCA cycle?
A.Depletes ATP stores
B.Depletes NADH stores
C.Leads to an NADH excess
D.Leads to the inhibition of ACC
Why does excessive alcohol consumption impair the TCA cycle?
A.Depletes ATP stores
B.Depletes NADH stores
C.Leads to an NADH excess
D.Leads to the inhibition of ACC
Increases gluconeogenesis:
1,25-dihydroxycholecalciferol
Leptin
Cortisol
Renin
CCK
Antidiuretic hormone
Increases gluconeogenesis:
1,25-dihydroxycholecalciferol
Leptin
Cortisol
Renin
CCK
Antidiuretic hormone
which of the cells of the immune system recognise gluten and cause CD?
CD4 T cells (Th1)
glutamine –> glutamate –> a-ketoglutarate generates lots of:
a) ATP
b) NH3
c) NH4
d) NADH
e) NAD
glutamine –> glutamate –> a-ketoglutarate generates lots of:
a) ATP
b) NH3
* *c) NH4**
d) NADH
e) NAD
palatoglossus muscle is innervated by?
a) glossopharnygeal
b) trigeminal
c) vagus nerve
d) hypoglossal
e) facial nerve
palatoglossus muscle is innervated by?
a) glossopharnygeal
b) trigeminal
* *c) vagus nerve**
d) hypoglossal
e) facial nerve
A 35-year-old man presents to the emergency department with hypotension following a road traffic accident. How does angiotensin II act to increase the filtration fraction in the kidney?
Vasoconstriction of the efferent glomerular arteriole
Vasoconstriction of the afferent glomerular arteriole
Vasodilationo of the efferent glomerular arteriole
Vasodilation of the afferent glomerular arteriole
Vasoconstriction of the renal artery
A 35-year-old man presents to the emergency department with hypotension following a road traffic accident. How does angiotensin II act to increase the filtration fraction in the kidney?
Vasoconstriction of the efferent glomerular arteriole
Vasoconstriction of the afferent glomerular arteriole
Vasodilationo of the efferent glomerular arteriole
Vasodilation of the afferent glomerular arteriole
Vasoconstriction of the renal artery
sublingual gland recieves parasympathetic innervation from which nerve?
a) glossopharnygeal
b) trigeminal
c) vagus nerve
d) hypoglossal
e) facial nerve
sublingual gland recieves parasympathetic innervation from which nerve?
a) glossopharnygeal
b) trigeminal
c) vagus nerve
d) hypoglossal
* *e) facial nerve**
A 61-year-old man is brought to the Emergency Department with confusion, nystagmus, and ataxia. Blood tests show a thiamine deficiency, confirming the suspected diagnosis of Wernicke’s encephalopathy.
What enzyme’s synthesis is dependent on this vitamin?
Amylase
Lysyl hydroxylase
Pyruvate dehydrogenase
Retinoic acid
Transaminase
A 61-year-old man is brought to the Emergency Department with confusion, nystagmus, and ataxia. Blood tests show a thiamine deficiency, confirming the suspected diagnosis of Wernicke’s encephalopathy.
What enzyme’s synthesis is dependent on this vitamin?
Amylase
Lysyl hydroxylase
Pyruvate dehydrogenase
Retinoic acid
Transaminase
which vitamins are normally excreted in urine and which vitamins can be stored by the body in the liver? [5]
excreteed in urine = vitamin B & K
stored in liver = vitamin ADEK
A 47-year-old lady is diagnosed as suffering from a phaeochromocytoma. From which of the following amino acids are catecholamines primarily derived?
aspatime
glutamine
arginine
tyrosine
alanine
A 47-year-old lady is diagnosed as suffering from a phaeochromocytoma. From which of the following amino acids are catecholamines primarily derived?
aspatime
glutamine
arginine
tyrosine
alanine
acetyl co-A is the input for TCA. acetyl co-A can be produced by three ways. What are they? [3]
1.Glycolysis of glucose to pyruvate
•Converted to acetyl-CoA using pyruvate dehydrogenase complex (PDC)
•Produces 2 reduced NAD molecules per glucose
•1 reduced NAD per pyruvate
2.Transamination of glucogenic amino acids to pyruvate
• Converted to acetyl-CoA using pyruvate dehydrogenase complex (PDC)
3.Beta-oxidation of fatty acids directly to acetyl-CoA
•Produces 1 NADH and 1 FADH2 per acetyl-CoA
During vigorous exercise, the body cannot intake enough oxygen to maintain the respiratory needs of all its muscles in an aerobic state. At this point, anaerobic metabolism begins and this relies on glycolysis for the production of energy.
Which of the following enzymes is responsible for catalysing the rate limiting step in this process?
Hexokinase
PFK-1
Pyruvate kinase
PDH
Glucose phosphorylase
During vigorous exercise, the body cannot intake enough oxygen to maintain the respiratory needs of all its muscles in an aerobic state. At this point, anaerobic metabolism begins and this relies on glycolysis for the production of energy.
Which of the following enzymes is responsible for catalysing the rate limiting step in this process?
Hexokinase
PFK-1
Pyruvate kinase
PDH
Glucose phosphorylase
The afferent limb of the gag reflex is supplied by which nerve?
a) facial nerve
b) trigeminal nerve
c) glossopharyngeal nerve
d) hypoglossal nerve
e) vagus nerve
The afferent limb of the gag reflex is supplied by which nerve?
a) facial nerve
b) trigeminal nerve
c) glossopharyngeal nerve
d) hypoglossal nerve
e) vagus nerve
Where is the majority of secretin secreted from?
S cells in upper small intestine
Zona glomerulosa of adrenal cortex
I cells in upper small intestine
D cells in the pancreas & stomach
Sertoli cells
G cells in antrum of the stomach
Where is the majority of secretin secreted from?
S cells in upper small intestine
Zona glomerulosa of adrenal cortex
I cells in upper small intestine
D cells in the pancreas & stomach
Sertoli cells
G cells in antrum of the stomach
which of the following would cause cardiomyopathy if a patient had a deficiency?
phosphorous
iron
selenium
zinc
copper
which of the following would cause cardiomyopathy if a patient had a deficiency?
phosphorous
iron
selenium
zinc
copper
Name two symptoms of PKU (2 marks)
Symptoms can be split based on their causes for example individuals with PKU have fair skin, blonde hair –> due to reduction in the production of melanin.
CNS abnormalities –> due to reduced neurotransmitter production and can lead to jerking, tremors, seizures
Which vitamin is involved in the formation of collagen?
Vit A
Vit B
Vit C
Vit D
Vit E
Which vitamin is involved in the formation of collagen?
Vit A
Vit B
Vit C
Vit D
Vit E
which vitamin causes production of CCR9 & a4b9 in gut honing T cells?
vitamin A
vitamin B
vitamin C
vitamin D
vitamin E
which vitamin causes production of CCR9 & a4b9 in gut honing T cells?
vitamin A
vitamin B
vitamin C
vitamin D
vitamin E
which nerve innervates sensation to the face?
a) trigeminal nerve
b) facial nerve
c) glossopharnyngeal
d) vagus nerve
e) hypoglossal
which nerve innervates sensation to the face?
- *a) trigeminal nerve**
b) facial nerve
c) glossopharnyngeal
d) vagus nerve
e) hypoglossal
which vagus nerve (left or right), innervates the
i) anterior stomach wall? [1]
ii) posterior stomach wall? [2]
Left vagus innervates anterior wall [1]
Right vagus innervates posterior wall []1
Which one of the following actions is directly caused by gastrin?
Increases pancreatic secretions rich in digestive enzymes
Increases pepsinogen secretion
Decreases gastric emptying
Stimulates aldosterone release
Increases plasma phosphate
Increases proximal tubule Na+/H+ activity
Which one of the following actions is directly caused by gastrin?
Increases pancreatic secretions rich in digestive enzymes
Increases pepsinogen secretion
Decreases gastric emptying
Stimulates aldosterone release
Increases plasma phosphate
Increases proximal tubule Na+/H+ activity
Which one of the peritoneal ligaments contains the hepatic artery, hepatic portal vein and common bile duct?
Gastrocolic ligament
Hepatoduodenal ligament
Splenorenal ligament
Hepatogastric ligament
Gastrosplenic ligament
Falciform ligament
Which one of the peritoneal ligaments contains the hepatic artery, hepatic portal vein and common bile duct?
Gastrocolic ligament
Hepatoduodenal ligament
Splenorenal ligament
Hepatogastric ligament
Gastrosplenic ligament
Falciform ligament
which intermediary is needed for transamination to occur? [1]
which enzyme is needed for transamination to occur? [1]
intermediary= **pyridoxal phosphate (from vitamin B6)** enzyme = **transaminase**
Von Gierkes disease is caused by a mutation in which gene?
a) PYGT
b) PYGL
c) G6PC
d) HGD
e) G1PC
Von Gierkes disease is caused by a mutation in which gene?
a) PYGT
b) PYGL
* *c) G6PC**
d) HGD
e) G1PC
which nerve innervates the muscles of facial expression?
a) trigeminal nerve
b) facial nerve
c) glossopharnyngeal
d) vagus nerve
e) hypoglossal
which nerve innervates the muscles of facial expression?
a) trigeminal nerve
* *b) facial nerve**
c) glossopharnyngeal
d) vagus nerve
e) hypoglossal
what is role of paneth cells? [1]
where located? [1]
- paneth cells: secrete antimicrobe substances; H&E= pink
Which layer of the gastrointestinal tract contains Meissners plexus?
Muscularis externa
Submucosa
Serosa
Mucosa
Which layer of the gastrointestinal tract contains Meissners plexus?
Muscularis externa
Submucosa
Serosa
Mucosa
A 39-year-old lady has recurrent attacks of biliary colic. What is the approximate volume of bile to enter the duodenum per 24 hours?
500 mL
50 mL
100 mL
2000 mL
150 mL
A 39-year-old lady has recurrent attacks of biliary colic. What is the approximate volume of bile to enter the duodenum per 24 hours?
500 mL
50 mL
100 mL
2000 mL
150 mL
Which one of the following inhibits gastric acid secretion?
Histamine
Nausea
Calcium
Parasympathetic vagal stimulation
Gastrin
Which one of the following inhibits gastric acid secretion?
Histamine
Nausea
Calcium
Parasympathetic vagal stimulation
Gastrin
which metabolic disease is caused by mutation in glycogen phosphorylase in liver?
a) McArdles Disease
b) Hers Disease
c) von Gierkes
d) Maple syrup disease
which metabolic disease is caused by mutation in glycogen phosphorylase in liver?
a) McArdles Disease
* *b) Hers Disease**
c) von Gierkes
d) Maple syrup disease
where do u find hormone receptors (3)
- nucleus (typically steroid hormones)
- cytoplasm
- plasma membrane
which metabolic disorder means that the following reaction cant occur?
pyruvate –> glucose-6-P –> glucose
a) von Gierkes
b) Hers
c) McArdles
d) Galactosaemia
e) hereditary fructose intolerance
which metabolic disorder means that the following reaction cant occur?
pyruvate –> glucose-6-P –> glucose
- *a) von Gierkes**
b) Hers
c) McArdles
d) Galactosaemia
e) hereditary fructose intolerance
A 17-year-old lady presents with right iliac fossa pain and diagnosed as having acute appendicitis. You take her to theatre to perform a laparoscopic appendicectomy. During the procedure the scrub nurse distracts you and you inadvertently avulse the appendicular artery. The ensuing haemorrhage is likely to be supplied directly from which vessel?
IMA
SMA
Ileo-colic artery
Internal iliac artery
None of the above
A 17-year-old lady presents with right iliac fossa pain and diagnosed as having acute appendicitis. You take her to theatre to perform a laparoscopic appendicectomy. During the procedure the scrub nurse distracts you and you inadvertently avulse the appendicular artery. The ensuing haemorrhage is likely to be supplied directly from which vessel?
IMA
SMA
Ileo-colic artery
Internal iliac artery
None of the above
the coeliac trunk arises from the abdominal aorta at which vertebral level?
T12
L1
L2
L3
L4
the coeliac trunk arises from the abdominal aorta at which vertebral level?
T12
L1
L2
L3
L4
Which one of the following actions is directly caused by renin?
Stimulates ADH release
Stimulates thirst
Converts angiotensinogen to angiotensin I
Inhibits glucagon secretion
Decreases appetite
Vasoconstriction of vascular smooth muscle
Which one of the following actions is directly caused by renin?
Stimulates ADH release
Stimulates thirst
Converts angiotensinogen to angiotensin I
Inhibits glucagon secretion
Decreases appetite
Vasoconstriction of vascular smooth muscle
A 22-year-old male presents to his general practitioner with a 4-month history of headaches, palpitations, and heavy sweating. He also reports some non-intentional weight loss. On examination, the patient is sweating heavily and is tachycardic. It is suspected that the man may have a malignancy affecting the tissue responsible for the secretion of adrenaline.
Where is the most likely site of the malignancy?
Adrenal cortex
Adrenal medulla
Medulla oblongata
Parathyroid gland
Thyroid
A 22-year-old male presents to his general practitioner with a 4-month history of headaches, palpitations, and heavy sweating. He also reports some non-intentional weight loss. On examination, the patient is sweating heavily and is tachycardic. It is suspected that the man may have a malignancy affecting the tissue responsible for the secretion of adrenaline.
Where is the most likely site of the malignancy?
Adrenal cortex
Adrenal medulla
Medulla oblongata
Parathyroid gland
Thyroid
which gastric cell produces histamine in to activate stomach acid creation?
a) parietal cells
b) G cells
c) chief cells
d) ECL likes
e) mucous secreting cells
which gastric cell produces histamine in to activate stomach acid creation?
a) parietal cells
b) G cells
c) chief cells
d) ECL cells
e) mucous secreting cells
which vitamin deficiency is associated with beri beri?
- vit. A
- vit B1
- vit. B2
- vit. B3
- vit. B4
which vitamin deficiency is associated with beri beri?
- vit. A
- *- vit B1**
- vit. B2
- vit. B3
- vit. B4
what is the equation for converting pyruvate to acetyl co A?
- pyruvate + CoA + NAD+ –> acetyl Co-A + Co2 + NADH
An 18-year-old male is admitted with confusion and myoclonus. A blood test reveals a high ammonium level. He has a family history of a urea cycle disorder.
What enzyme deficiency is present?
Carbomyl phosphate synthetase I
Glycogen phosphorylase
Isocitrate dehydrogenase
PFK-1
Glyocgen synthase
An 18-year-old male is admitted with confusion and myoclonus. A blood test reveals a high ammonium level. He has a family history of a urea cycle disorder.
What enzyme deficiency is present?
Carbomyl phosphate synthetase I
Glycogen phosphorylase
Isocitrate dehydrogenase
PFK-1
Glyocgen synthase
A 6-year-old male patient presents with signs and symptoms of severe fasting hypoglycaemia. On examination, he has hepatomegaly. His blood lactate levels, uric acid and triglycerides are raised. After extensive investigations, he is diagnosed with glycogen storage disease I (Von Gierke disease).
Which enzyme is deficient in this condition?
Glucose-6-phosphatase
Glucose-6-phosphatase dehydrogenase
a-1,6 glucosidase
Myophosphorylase
Glucocerebrosidase
A 6-year-old male patient presents with signs and symptoms of severe fasting hypoglycaemia. On examination, he has hepatomegaly. His blood lactate levels, uric acid and triglycerides are raised. After extensive investigations, he is diagnosed with glycogen storage disease I (Von Gierke disease).
Which enzyme is deficient in this condition?
Glucose-6-phosphatase
Glucose-6-phosphatase dehydrogenase
a-1,6 glucosidase
Myophosphorylase
Glucocerebrosidase
what are two seperate roles of aldosterone? [2]
- restores BP, reabsorbed salt & water lvls (not excrete as much) [1]
- restores K loss [1]
(two totally differnet systems! )
which are the only two hormones that are released frm posterior pituitary gland? [2]
ADH
Oxytocin
the hepatoduodenal ligament is found which of the following:
a) greater omentum
b) lesser omentum
c) mesocolon
d) mesentary
the hepatoduodenal ligament is found which of the following:
a) greater omentum
b) lesser omentum
c) mesocolon
d) mesentary

does the spleen develop in the dorsal or ventral mesogastrium?
does the spleen develop in the dorsal or ventral mesogastrium?
: dorsal mesogastrium
what do the suprahyoid muscles do to the hyoid bone when swallowing?
what do the infrahyoid muscles do to the hyoid bone when swallowing?
what do the suprahyoid muscles do to the hyoid bone when swallowing?
elevate hyoid
what do the infrahyoid muscles do to the hyoid bone when swallowing?
depress hyoid
Which of the following is true during exercise?
A.Glycogenesis and lipogenesis are favoured
B.Glycogenolysis and lipolysis are inhibited
C.ATP is the primary driver of increased glycolysis
D.Ca2+ and AMP promote glycolysis
Which of the following is true during exercise?
A.Glycogenesis and lipogenesis are favoured
B.Glycogenolysis and lipolysis are inhibited
C.ATP is the primary driver of increased glycolysis
D.Ca2+ and AMP promote glycolysis: Drop in pH due to lactic acid accumulation inhibits glycolysis + oxidative phosphorylation
which Ig is the only antibody capable of crossing the placenta to give passive immunity to the fetus?
a) IgG
b) IgM
c) IgA
d) IgE
e) IgD
which Ig is the only antibody capable of crossing the placenta to give passive immunity to the fetus?
- *a) IgG**
b) IgM
c) IgA
d) IgE
e) IgD
growth hormone is released from anterior pituitary gland after stimulation by growth hormone releasing hormone. which hormone does it indirectly cause the release of to increase bone and muscle mass?
- AMP
- cAMP
- IP3
- IGF-1
- DAG
growth hormone is released from anterior pituitary gland after stimulation by growth hormone releasing hormone. which hormone does it indirectly cause the release of to increase bone and muscle mass?
- AMP
- cAMP
- IP3
- *- IGF-1**
- DAG
which one of the followings statements is true of glucagon?
- produced in response to hyperglycaemia
- released by beta cells
- inhibits gluconeogenesis
- produced in response to an increase in amino acids
- composed of 2 alpha polypeptide chains linked by H bonds
which one of the followings statements is true of glucagon?
- produced in response to hyperglycaemia
- released by beta cells
- inhibits gluconeogenesis
- *- produced in response to an increase in amino acids**
- composed of 2 alpha polypeptide chains linked by H bonds
- What is the gene responsible for the mutation of which can induce osmotic diarrhea to the patient?
- SLC5A1
- SLC5A2
- SLC5A3
- SLC5A4
•What is the gene responsible for the mutation of which can induce osmotic diarrhea to the patient?
•SLC5A1
- SLC5A2
- SLC5A3
- SLC5A4
Latency on a nerve conduction study describes:
a) distance between 2 different stimulation sites
b) height of electrical activity
c) distance betwen stimulation site and muscle sensor
d) time from stimulation to start of electrical activity
Latency on a nerve conduction study describes:
a) distance between 2 different stimulation sites
b) height of electrical activity
c) distance betwen stimulation site and muscle sensor
* *d) time from stimulation to start of electrical activity**
Which cycle is used in gluconeogenesis to ger pyruvate –> phosphoenolpyruvate (PEP) ?
a) Krebs Cycle
b) Cori Cycle
c) Malate Cycle
d) Glyoxylate cycle
e) Carnitine shuttle
Which cycle is used in gluconeogenesis to ger pyruvate –> phosphoenolpyruvate (PEP) ?
a) Krebs Cycle
b) Cori Cycle
* *c) Malate Cycle**
d) Glyoxylate cycle
e) Carnitine shuttle
gliadin binds to which antibody in the gut with a patient with CD?
- IgA
- IgD
- IgG
- IgM
- IgE
gliadin binds to which antibody in the gut with a patient with CD?
- *- IgA**
- IgD
- IgG
- IgM
- IgE
•IN COELIAC DISEASED PATIENTS, the IgA along with gliadin do not get broken down and are transferred from the apical membrane of the enterocytes down to the basolateral membrane
A 52-year-old male is brought to the emergency department with frank haematemesis by the ambulance. Urgent resuscitation measures are taken and an urgent oesophagogastroduodenoscopy (OGD) is performed. An active bleed is seen in the distal part of the lesser curvature of the stomach and is controlled with endoclips and adrenaline. He has a past medical history of gastric ulcers.
Which artery is the most likely cause of the bleed
Left gastric artery
Right gastric artery
Left gastroepiploic artery
Right gastroepiploic artery
Short gastric artery
A 52-year-old male is brought to the emergency department with frank haematemesis by the ambulance. Urgent resuscitation measures are taken and an urgent oesophagogastroduodenoscopy (OGD) is performed. An active bleed is seen in the distal part of the lesser curvature of the stomach and is controlled with endoclips and adrenaline. He has a past medical history of gastric ulcers.
Which artery is the most likely cause of the bleed
Left gastric artery
Right gastric artery
Left gastroepiploic artery
Right gastroepiploic artery
Short gastric artery
adrenal glands are able to produce highly different enzymes from which starting molecule? [1]
cholesterol
What forms the the borders of Hesselbach’s triangle?
- Inguinal ligament laterally, inferior epigastric vessels laterally, pubic tubercle medially
- Inguinal ligament laterally, inferior epigastric vessels laterally, umibilicus medially
- Inguinal ligament laterally, ASIS laterally, pubic tubercle medially
- Inguinal ligament laterally, inferior epigastric vessels laterall, lateral border of the rectus sheath medially
- Inguinal ligament laterally, ASIS laterally, lateral border of the rectus sheath medially
What forms the the borders of Hesselbach’s triangle?
- Inguinal ligament laterally, inferior epigastric vessels laterally, pubic tubercle medially
- Inguinal ligament laterally, inferior epigastric vessels laterally, umibilicus medially
- Inguinal ligament laterally, ASIS laterally, pubic tubercle medially
- *- Inguinal ligament laterally, inferior epigastric vessels laterally, lateral border of the rectus sheath medially**
- Inguinal ligament laterally, ASIS laterally, lateral border of the rectus sheath medially

which of the following is not a role of micronutrients
- co-factors
- co-enzymes
- antioxidants
- control of gene expression
5 oxidants
which of the following is not a role of micronutrients
- co-factors
- co-enzymes
- antioxidants
- control of gene expression
* *5 oxidants**
Where is the majority of aldosterone secreted from?
Posterior pituitary
Zona glomerulosa of adrenal cortex
Zona fasciculata of adrenal cortex
Zona reticularis of adrenal cortex
Juxtaglomerular cells
Adrenal medulla
Where is the majority of aldosterone secreted from?
Posterior pituitary
Zona glomerulosa of adrenal cortex
Zona fasciculata of adrenal cortex
Zona reticularis of adrenal cortex
Juxtaglomerular cells
Adrenal medulla
growth hormone is released from anterior pituitary gland after stimulation by growth hormone releasing hormone. which hormone works to inhibit this reaction? [1]
growth hormone is released from anterior pituitary gland after stimulation by growth hormone releasing hormone. which hormone works to inhibit this reaction? [1]
somatostatin
bile salts are secreted by:
a) parietal cells
b) enterocytes
c) goblet cells
d) chief cells
e) hepatocytes
bile salts are secreted by:
a) parietal cells
b) enterocytes
c) goblet cells
d) chief cells
e) hepatocytes
Name and briefly explain two properties of MHC genes that help maximise the likelihood that any particular peptide can be presented by MHC molecules for recognition by T cells.
MHC genes are:
polygenic – more than one type of both class I and class II ( 1 mark)
polymorphic – multiple alleles in population means most individuals are heterozygous ( 1 mark)
•Which are the three primary histological characteristics of celiac disease?
- Lymphatic infiltration
- Crypt hyperplasia
- Flattened villi
what does this describe: ‘directly anterior to the sulcus terminalis and extend in a V-shaped line across the root of the tongue’
- foliate papillae
- lingual tonsil
- palatine tonsil
- vallate papillae
- foramen cecum of tongue
what does this describe: ‘directly anterior to the sulcus terminalis and extend in a V-shaped line across the root of the tongue’
- foliate papillae
- lingual tonsil
- palatine tonsil
- vallate papillae
- foramen cecum of tongue
Which one of the following actions is directly caused by gastrin?
Stimulates aldosterone release
Increases pancreatic secretions rich in digestive enzymes
Increases gastric H+ secretion
Decreases gastric emptying
Increases pancreatic bicarbonate secretion
Increases gut absorption of calcium
Which one of the following actions is directly caused by gastrin?
Stimulates aldosterone release
Increases pancreatic secretions rich in digestive enzymes
Increases gastric H+ secretion
Decreases gastric emptying
Increases pancreatic bicarbonate secretion
Increases gut absorption of calcium
What type of cells line the villi of the small intestine?
•Simple columnar epithelial cells (enterocytes)
which metabolism disorder causes a second wind of exercise?
a) von Gierkes
b) Hers
c) McArdles
d) Galactosaemia
e) hereditary fructose intolerance
which metabolism disorder causes a second wind of exercise?
a) von Gierkes
b) Hers
* *c) McArdles**
d) Galactosaemia
e) hereditary fructose intolerance
what are the two differing roles of ADH :)
ADH:
- regulates osmolality of blood serum (increases reabsorbtion & causes dilution of blood serum)
- vasoconstriction of arterial BP
which cells do you find lining peyers patches?
a) G cells
b) D cells
c) T cells
d) M cells
e) B cells
which cells do you find lining peyers patches?
a) G cells
b) D cells
c) T cells
* *d) M cells**
e) B cell
where is Fe absorbed in the body?
a) duodenum
b) jejenum
c) ileum
d) ascending colon
e) transverse colon
where is Fe absorbed in the body?
- *a) duodenum**
b) jejenum
c) ileum
d) ascending colon
e) transverse colon
Which muscle fiber type is more abundant in a marathon runner? What features make this fiber type suitable for this chosen sport? [4]
Type I Slow Oxidative
- High mitochondrial content -> good TCA cycle capabilities therefore lots of ATP produced aerobically
- High myoglobin content -> good oxygen delivery
- Good for frequent and prolonged contraction, suitable for a marathon run.
A 55-year-old man is admitted with a brisk haematemesis. He is taken to the endoscopy department and an upper GI endoscopy is performed by the gastroenterologist. He identifies an ulcer on the posterior duodenal wall and spends an eternity trying to control the bleeding with all the latest haemostatic techniques. He eventually asks the surgeons for help. A laparotomy and anterior duodenotomy are performed, as the surgeon opens the duodenum a vessel is spurting blood into the duodenal lumen. From which of the following does this vessel arise?
Left gastric artery
Common hepatic artery
Right hepatic artery
SMA
Splenic artery
A 55-year-old man is admitted with a brisk haematemesis. He is taken to the endoscopy department and an upper GI endoscopy is performed by the gastroenterologist. He identifies an ulcer on the posterior duodenal wall and spends an eternity trying to control the bleeding with all the latest haemostatic techniques. He eventually asks the surgeons for help. A laparotomy and anterior duodenotomy are performed, as the surgeon opens the duodenum a vessel is spurting blood into the duodenal lumen. From which of the following does this vessel arise?
Left gastric artery
Common hepatic artery
Right hepatic artery
SMA
Splenic artery
what type of disease if famial hypercholeserolemia?
a) X linked recessive
b) autosomal dom
c) autosomal rec
d) Y-linked
e) X-linked dom
what type of disease if famial hypercholeserolemia?
a) X linked recessive
* *b) autosomal dom**
c) autosomal rec
d) Y-linked
e) X-linked dom
What is the treatment for coeliac disease?
•Elimination of gluten-containing food (e.g. wheat, rye, barley) from the diet
Filtration fraction:
Can be estimated using creatinine clearance
GFR * plasma concentration
Plasmacreatinine / urinarycreatinine
Glomerular filtration rate / renal blood flow
Renal plasma flow / (1 - Haematocrit)
Is typically around 0.20
Filtration fraction:
Can be estimated using creatinine clearance
GFR * plasma concentration
Plasmacreatinine / urinarycreatinine
Glomerular filtration rate / renal blood flow
Renal plasma flow / (1 - Haematocrit)
Is typically around 0.20
name for the electron carrier in ETC? [1]
ubiqunione
which nerve is being tested here?
a) median
b) ulnar
c) radius
d) axillary

which nerve is being tested here?
- *a) median**
b) ulnar
c) radius
d) axillary
What is the rate limiting enzyme of glycolysis?
PFK1
Glycogen synthase
Glyocgen phosphorylase
Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase
Isocitrate dehydrogenase
What is the rate limiting enzyme of glycolysis?
PFK1
Glycogen synthase
Glyocgen phosphorylase
Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase
Isocitrate dehydrogenase
where do steroid hormones most commonly bind to cell? [1]
in nucleus - alter gene expression
what type of bacteria is H. pylori?
gram-postive
gram-negative
what type of bacteria is H. pylori?
gram-postive
gram-negative
Hers Disease and von Gierkes disease are both types of glycogen storage diseases that result in hypoglycaemia. Which of these diseases would result in more mild hypoglycaemia and why? (4)
Hers disease result in more mild hypoglycemia (1)
Hers disease PYGL gene is defected, so defect in glycogen phoshporylase means can break down liver glycogen (1)
But can still undergo gluconeogensis (1)
von Gierkes disease is defect in glucose-6-phosphatase, so cant break down glycogen –> glucose at all. (1)
Which one of the following actions is directly caused by CCK?
Decreases gastric emptying
Decreases pepsinogen secretion
Decreases gallbladder contraction
Increases gastric motility
Decreases appetite
Decreases gastric H+ secretion
Which one of the following actions is directly caused by CCK?
Decreases gastric emptying
Decreases pepsinogen secretion
Decreases gallbladder contraction
Increases gastric motility
Decreases appetite
Decreases gastric H+ secretion
which type of cells are bile salts secreted from?
- goblet cells
- paneth cells
- enteroendocrine cells
- hepatocytes
- parietal cells
which type of cells are bile salts secreted from?
- goblet cells
- paneth cells
- enteroendocrine cells
- *- hepatocytes**
- parietal cells
Glomerular filtration rate:
Urine flow rate * urine concentration
Is typically around 100 ml/min
UPAH * V / PPAH
GFR * plasma concentration
Is typically around 0.20
Renal plasma flow / (1 - Haematocrit)
Glomerular filtration rate:
Urine flow rate * urine concentration
Is typically around 100 ml/min
UPAH * V / PPAH
GFR * plasma concentration
Is typically around 0.20
Renal plasma flow / (1 - Haematocrit)
how is fructose absorbed in the mucosal phase of carbohydrate digestion?
a) primary active transport
b) secondary active transport
c) simple diffusion
d) faciliated diffusion
e) paracellular transport
how is fructose absorbed in the mucousal phase of digestion?
a) primary active transport
b) secondary active transport
c) simple diffusion
* *d) faciliated diffusion**
e) paracellular transport
glucose and galactose go via 2 AT through SGLT but fructose does fac d.
the anterior and posterior pituitary gland are both controlled by which structure? [1]
hypothalamus !
What is the best way to describe a silent mutation
A single base mutation that changes the amino acid, but there is no obvious clinical effect
A single base mutation that changes the amino acid, but there is no obvious clinical effect at birth
A single base mutation that changes the amino acid, causing changes in 2 & 3 structure of protein
A single base mutation that does not change the amino acid and does not affect the phenotype or transcription of that gene
A single base mutation that does not change the AA but may affect transcription or translation of the gene
What is the best way to describe a silent mutation
A single base mutation that changes the amino acid, but there is no obvious clinical effect
A single base mutation that changes the amino acid, but there is no obvious clinical effect at birth
A single base mutation that changes the amino acid, causing changes in 2 & 3 structure of protein
A single base mutation that does not change the amino acid and does not affect the phenotype or transcription of that gene
A single base mutation that does not change the AA but may affect transcription or translation of the gene
which type of receptor is insulin receptor?
a) enzyme-linked
b) GPCR
c) ion channel
d) tyrosine-kinase
which type of receptor is insulin receptor?
a) enzyme-linked
b) GPCR
c) ion channel
* *d) tyrosine-kinase**
which cells found in the small intestine that are modified enterocytes that cover lymphoid nodules
- parietal cells
- goblet cells
- paneth cells
- enteroendocrine cells
- m cells
which cells found in the small intestine that are modified enterocytes that cover lymphoid nodules
- parietal cells
- goblet cells
- paneth cells
- enteroendocrine cells
- *- m cells**
Which ligament is at risk in this boy?
- radial collateral ligament
- ulnar collateral ligament
- annular ligament
- deltoid ligament

Which ligament is at risk in this boy?
- radial collateral ligament
- ulnar collateral ligament
- *- annular ligament**
- deltoid ligament
A 64-year-old man is admitted with a COPD exacerbation. He is hypoxic on admission with an SpO2 of 72%. He has a lactic acidosis on blood analysis.
What is the rate limiting enzyme of the process which has resulted in the lactic acidosis?
HMG-CoA reductase
Fructose-1,6 biphosphatase
PFK1
Glycgen synthase
Glucose 6 P deH
A 64-year-old man is admitted with a COPD exacerbation. He is hypoxic on admission with an SpO2 of 72%. He has a lactic acidosis on blood analysis.
What is the rate limiting enzyme of the process which has resulted in the lactic acidosis?
HMG-CoA reductase
Fructose-1,6 biphosphatase
PFK1 - The rate limiting enzyme for glycoloysis is phosphofructokinase (PFK1)
Glycgen synthase
Glucose 6 P deH
Which substance can be used to achieve the most accurate measurement of the glomerular filtration rate?
Glucose
Protein
Inulin
Creatitine
PAH acid
Which substance can be used to achieve the most accurate measurement of the glomerular filtration rate?
Glucose
Protein
Inulin
Creatitine
PAH acid
which antibody protects agaisnt parasitic worms?
a) IgG
b) IgM
c) IgA
d) IgE
e) IgD
which antibody protects agaisnt parasitic worms?
a) IgG
b) IgM
c) IgA
* *d) IgE**
e) IgD
glutamate is an amino acid that also acts as an important …
a) steroid hormone
b) neurotransmitter
c) secondary messenger
d) source of metabolic energy
glutamate is an amino acid that also acts as an important …
a) steroid hormone
b) neurotransmitter
c) secondary messenger
d) source of metabolic energy
TAG transport is mediated by:
a) chylomicrons & IDLs
b) chylomicrons & VLDLs
c) chylomicrons & LDLs
d) chylomicrons & HDLs
e) VLDLs and LDLs
TAG transport is mediated by:
a) chylomicrons & IDLs
* *b) chylomicrons & VLDLs**
c) chylomicrons & LDLs
d) chylomicrons & HDLs
e) VLDLs and LDLs
which of the following messengers are use paracrine siginalling in to control stomach acid secretions?
a) histamine only
b) acetylcholine only
c) gastrin & histamine
d) somatostatin & gastrin
e) somatostain & histamine
which of the following messengers are use paracrine siginalling in to control stomach acid secretions?
a) histamine only
b) acetylcholine only
c) gastrin & histamine
d) somatostatin & gastrin
* *e) somatostain & histamine**

You are developing a new drug for diabetes which acts to decrease synthesis of glucose in the liver from non-carbohydrate carbon substrates. You want to develop a drug which targets the the rate limiting enzyme.
What enzyme will you target?
Fructose 1,6 biphosphatase
HMG-CoA synthase
HMG-CoA reductase
Glutamine-PRPP amidotransferase
Acetyl-CoA carboxylase
You are developing a new drug for diabetes which acts to decrease synthesis of glucose in the liver from non-carbohydrate carbon substrates. You want to develop a drug which targets the the rate limiting enzyme.
What enzyme will you target?
Fructose 1,6 biphosphatase The rate limiting enzyme for gluconeogenesis is fructose 1,6 bisphosphatase
HMG-CoA synthase
HMG-CoA reductase
Glutamine-PRPP amidotransferase
Acetyl-CoA carboxylase
Which one of the following actions is directly caused by somatostatin?
Increases pancreatic bicarbonate secretion
Decreases pancreatic secretions
Stimulates release of insulin-like growth factors
Increases glycogenolysis
Increases gut absorption of calcium
Stimulates thirst
Which one of the following actions is directly caused by somatostatin?
Increases pancreatic bicarbonate secretion
Decreases pancreatic secretions
Stimulates release of insulin-like growth factors
Increases glycogenolysis
Increases gut absorption of calcium
Stimulates thirst
which dietary molecule is essential for transmination to occur?
vitamin B6
vitamin B12
vitamin C
vitamin B3
which dietary molecule is essential for transmination to occur?
vitamin B6
vitamin B12
vitamin C
vitamin B3
statins reduce circulating blood cholesterol in two ways. what are these? (2)
statins block the activity of HMG-Co A reductase. so less cholesterol is made from acetly co-A (acetyl co-A –> cholesterol) (1)
causes more LDL receptors to be made & take in MORE LDLs -> reducing blood LDLs
which is the sensory nerve innervation for gagging?
a) trigeminal nerve
b) facial nerve
c) glossopharnyngeal
d) vagus nerve
e) hypoglossal
which is the sensory nerve innervation for gagging?
a) trigeminal nerve
b) facial nerve
c) glossopharnyngeal
d) vagus nerve
e) hypoglossal
which of the following is correct?
glucagon works on the liver and muscles to build up glycogen stores
insulin works on liver to build glycogen stores
insulin works on the muscle and liver to build glycogen stores
glucagon works on the liver and muscles to break down glycogen stores
insulin works on the muscle and liver to break down glycogen stores
which of the following is correct?
glucagon works on the liver and muscles to build up glycogen stores
insulin works on liver to build glycogen stores
insulin works on the muscle and liver to build glycogen stores
glucagon works on the liver and muscles to break down glycogen stores
insulin works on the muscle and liver to break down glycogen stores
1. insulin: muscle and liver - builds glycogen stores
2. glucagon: only liver - breaks down glyocgen stores to release glucose
3. adrenaline: muscles via a & b adrergic receptors - release glucose
4 calcium: muscles via a & b adrergic receptors - release glucose
Increases pepsinogen secretion:
VIP
Renin
CCK
Gastrin
Secretin
Ghrelin
Increases pepsinogen secretion:
VIP
Renin
CCK
Gastrin
Secretin
Ghrelin
Which one of the following actions is directly caused by antidiuretic hormone?
Increases Na+ reabsorption in the renal distal tubule
Stimulates aldosterone release
Up-regulates alpha-1 receptors on arterioles
Increases plasma calcium
Vasoconstriction of vascular smooth muscle
Promotes water reabsorption in the collecting ducts of the kidneys by the insertion of aquaporin-2 channels
Which one of the following actions is directly caused by antidiuretic hormone?
Increases Na+ reabsorption in the renal distal tubule
Stimulates aldosterone release
Up-regulates alpha-1 receptors on arterioles
Increases plasma calcium
Vasoconstriction of vascular smooth muscle
Promotes water reabsorption in the collecting ducts of the kidneys by the insertion of aquaporin-2 channels
Which one of the following stimulates gastric acid secretion?
CCK
Gastric inhibitory peptide
Secretin
Histamine
Somatostatin
Which one of the following stimulates gastric acid secretion?
CCK
Gastric inhibitory peptide
Secretin
Histamine
Somatostatin
if you bang your elbow and get pins & needles running down you hand, which nerve is most likely affected?
a) median
b) radial
c) ulnar
d) musculocutaneous
if you bang your elbow and get pins & needles running down you hand, which nerve is most likely affected?
a) median
b) radial
* *c) ulnar**
d) musculocutaneous
Which one of the following is the main inhibitory neurotransmitter in the spinal cord?
Adrenaline
Glutamate
Serotonin
Dopamine
Glycine
Which one of the following is the main inhibitory neurotransmitter in the spinal cord?
Adrenaline
Glutamate
Serotonin
Dopamine
Glycine
Glycine is the principal inhibitory neurotransmitter of the spinal cord
A 52-year-old male presents to his general practitioner with a two-month history of abdominal pain, occasional haematemesis and significant weight loss. He is sent for a gastroscopy, which identifies multiple gastric ulcers and thickened gastric folds. It is therefore suspected that the patient may have a gastrinoma and is sent for a secretin stimulation test (involves exogenous secretin administration) to confirm the diagnosis.
What is the mechanism of action of this exogenous hormone?
Carbohydrate digestion
Decreases gastric acid secretion
Stimulates gallbladder contractin
Stimulates gastric acid secretion
Stimulates pancreatic enzyme secretion
A 52-year-old male presents to his general practitioner with a two-month history of abdominal pain, occasional haematemesis and significant weight loss. He is sent for a gastroscopy, which identifies multiple gastric ulcers and thickened gastric folds. It is therefore suspected that the patient may have a gastrinoma and is sent for a secretin stimulation test (involves exogenous secretin administration) to confirm the diagnosis.
What is the mechanism of action of this exogenous hormone?
Carbohydrate digestion
Decreases gastric acid secretion
Stimulates gallbladder contractin
Stimulates gastric acid secretion
Stimulates pancreatic enzyme secretion
A patient has pins and needles in this distribution, which nerve is compressed?

a) ulnar
b) median
c) radius
d) musculocutanous
A patient has pins and needles in this distribution, which nerve is compressed?
a) ulnar
* *b) median**
c) radius
d) musculocutanous
which enzyme is not present in skeletal muscle?
a) debranching enzyme
b) phosphoglucomutase
c) glucose-6-phosphatase
d) glycogen phosphorylase
e) pyruvate dehydrogenase
which enzyme is not present in skeletal muscle?
a) debranching enzyme
b) phosphoglucomutase
* *c) glucose-6-phosphatase**
d) glycogen phosphorylase
e) pyruvate dehydrogenase
what are the two different pathways molecules that insulin activates to cause overall activation of glycogen synthase/ [2]
insulin
- *- activates phosphodiesterase**
- *- activates protein phosphastase**
which nerve innervates the muscles that causes gagging?
a) trigeminal nerve
b) facial nerve
c) glossopharnyngeal
d) vagus nerve
e) hypoglossal
which nerve innervates the muscles that causes gagging?
a) trigeminal nerve
b) facial nerve
c) glossopharnyngeal
d) vagus nerve
e) hypoglossal
which nerve plexi do u find in the oesphagus? [2] and where do find them?
- meissner plexus: submucosal tissue
- auerbach’s plexus: myenteric - betweeen circ and long. muscle layer
during the mechanism of T cell gut honing, what do gut dendritic cells secrete?
a) CCR9
b) retinoic acid
c) a4B7
d) MADCAM
e) IgA
during the mechanism of T cell gut honing, what do gut dendritic cells secrete?
a) CCR9
b) retinoic acid - activates T cells to make a4B7 & CCR9
c) a4B7
d) MADCAM
e) IgA
which nerve provides special sensory innervation to anterior portion of tongue?
a) glossopharnygeal
b) trigeminal
c) vagus nerve
d) hypoglossal
e) facial nerve
which nerve provides special sensory innervation to anterior portion of tongue?
a) glossopharnygeal
b) trigeminal
c) vagus nerve
d) hypoglossal
* *e) facial nerve**
what is the difference between McArdles Disease and Hers Disease? [2]
Hers disease: glycogen phosphorylase in liver [1]
McArdles caused by: deficiency in glycogen phosophorylase gene: PYGM. cant breakdown glycogen in the muscle = muscle weakness [1]
Which of the following best describes the mechanism of the body’s response to a decrease in blood pressure?
Decreased HR and vasoconstriction
Decreased epithelial sodium channels in DCT
Increased bradykinin
Insertion of AQP-2 channels in CD
Insertion of AQP-2 channels in thick ascending loop of Henle
Which of the following best describes the mechanism of the body’s response to a decrease in blood pressure?
Decreased HR and vasoconstriction
Decreased epithelial sodium channels in DCT
Increased bradykinin
Insertion of AQP-2 channels in CD
Insertion of AQP-2 channels in thick ascending loop of Henle
intermediate density lipoproteins cause left over chylomicrons to become:
a) HDLs & LDLs
b) VLDL & HDLs
c) VLDL & LDLs
d) HDLs
e) LDLs
intermediate density lipoproteins cause left over chylomicrons to become:
a) HDLs & LDLs
b) VLDL & HDLs
c) VLDL & LDLs
d) HDLs
e) LDLs
the receptive reflex in the proximal part of the stomach causes what to be released?
a) Ach
b) CCK
c) NO
d) Ca2+
e) cAMP
the receptive reflex in the proximal part of the stomach causes what to be released?
a) Ach
* *b) CCK - vagal-vagal interaction that causes proximal stomach stretch so not immediatly full**
c) NO
d) Ca2+
e) cAMP
fats (& cholesterol) absorbed from GI tract, turn into chylomicrons and go into lymphatic system:
here they interact with HDLs - how? (2)
fats (& cholesterol) absorbed from GI tract, turn into chylomicrons and go into lymphatic system:
here they interact with HDLs
- ApoC2 added: allows chylomicrons to give its triglycerides to peripheral cells
- ApoE added: allows chylomicron remenant to be taken up by the liver to deliver FA & cholesterol
what is insulin initially synthesised as? [1]
preproinsulin
gets turned into proinsulin, then at GA = insulin
A 6-day-old child is referred to a community paediatrician by a general physician for poor feeding, vomiting and increasing lethargy. The child was born at term via spontaneous vaginal delivery, and his antenatal scans report no complications.
On examination, the baby looks floppy and tired. His nappy is wet and has a characteristic maple syrup odour.
Given the most likely diagnosis, which of the following is a known complication if left untreated?
Metabolic and resp acidosis
Metabolic alkalosis
Resp alkalosis
Metabolic acidosis
Resp acidosis
A 6-day-old child is referred to a community paediatrician by a general physician for poor feeding, vomiting and increasing lethargy. The child was born at term via spontaneous vaginal delivery, and his antenatal scans report no complications.
On examination, the baby looks floppy and tired. His nappy is wet and has a characteristic maple syrup odour.
Given the most likely diagnosis, which of the following is a known complication if left untreated?
Metabolic and resp acidosis
Metabolic alkalosis
Resp alkalosis
Metabolic acidosis
Resp acidosis
If left untreated, alpha-ketoacids build up in the blood resulting in metabolic acidosis (ketoacidosis).
what type of transport do proteins undergo during mucosal phase of digestion?
- facilitated diffusion
- primary active transport
- secondary active transport
- endocytosis
what type of transport do proteins undergo during mucosal phase of digestion?
- facilitated diffusion
- primary active transport
- *- secondary active transport**
- endocytosis
A 60-year-old male patient experiences uncontrolled hepatic bleeding during liver resection surgery. The ‘Pringle manoeuvre’ is performed whereby the hepatic artery, portal vein and common bile duct are clamped, thus interrupting the blood flow. The structures mentioned form the anterior boundary of the epiploic foramen.
Which other vessel forms a boundary to this region?
Abdominal aorta
IVC
Thoracic aorta
Common hepatic artery
Right renal artery
A 60-year-old male patient experiences uncontrolled hepatic bleeding during liver resection surgery. The ‘Pringle manoeuvre’ is performed whereby the hepatic artery, portal vein and common bile duct are clamped, thus interrupting the blood flow. The structures mentioned form the anterior boundary of the epiploic foramen.
Which other vessel forms a boundary to this region?
Abdominal aorta
IVC
Thoracic aorta
Common hepatic artery
Right renal artery
You are designing a research project looking at the effects of prolonged fasting on lipid stores. You want to study the effects of diet on breakdown of fats. You decide to monitor the concentrations of the rate limiting enzyme of this process in response to a high glucose load.
What enzyme will you measure?
Glycogen phosphorylase
Isocitrate dehydrogenase
PFK-1
Glycogen synthase
Cartinine-palmitoyl transferase
You are designing a research project looking at the effects of prolonged fasting on lipid stores. You want to study the effects of diet on breakdown of fats. You decide to monitor the concentrations of the rate limiting enzyme of this process in response to a high glucose load.
What enzyme will you measure?
Glycogen phosphorylase
Isocitrate dehydrogenase
PFK-1
Glycogen synthase
Cartinine-palmitoyl transferase -
The rate limiting enzyme for lipolysis is carnitine-palmitoyl transferase I
- Commonest HLA in people with celiac disease is..
- HLA-DQ1
- HLA-DQ2
- HLA-DQ3
- HLA-DQ4
- Commonest HLA in people with celiac disease is..
- HLA-DQ1
•HLA-DQ2
- HLA-DQ3
- HLA-DQ4
Give 3 mechanisms by which absorption is achieved in the small intestine?
- Simple diffusion
- Active transport e.g. Na+/K+ATPase for absorption of glucose
- Facilitated diffusion (a carrier-mediated transport system to allow faster absorption compared with simple diffusion e.g. proteins)
Which one of the following actions is directly caused by growth hormone?
Inhibits glucagon secretion
Increases gluconeogenesis
Increases glycogenolysis
Inhibits insulin secretion
Decreases gastric H+ secretion
Increases renal reabsorption of calcium
Which one of the following actions is directly caused by growth hormone?
Inhibits glucagon secretion
Increases gluconeogenesis
Increases glycogenolysis
Inhibits insulin secretion
Decreases gastric H+ secretion
Increases renal reabsorption of calcium
what is the intermediate used in transamination? [1]
which vitamin is used as an intermediate in transamination? [1]
pyroxidal phosphate
derived from vitamin B6
With regards to the gastrointestinal tract, submucosa:
Contains the lamina propria
Contains Auerbach’s (myenteric) plexus
Contains Meissner’s plexus
Contains the muscularis mucosae
With regards to the gastrointestinal tract, submucosa:
Contains the lamina propria
Contains Auerbach’s (myenteric) plexus
Contains Meissner’s plexus
Contains the muscularis mucosae
Why does late onset of coeliac disease occur?
•A change in the composition of gut flora (e.g. due to infection, stress, hormones etc.) can trigger the activation of the genes for coeliac disease
which enzyme breaks alpha 1-4 glycosidic bonds?
a) debranching enzyme
b) phosphoglucomutase
c) glucose-6-phosphatase
d) glycogen phosphorylase
e) pyruvate dehydrogenase
which enzyme breaks alpha 1-4 glycosidic bonds?
a) debranching enzyme
b) phosphoglucomutase
c) glucose-6-phosphatase
* *d) glycogen phosphorylase**
e) pyruvate dehydrogenase
Which one of the following actions is directly caused by somatostatin?
Increases gastric motility
Increases growth hormone secretion
Increases appetite
Promotes water reabsorption in the collecting ducts of the kidneys by the insertion of aquaporin-2 channels
Increases renal conversion of 25-hydroxycholecalciferol to 1,25-dihydroxycholecalciferol
Decreases gallbladder contraction
Which one of the following actions is directly caused by somatostatin?
Increases gastric motility
Increases growth hormone secretion
Increases appetite
Promotes water reabsorption in the collecting ducts of the kidneys by the insertion of aquaporin-2 channels
Increases renal conversion of 25-hydroxycholecalciferol to 1,25-dihydroxycholecalciferol
Decreases gallbladder contraction
where in the GI tract are bile acids mostly absorbed?
a) duodenum
b) jejunum
c) ileum
d) ascending colon
e) transverse colon
where in the GI tract are bile acids mostly absorbed?
a) duodenum
b) jejunum
c) ileum
d) ascending colon
e) transverse colon
(also absorbed in colon, but less so)
movement of water in gut crypt cells is controlled by which transporters?
a) aquaporins
b) ENAC
c) ROMK
d) CFTR
e) Na/K/Cl2
movement of water in gut crypt cells is controlled by which transporters?
a) aquaporins
b) ENAC
c) ROMK
* *d) CFTR**
e) Na/K/Cl2

A patient becomes dehydrated which leads to increased absorption of water in the collecting duct. If you were to measure the concentration of his urine you would find that it is near to 1200mOsm/L
Where in the nephron would you expect a similar osmolarity to be found?
PCT
Descending loop of Henle
Tip of loop of Henle
Thin ascending Loop of Henle
Thick ascending Loop of Henle
A patient becomes dehydrated which leads to increased absorption of water in the collecting duct. If you were to measure the concentration of his urine you would find that it is near to 1200mOsm/L
Where in the nephron would you expect a similar osmolarity to be found?
PCT
Descending loop of Henle
Tip of loop of Henle
Thin ascending Loop of Henle
Thick ascending Loop of Henle
. Name the co factor required by phenylalanine hydroxylase ( 1 mark)
- Tetrahydrobiopterin
Which one of the following best accounts for the action of PTH in increasing serum calcium levels?
Activation of vit. D to increase absorption of calcium from the small intestine
Direct stimulation of osteoclasts to absorb bone with release of calcium
Stimulation of phosphate absorbtion at the DCT of the kidney
Decreased porosity of the vessels at the Bowmans capsule to calcium
Vasospasm of the afferent renal arteriole thereby reducing GFR and calcium urinary loss
Which one of the following best accounts for the action of PTH in increasing serum calcium levels?
Activation of vit. D to increase absorption of calcium from the small intestine
Direct stimulation of osteoclasts to absorb bone with release of calcium
Stimulation of phosphate absorbtion at the DCT of the kidney
Decreased porosity of the vessels at the Bowmans capsule to calcium
Vasospasm of the afferent renal arteriole thereby reducing GFR and calcium urinary loss
PTH increases the activity of 1-α-hydroxylase enzyme, which converts 25-hydroxycholecalciferol to 1,25-dihydroxycholecalciferol, the active form of vitamin D.
Osteoclasts do not have a PTH receptor and effects are mediated via osteoblasts.
what is the precursor for all steriod hormones, which occurs after conversion of cholesterol? [1]
In all steroid-producing human tissue, the conversion of cholesterol to pregnenolone is an essential step. Pregnenolone is the precursor for all steroid hormones, and its formation represents the rate-limiting step of steroid synthesis
ID the branch of the brachial plexus identified by the arrow
axillary
radial
median
ulnar

ID the branch of the brachial plexus identified by the arrow
axillary
radial
median
ulnar
A 46-year-old gentleman presents to the general practice with a 2-week history of a tickly non-productive cough. There are no associated symptoms. The patient’s respiratory examination is normal. The gentleman started taking ACE inhibitors at around the same time as the symptom started. You decide the patient’s cough is likely due to the new medication, and prescribe an angiotensin receptor blocker in place of the ACE inhibitor. A lot of antihypertensive medication target elements of the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone-system. Angiotensin I is a hormone that is important in the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone-system. It is derived from the hydrolysis of angiotensinogen in a reaction catalysed by which enzyme?
Carbonic anhydrase
ACE
Cycoloxygenase-2
Renin
Amylase
A 46-year-old gentleman presents to the general practice with a 2-week history of a tickly non-productive cough. There are no associated symptoms. The patient’s respiratory examination is normal. The gentleman started taking ACE inhibitors at around the same time as the symptom started. You decide the patient’s cough is likely due to the new medication, and prescribe an angiotensin receptor blocker in place of the ACE inhibitor. A lot of antihypertensive medication target elements of the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone-system. Angiotensin I is a hormone that is important in the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone-system. It is derived from the hydrolysis of angiotensinogen in a reaction catalysed by which enzyme?
Carbonic anhydrase
ACE
Cycoloxygenase-2
Renin
Amylase
Identifiy two histological features of CD
- **villus atrophy
- crypt hyperplasia**
how are lipids absorbed in the mucosal phase of lipid digestion?
a) primary active transport
b) secondary active transport
c) simple diffusion
d) faciliated diffusion
e) paracellular transport
how are lipids absorbed in the mucosal phase of lipid digestion?
a) primary active transport
b) secondary active transport
* *c) simple diffusion**
d) faciliated diffusion
e) paracellular transport
which micronutrient helps to improve childrens learning ability and cognitive development? (1)
Why? (1)
iron helps to improve childrens learning ability and cognitive development: Fe helps Hb to carry oxygen to neurons in brain
Where in the body is angiotensinogen produced?
Adrenal cortex
Liver
Lungs
Kidneyss
Pancreas
Where in the body is angiotensinogen produced?
Adrenal cortex
Liver
Lungs
Kidneyss
Pancreas
ileal brake is caused be what entering the ileum?
a) proteins
b) carbs
c) fats
d) minerals
e) vitamins
ileal brake is caused be what entering the ileum?
a) proteins
b) carbs
* *c) fats**
d) minerals
e) vitamins
- fats reach the ileum (even tho theyre meant to have been absorbed in duodenum)
- causes release of peptide YY & glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) by enteroendocrine cells
= slows gastric emptying
A patient presents to their GP with dehydration due to diarrhoea and vomiting. This is detected by the kidneys as reduced renal perfusion causing the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system to be activated.
Which part of the adrenal gland is needed as part of this system?
JXG cells
Pulmonary endothelium
Zona glomerulosa
Zona fasciculata
Zona reticularis
A patient presents to their GP with dehydration due to diarrhoea and vomiting. This is detected by the kidneys as reduced renal perfusion causing the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system to be activated.
Which part of the adrenal gland is needed as part of this system?
JXG cells
Pulmonary endothelium
Zona glomerulosa - aldosterone is secreted from the zona glom
Zona fasciculata
Zona reticularis
what colour does CLO test go if H. pylori is present?
a) blue
b) yellow
c) green
d) orange
e) purple
what colour does CLO test go if H. pylori is present?
a) blue
b) yellow
c) green
* *d) orange / red**
e) purple
What effect does angiotensin II have on common renal measurements?
Decreased GFR, decreased renal plasma flow, no change in filtration fraction
Increased GFR, no change in renal plasma flow, increase in filtration fraction
Decreased GFR, no change in renal plasma flow, decrease in filtration fraction
Decreased GFR, increased renal plasma flow, decrease in filtration fraction
Increased GFR, decreased renal plasma flow, increase in filtration fraction
Increased GFR, increased renal plasma flow, no change in filtration fraction
What effect does angiotensin II have on common renal measurements?
Decreased GFR, decreased renal plasma flow, no change in filtration fraction
Increased GFR, no change in renal plasma flow, increase in filtration fraction
Decreased GFR, no change in renal plasma flow, decrease in filtration fraction
Decreased GFR, increased renal plasma flow, decrease in filtration fraction
Increased GFR, decreased renal plasma flow, increase in filtration fraction
Increased GFR, increased renal plasma flow, no change in filtration fraction
metabolism of glutamine releases a lot of what?
urea
NH3
NH4+
uric acid
NADH
metabolism of glutamine releases a lot of what?
urea
NH3
NH4+
uric acid
NADH
- a-keto glutarate glutamate glutamine: generates free ammonia (as NH4+)
- a-ketoglutarate is needed for TCA cycle for energy.*
- Glutamine has 2 amino groups, glutmate has 1, a-keto glutarate has 0 - so each step removes/adds an amino group so the metabolism of glutamine releases a lot of ammonium.*
what do chief cells secrete in children? [1]
function? [1]
what do chief cells secrete in children? [1]
chymosin / rennin
function? [1]
coagulate milk allowing it to be retained longer in the stomach
Where is the majority of somatostatin secreted from?
P/D1 cells lining the fundus of the stomach and epsilon cells of the pancreas
S cells in upper small intestine
Sertoli cells
D cells in the pancreas & stomach
I cells in upper small intestine
Zona glomerulosa of adrenal cortex
Where is the majority of somatostatin secreted from?
P/D1 cells lining the fundus of the stomach and epsilon cells of the pancreas
S cells in upper small intestine
Sertoli cells
D cells in the pancreas & stomach
I cells in upper small intestine
Zona glomerulosa of adrenal cortex
Which one of the following hormonal agents will increase secretions of water and electrolytes in pancreatic juice?
- secretin
- aldosterone
- somatostatin
- cholecystokinin
- adrenaline
Which one of the following hormonal agents will increase secretions of water and electrolytes in pancreatic juice?
- secretin
- aldosterone
- somatostatin
- cholecystokinin
- adrenaline
The thoracic duct of the lymphatic system empties in the..
- Left subclavian vein
- Left internal jugular vein
- Left brachiocephalic vein
- Left hemiazygos vein
The thoracic duct of the lymphatic system empties in the..
•Left subclavian vein
- Left internal jugular vein
- Left brachiocephalic vein
- Left hemiazygos vein
cells can make which vitamin from tryptophan if they are deficient in it?
vitamin B1
vitamin B2
vitamin B3
vitamin B4
vitamin B5
cells can make which vitamin from tryptophan if they are deficient in it?
vitamin B1
vitamin B2
vitamin B3
vitamin B4
vitamin B5
A 6-month-old boy presents to the genetics clinic with a one-month history of swallowing and movement difficulties.
A genetic test is done for rare diseases which demonstrates a four base-pair insertion on chromosome 15, causing defects in the enzyme hexosaminidase A.
What type of genetic mutation is this?
Frameshift
Missense
Nonsense
Silent
Synonymous
A 6-month-old boy presents to the genetics clinic with a one-month history of swallowing and movement difficulties.
A genetic test is done for rare diseases which demonstrates a four base-pair insertion on chromosome 15, causing defects in the enzyme hexosaminidase A.
What type of genetic mutation is this?
Frameshift
Missense
Nonsense
Silent
Synonymous
Name the major types of MHC class I and MHC class II molecules in humans?
Class I: HLA-A, B and C
Class II: HLA-DR, DP and DQ
A 16-year-old boy presents to the Emergency Department with acute onset pain in the right iliac fossa, nausea, vomiting, and fever. He has no significant past medical or surgical history. On examination, you find rebound tenderness at McBurney’s point, guarding, and a positive Rovsing’s sign. You strongly suspect appendicitis and the patient is later taken for surgery.
Which of these is most likely to be a physiological response in this scenario?
Increased glucagon secretion
Increased insulin secretion
Reducde cortisol secretion
Increased T4 secretion
Reduced ACTH secretion
A 16-year-old boy presents to the Emergency Department with acute onset pain in the right iliac fossa, nausea, vomiting, and fever. He has no significant past medical or surgical history. On examination, you find rebound tenderness at McBurney’s point, guarding, and a positive Rovsing’s sign. You strongly suspect appendicitis and the patient is later taken for surgery.
Which of these is most likely to be a physiological response in this scenario?
Increased glucagon secretion: physiological stresses increase secretion of glucagon !!
Increased insulin secretion
Reducde cortisol secretion
Increased T4 secretion
Reduced ACTH secretion
You are designing a research project looking at the pathophysiology of abetalipoproteinemia. You decide that a suitable target would be the rate limiting enzyme of lipogenesis.
What enzyme will you target?
Carbomyl phosphate synthestase I
Acetly CoA carboxylase
Glycogen phosphorylase
Isocitratre dehydrogenase
PFK-1
You are designing a research project looking at the pathophysiology of abetalipoproteinemia. You decide that a suitable target would be the rate limiting enzyme of lipogenesis.
What enzyme will you target?
Carbomyl phosphate synthestase I
Acetly CoA carboxylase
Glycogen phosphorylase
Isocitratre dehydrogenase
PFK-1
Lipogenesis is the process by which acetyl-CoA is converted to fatty acids. The rate limiting enzyme for lipogenesis is acetyl CoA carboxylase.
The most effective class of gastric anti-secretory drug
a. Proton pump inhibitors
b. Histamine (H2) receptor blocker
c. Aluminium hydroxide
d. Amoxycillin
The most effective class of gastric anti-secretory drug
a.Proton pump inhibitors
b. Histamine (H2) receptor blocker
c. Aluminium hydroxide
d. Amoxycillin
Which one of the following actions is directly caused by somatostatin?
Decreases gastric emptying
Increases secretion of melanocyte-stimulating hormone (MSH) and corticotrophin-releasing hormone (CRH)
Increases renal reabsorption of calcium
Increases gastric H+ secretion
Increases glycogenolysis
Increases growth hormone secretion
Which one of the following actions is directly caused by somatostatin?
Decreases gastric emptying
Increases secretion of melanocyte-stimulating hormone (MSH) and corticotrophin-releasing hormone (CRH)
Increases renal reabsorption of calcium
Increases gastric H+ secretion
Increases glycogenolysis
Increases growth hormone secretion
which of the following have supranuclear granules?
- goblet cells
- paneth cells
- enteroendocrine cells
- m cells
- parietal cells
which of the following have supranuclear granules?
- goblet cells
- *- paneth cells**
- enteroendocrine cells
- m cells
- parietal cells

Which ligament in the knee is being tested here?
- anterior cruciate ligament
- posterior cruciate ligament
- medial collateral ligament
- lateral collateral ligament

Which ligament in the knee is being tested here?
- anterior cruciate ligament
- *- posterior cruciate ligament**
- medial collateral ligament
- lateral collateral ligament
which of the following binds to basophils and mast cells and activates these cells to produce antimicrobial factors to participate in respiratory immune defense in humans?
- IgA
- IgM
- IgE
- IgD
- IgG
which of the following binds to basophils and mast cells and activates these cells to produce antimicrobial factors to participate in respiratory immune defense in humans?
- IgA
- IgM
- IgE
- *- IgD**
- IgG
which micronutrient is important in imprinting home to the gut mucosa from peyers patches?
a) Vitamin A
b) Vitamin B
c) Vitamin C
d) Vitamin D
e) Vitamin E
which micronutrient is important in imprinting home to the gut mucosa from peyers patches?
- *a) Vitamin A**
b) Vitamin B
c) Vitamin C
d) Vitamin D
e) Vitamin E
makes retinoic acid !!
- gut dendritic cells use retinoic acid to inform the niave T cells
- causes niave T cells to change transcription to express CCR9 & a4B& to do gut honing
What effect does vasodilation of afferent arterioles have on common renal measurements?
Decreased GFR, increased renal plasma flow, decrease in filtration fraction
Decreased GFR, decreased renal plasma flow, no change in filtration fraction
Increased GFR, increased renal plasma flow, no change in filtration fraction
Increased GFR, decreased renal plasma flow, increase in filtration fraction
Decreased GFR, no change in renal plasma flow, decrease in filtration fraction
Increased GFR, no change in renal plasma flow, increase in filtration fraction
What effect does vasodilation of afferent arterioles have on common renal measurements?
Decreased GFR, increased renal plasma flow, decrease in filtration fraction
Decreased GFR, decreased renal plasma flow, no change in filtration fraction
Increased GFR, increased renal plasma flow, no change in filtration fraction
Increased GFR, decreased renal plasma flow, increase in filtration fraction
Decreased GFR, no change in renal plasma flow, decrease in filtration fraction
Increased GFR, no change in renal plasma flow, increase in filtration fraction
A 16-year-old boy presents with muscle pain during exercise, early fatigue, and dark urine. He is diagnosed with McArdle’s disease.
What is the rate-limiting enzyme for the defective pathway in this disease?
Isocitrate dehydrogenase
Phosphofructokinase-1
Glycogen synthase
Glyocgen phosphorylase
Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase
A 16-year-old boy presents with muscle pain during exercise, early fatigue, and dark urine. He is diagnosed with McArdle’s disease.
What is the rate-limiting enzyme for the defective pathway in this disease?
Isocitrate dehydrogenase
Phosphofructokinase-1
Glycogen synthase
Glyocgen phosphorylase
Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase
vegans are likely to be deficient in which two vitamins? [2]
B12 & vitamin D
Increases glycogenolysis:
Cortisol
Somatostatin
Gastrin
Glucagon
Growth hormone
Ghrelin
Increases glycogenolysis:
Cortisol
Somatostatin
Gastrin
Glucagon
Growth hormone
Ghrelin
Which cell secretes hydrochloric acid?
a. Mast cell
b. Columnar cell
c. Parietal cell
d. Chief cell
e. Goblet cell
Which cell secretes hydrochloric acid?
a. Mast cell
b. Columnar cell
c.Parietal cell
d. Chief cell
e. Goblet cell
which apoprotein acts as recognition signal for LDL to be taken up by peripheral cells?
- Apo B48
- Apo B100
- Apo C2
- Apo E
- Apo B10
which apoprotein acts as recognition signal for LDL to be taken up by peripheral cells?
- Apo B48
- *- Apo B100**
- Apo C2
- Apo E
- Apo B10
which cells found in the small intestine secrete antimicrobe substances?
- enterocytes
- goblet cells
- paneth cells
- enteroendocrine cells
- m cells
which cells found in the small intestine secrete antimicrobe substances?
- enterocytes
- goblet cells
- *- paneth cells**
- enteroendocrine cells
- m cells
which lipoprotein carries fats from the liver to peripheral cells:
a) chylomicrons
b) VLDLs
c) IDLs
d) LDLs
e) HDLs
which lipoprotein carries fats from the liver to peripheral cells:
a) chylomicrons
* *b) VLDLs**
c) IDLs
d) LDLs
e) HDLs
A 63-year-old man attends the dialysis unit three times a week to receive haemofiltration. In normal functioning kidneys, what detects changes in salt concentrations (such as sodium chloride) and adapts the glomerular filtration rate accordingly?
Juxtaglomerular cells
Mesengial cells
Podocytes
Macula Densa
Prinicpal cells
A 63-year-old man attends the dialysis unit three times a week to receive haemofiltration. In normal functioning kidneys, what detects changes in salt concentrations (such as sodium chloride) and adapts the glomerular filtration rate accordingly?
Juxtaglomerular cells
Mesengial cells
Podocytes
Macula Densa
Prinicpal cells
lipoprotein lipase breaks down fats from inside lipoproteins and carries them into the cells. Which apoprotein is it activated by?
- Apo B48
- Apo B100
- Apo C2
- Apo E
- Apo B10
lipoprotein lipase breaks down fats from inside lipoproteins and carries them into the cells. Which apoprotein is it activated by?
- Apo B48
- Apo B100
- *- Apo C2**
- Apo E
- Apo B10
which of the following is correct?
- glycogen synthase is activated by addition of P, glycogen phosphorylase is activated by removal of P
- glycogen synthase is activated by removal of P, glycogen phosphorylase is activated by addition of P
- glycogen synthase is inhibited by addition of P, glycogen phosphorylase is inhibited by removal of P
- glycogen synthase is inhibited by removal of P, glycogen phosphorylase is inhibited by addition of P
which of the following is correct?
- glycogen synthase is activated by addition of P, glycogen phosphorylase is activated by removal of P
- *- glycogen synthase is activated by removal of P, glycogen phosphorylase is activated by addition of P**
- glycogen synthase is inhibited by addition of P, glycogen phosphorylase is inhibited by removal of P
- glycogen synthase is inhibited by removal of P, glycogen phosphorylase is inhibited by addition of P
glycogen synthase is activated by removing P, inactivated by adding P
glycogen phosphorylase is activated by adding P, inactivated by removing P
the duodenal and jejunal breaks cause what to be released?
a) Ach
b) CCK
c) NO
d) Ca2+
e) cAMP
the duodenal and jejunal breaks cause what to be released?
a) Ach
* *b) CCK**
c) NO
d) Ca2+
e) cAMP
- release of CCK activates vagal efferents
- as a result of vagal efferents:
- reduces opening of pyloric sphincter
- reductions contractions in corpus
- enhances relaxation of fundus
effect of insulin of gluconeogenesis? [1]
insulin inhibits gluconeogenesis
what is used to capture this image?
a) CT
b) MRI T1
c) MRI T2
d) plain radiograph

what is used to capture this image?
- *a) CT**
b) MRI T1
c) MRI T2
d) plain radiograph
The presence of particular IgA antibodies in the blood can be used to diagnose coeliac disease. Name two antigens recognised by these antibodies?
Tissue transglutaminase (tTG) or endomysium Gluten
- A patient with suspected celiac disease has IgA anti-TTG test which comes back within normal range. What could contribute to the false negative nature of this investigation? (2)
- What could be done to verify the patient’s celiac disease? (3)
1. A patient with suspected celiac disease has IgA anti-TTG test which comes back within normal range. What could contribute to the false negative nature of this investigation? (2)
- IgA deficient patient (1)
- Patient isn’t actively consuming gluten (1)
2. What could be done to verify the patient’s celiac disease?
- Perform total IgA blood test to assess IgA status of pt (1)
- IgG-anti-TTG (1)
- Ask patient to consume gluten for some time before redoing the tests (1)
- Duodenal biopsy (after patient consumes gluten!!) (1)
where is the largest microbial colony found in the GI tract?
a) stomach
b) duodenum
c) jejunum
d) ileum
e) colon
where is the largest microbial colony found in the GI tract?
a) stomach
b) duodenum
c) jejunum
d) ileum
* *e) colon**
- not in small intestine bc: difficult env. for growth
The flat bones of the skull are formed by intramembranous ossification
True
False
The flat bones of the skull are formed by intramembranous ossification
True
False
immune cells have increased requirement for which co factor
- B6
- NADPH
- NADH
- FADH
- B12
immune cells have increased requirement for which co factor
- B6
- *- NADPH - made via the pentose phosphate pathway**
- NADH
- FADH
- B12
Which one of the peritoneal ligaments connects the liver to the anterior abdominal wall?
Falciform ligament
Gastrocolic ligament
Splenorenal ligament
Hepatogastric ligament
Gastrosplenic ligament
Hepatoduodenal ligament
Which one of the peritoneal ligaments connects the liver to the anterior abdominal wall?
Falciform ligament
Gastrocolic ligament
Splenorenal ligament
Hepatogastric ligament
Gastrosplenic ligament
Hepatoduodenal ligament
describe the role of Apo B100 on low densit lipoproteins (2)
Apo B100 causes LDLs to be taken up by cells (1)
because only taken up via receptor mediated endocytosis (1)
Which layer of the gastrointestinal tract contains Auerbach’s (myenteric) plexus?
Muscularis externa
Submucosa
Serosa
Mucosa
Which layer of the gastrointestinal tract contains Auerbach’s (myenteric) plexus?
Muscularis externa
Submucosa
Serosa
Mucosa
zollinger-ellison syndrome (ZES) causes innappropriate secretions from which cell?
a) parietal cells
b) G cells
c) chief cells
d) ECL likes
e) mucous secreting cells
zollinger-ellison syndrome (ZES) causes innappropriate secretions from which cell?
a) parietal cells
* *b) G cells - causes increased gastrin productio n**
c) chief cells
d) ECL likes
e) mucous secreting cells
submanidublar gland recieves parasympathetic innervation from which nerve?
a) glossopharnygeal
b) trigeminal
c) vagus nerve
d) hypoglossal
e) facial nerve
submanidublar gland recieves parasympathetic innervation from which nerve?
a) glossopharnygeal
b) trigeminal
c) vagus nerve
d) hypoglossal
* *e) facial nerve**
Which one of the following actions is directly caused by secretin?
Vasoconstriction of vascular smooth muscle
Decreases pepsinogen secretion
Stimulates parietal cell maturation
Increases pancreatic bicarbonate secretion
Increases pancreatic secretions rich in digestive enzymes
Stimulates release of insulin-like growth factors
Which one of the following actions is directly caused by secretin?
Vasoconstriction of vascular smooth muscle
Decreases pepsinogen secretion
Stimulates parietal cell maturation
Increases pancreatic bicarbonate secretion
Increases pancreatic secretions rich in digestive enzymes
Stimulates release of insulin-like growth factors
parotid gland recieves parasympathetic innervation from which nerve?
a) glossopharnygeal
b) trigeminal
c) vagus nerve
d) hypoglossal
e) facial nerve
parotid gland recieves parasympathetic innervation from which nerve?
- *a) glossopharnygeal**
b) trigeminal
c) vagus nerve
d) hypoglossal
e) facial nerve
hypocalcemia causes the release of which hormone to regulate Ca2+ levels?
- TSH
- PTH
- FH
- GHRH
- ADH
hypocalcemia causes the release of which hormone to regulate Ca2+ levels?
- TSH
- *- PTH**
- FH
- GHRH
- ADH
With respect to the phosphorylation of glucose, which one of the following is most associated with glucokinase?
High affinity for glucose (low Km)
Induced by insulin
Low capacity (low Vmax)
Not affected by insulin
When glucose levels are low helps sequester glucose in the tissues
Located in most tissues
With respect to the phosphorylation of glucose, which one of the following is most associated with glucokinase?
High affinity for glucose (low Km)
Induced by insulin
Low capacity (low Vmax)
Not affected by insulin
When glucose levels are low helps sequester glucose in the tissues
Located in most tissues
Where is the majority of CCK secreted from?
P/D1 cells lining the fundus of the stomach and epsilon cells of the pancreas
S cells in upper small intestine
Sertoli cells
D cells in the pancreas & stomach
I cells in upper small intestine
Zona glomerulosa of adrenal cortex
Where is the majority of CCK secreted from?
P/D1 cells lining the fundus of the stomach and epsilon cells of the pancreas
S cells in upper small intestine
Sertoli cells
D cells in the pancreas & stomach
I cells in upper small intestine
Zona glomerulosa of adrenal cortex
A 56-year-old man has chronic pancreatitis and is struggling to absorb fat-soluble components of his diet.
Which of the following is a fat-soluble vitamin which has a role as an anti-oxidant during processes such as immune function and protection of cell membranes?
Vit B
Vit E
Vit K
Vit C
Vit B
A 56-year-old man has chronic pancreatitis and is struggling to absorb fat-soluble components of his diet.
Which of the following is a fat-soluble vitamin which has a role as an anti-oxidant during processes such as immune function and protection of cell membranes?
Vit B
Vit E
Vit K
Vit C
Vit B
Which one of the peritoneal ligaments contains the short gastric vessels?
Splenorenal ligament
Gastrosplenic ligament
Hepatoduodenal ligament
Hepatogastric ligament
Falciform ligament
Gastrocolic ligament
Which one of the peritoneal ligaments contains the short gastric vessels?
Splenorenal ligament
Gastrosplenic ligament
Hepatoduodenal ligament
Hepatogastric ligament
Falciform ligament
Gastrocolic ligament
which vitamin deficiency is associated with pellegra?
- vit. A
- vit B1
- vit. B2
- vit. B3
- vit. B4
which vitamin deficiency is associated with pellegra?
- vit. A
- vit B1
- vit. B2
- *- vit. B3**
- vit. B4
excess LDLs in the blood stream can cause production of which type of cells? (1)
foam cells (where macrophages engulf LDL and become foam cells) stick to BV walls and make atheroma plaque
which vitamin is used in the as a cofactor in the Krebs Cycle and glycolysis?
- vitamin B1
- vitamin B2
- vitamin B3
- vitamin B6
- vitamin B12
which vitamin is used in the as a cofactor in the Krebs Cycle and glycolysis?
- vitamin B1
- vitamin B2
- vitamin B3
- vitamin B6
- vitamin B12
where are CD4 T cells usually found in the gut?
- epithelium
- submucosa
- lamina propria
- muscularis mucosa
where are CD4 T cells usually found in the gut?
- epithelium
- submucosa
- *- lamina propria**
- muscularis mucosa
which apoprotein do chylomicrons have on them:
a) B100
b) B49
c) B101
d) B48
e) B102
which apoprotein do chylomicrons have on them:
a) B100
b) B49
c) B101
* *d) B48**
e) B102
Which one of the following actions is directly caused by VIP?
Increases proximal tubule Na+/H+ activity
Increases gallbladder contraction
Increases pancreatic bicarbonate secretion
Decreases pancreatic secretions
Increases secretion of water from pancreas and intestines
Up-regulates alpha-1 receptors on arterioles
Which one of the following actions is directly caused by VIP?
Increases proximal tubule Na+/H+ activity
Increases gallbladder contraction
Increases pancreatic bicarbonate secretion
Decreases pancreatic secretions
Increases secretion of water from pancreas and intestines
Up-regulates alpha-1 receptors on arterioles
From which of the following does the epigastric artery originate?
Internal iliac artery
External iliac artery
Superior vesical artery
Inferior vesical artery
None of the above
From which of the following does the epigastric artery originate?
Internal iliac artery
External iliac artery
Superior vesical artery
Inferior vesical artery
None of the above
The citric acid cycle is responsible for the major share of energy release and supply during aerobic respiration.
What is the rate limiting enzyme of the citric acid cycle?
PFK1
Glycogen synthase
Glyocgen phosphorylase
Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase
Isocitrate dehydrogenase
The citric acid cycle is responsible for the major share of energy release and supply during aerobic respiration.
What is the rate limiting enzyme of the citric acid cycle?
PFK1
Glycogen synthase
Glyocgen phosphorylase
Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase
Isocitrate dehydrogenase
Which one of the following is not an effect of cholecystokinin?
It causes gallbladder contraction
It increases the rate of gastric emptying
It relaxes the sphincter of oddi
It stimulates the pancreatic acinar cells
It has a trophoc effect on pancreatic acinar cells
Which one of the following is not an effect of cholecystokinin?
It causes gallbladder contraction
It increases the rate of gastric emptying
It relaxes the sphincter of oddi
It stimulates the pancreatic acinar cells
It has a trophoc effect on pancreatic acinar cells
The first antibodies to be produced in a humoral immune response are always:
a) IgG
b) IgM
c) IgA
d) IgE
e) IgD
The first antibodies to be produced in a humoral immune response are always:
a) IgG
* *b) IgM**
c) IgA
d) IgE
e) IgD
The first antibodies to be produced in a humoral immune response are always IgM, because IgM can be expressed without isotype switching (see Figs 4.20 and 9.8). These early IgM antibodies are produced before B cells have undergone somatic hypermutation and therefore tend to be of low affinity.
which lipoprotein carries fats from the liver to peripheral cells?
chylomicron
very low density lipo
intermediate DL
LDL
HDL
which lipoprotein carries fats from the liver to peripheral cells?
chylomicron
very low density lipo
intermediate DL
LDL
HDL
Which cell secretes pepsinogen?
a. Mast cell
b. Columnar cell
c. Parietal cell
d. Chief cell
e. Goblet cell
Which cell secretes pepsinogen?
a. Mast cell
b. Columnar cell
c. Parietal cell
d.Chief cell
e.Goblet cell
Name a function for Vitamin
A (1)
D (1)
E (1)
K (1)
A: component of visual pigments; anitoxidnat; prevents damage to lipids of cell surface membranes(1)
D: Aids in the use of calcium and phosphorus (1)
E: antioxidant 1)
K; part of blood clotting cascade (1)
which vitamin is used for closure of neural tube during development and if deficient, causes spina bifida:
zinc
copper
B9
B12
selenium
which vitamin is used for closure of neural tube during development and if deficient, causes spina bifida:
zinc
copper
B9 - folate !!
B12
selenium
what is labelled A? [1]
what change in stucture occurs here? [1]

pectinate line [1]
simple columnar –> stratified squamous nonk epithelium
chylomicrons pick up which two apoproteins from HDL?
a) ApoCII and ApoE
b) ApoCI and ApoB100
c) ApoCII and ApoB100
d) ApoC and ApoB48
e) ApoB48 and ApoB100
chylomicrons pick up which two apoproteins from HDL?
- *a) ApoCII and ApoE**
b) ApoCI and ApoB100
c) ApoCII and ApoB100
d) ApoC and ApoB48
e) ApoB48 and ApoB100
Prolactin is secreted from which part of the body?
Anterior pituitary
Hypothalamus
Parathyroid gland
Adrenal gland
Posterior pituitary
Prolactin is secreted from which part of the body?
Anterior pituitary
Hypothalamus
Parathyroid gland
Adrenal gland
Posterior pituitary
which of the following is autosomal dominant?
a) PKU
b) medium chain actly coenzyme dehydrogenase (MCAD)
c) von Gierkes disease
d) Maple Syrup Urine Disease
e) familal hypercholesterolemia
which of the following is autosomal dominant?
a) PKU
b) medium chain actly coenzyme dehydrogenase (MCAD)
c) von Gierkes disease
d) Maple Syrup Urine Disease
* *e) familal hypercholesterolemia**
Among all the masticatory muscles, X is the only one with horizontally arranged fibers.
X =?
a) medial pterygoid
b) lateral pterygoid
c) masseter
d) temporalis
Among all the masticatory muscles, X is the only one with horizontally arranged fibers.
X =?
a) medial pterygoid
b) lateral pterygoid
c) masseter
d) temporalis

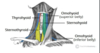
NSAIDS block which receptor on parietal cells?
a) M3
b) CCK2
c) H2
d) somatostatin receptor
e) prostaglandin receptor
NSAIDS block which receptor on parietal cells?
a) M3
b) CCK2
c) H2
d) somatostatin receptor
* *e) prostaglandin receptor - causes decresease in mucous and bicarbonate production :(**
Julie, a 54-year-old female, presents to her GP with a lump in her groin. It is not associated with pain but becomes more prominent when she coughs.
On examination, the GP notes the lump is inferior and lateral to the pubic tubercle, which aids his diagnosis of a femoral hernia. Therefore part of Julie’s bowel had entered the femoral canal which causes a bulge into the femoral triangle, an anatomical region in the upper thigh.
Laterally to medially, what contents can be found in this anatomical region?
Femoral nerve, femoral artery, femoral vein, empty space, lymphatics
Femoral artery, femoral vein, femoral nerve, empty space, lymphatics
Femoral nerve, femoral vein, femoral artery, empty space, lymphatics
Lymphatics, empty space, femoral nerve, femoral artery, femoral vein
Lymphatics, empty space, femoral vein, femoral artery, femoral nerve
Julie, a 54-year-old female, presents to her GP with a lump in her groin. It is not associated with pain but becomes more prominent when she coughs.
On examination, the GP notes the lump is inferior and lateral to the pubic tubercle, which aids his diagnosis of a femoral hernia. Therefore part of Julie’s bowel had entered the femoral canal which causes a bulge into the femoral triangle, an anatomical region in the upper thigh.
Laterally to medially, what contents can be found in this anatomical region?
Femoral nerve, femoral artery, femoral vein, empty space, lymphatics
Femoral artery, femoral vein, femoral nerve, empty space, lymphatics
Femoral nerve, femoral vein, femoral artery, empty space, lymphatics
Lymphatics, empty space, femoral nerve, femoral artery, femoral vein
Lymphatics, empty space, femoral vein, femoral artery, femoral nerve
Why is Nuria asked to go on a low protein diet (2 marks)
Phenylalanine is an amino acid and is normally present in protein based foods, such having too much protein could lead to a build-up of phenylalanine. In this case as Nuria is pregnant, if she has excess phenylalanine can affect the development of the foetus.
which micronutrient helps to improve childrens learning ability and cognitive development
- vitamin A
- vitamin B12
- zinc
- iron
- vitamin C
which micronutrient helps to improve childrens learning ability and cognitive development
- vitamin A
- vitamin B12
- zinc
- *- iron: Fe helps Hb to carry oxygen to neurons in brain**
- vitamin C
Which layer of the gastrointestinal tract contains the muscularis mucosae?
Submucosa
Mucosa
Serosa
Muscularis externa
Which layer of the gastrointestinal tract contains the muscularis mucosae?
Submucosa
Mucosa
Serosa
Muscularis externa
which part of the GI tract is associated with having lots of lacteals? [1]
jejunum
What is measured to obtain renal plasma flow?
Creatinine
Para-amino hippuric acid (PAH)
Inulin
Glucose
Protein
What is measured to obtain renal plasma flow?
Creatinine
Para-amino hippuric acid (PAH)
Inulin
Glucose
Protein
where do you find paneth cells in the colon? [1]
paneth cells are found in right side of colon only
B3 (niacin) is important in producing which two important molecules? [2]
which disease does a deficiency in B3 cause?
NAD & NADP
pellegra
The left colic artery supplies the upper and lower parts of the descending colon.
What artery does the left colic artery branch off?
SMA
Inferior gluteal artery
IMA
Inferior rectal artery
Inferior epigatric artery
The left colic artery supplies the upper and lower parts of the descending colon.
What artery does the left colic artery branch off?
SMA
Inferior gluteal artery
IMA
Inferior rectal artery
Inferior epigatric artery
Glomerular filtration rate:
Is typically around 0.20
Can be estimated using creatinine clearance
Glomerular filtration rate / renal blood flow
Plasmacreatinine / urinarycreatinine
UPAH * V / PPAH
Urine flow rate * urine concentration
Glomerular filtration rate:
Is typically around 0.20
Can be estimated using creatinine clearance
Glomerular filtration rate / renal blood flow
Plasmacreatinine / urinarycreatinine
UPAH * V / PPAH
Urine flow rate * urine concentration
during glucose metabolism, the if there is a little cAMP levels, which of the following occurs?
- glucagon and adrenaline activated
- insulin is activated
- glucagon an adrenaline inhibited
during glucose metabolism, the if there is a little cAMP levels, which of the following occurs?
- glucagon and adrenaline activated
- insulin is activated
- *- glucagon an adrenaline inhibited**
- *less glucose is released**
A 28-year-old man with a long-term history of alcohol is rushed to the emergency department following a prolonged seizure. His work-up fails to reveal any sinister causes of seizures. He has no history of epilepsy. The consultant attending to him believes that the seizure may be caused by a vitamin deficiency secondary to his chronic alcohol intake.
Which one of the following vitamin deficiency may have caused the seizure?
Vitamin B7
Vitamin B2
Vitamin B3
Vitamin B5
Vitamin B6
A 28-year-old man with a long-term history of alcohol is rushed to the emergency department following a prolonged seizure. His work-up fails to reveal any sinister causes of seizures. He has no history of epilepsy. The consultant attending to him believes that the seizure may be caused by a vitamin deficiency secondary to his chronic alcohol intake.
Which one of the following vitamin deficiency may have caused the seizure?
Vitamin B7
Vitamin B2
Vitamin B3
Vitamin B5
Vitamin B6 - Vitamin B6 (pyridoxine) is required for the synthesis of GABA


gastrin is secreted by G cells. which receptor does it bind to on parietal cells?
a) M3
b) CCK2
c) H2
d) somatostatin receptor
e) prostaglandin receptor
gastrin is secreted by G cells. which receptor does it bind to on parietal cells?
a) M3
* *b) CCK2**
c) H2
d) somatostatin receptor
e) prostaglandin receptor
interstilial cells of cajal are associated with a major influx of what?
a) Na+
b) K+
c) Ca2+
d) ACh
interstilial cells of cajal are associated with a major influx of what?
a) Na+
b) K+
* *c) Ca2+**
d) ACh
into SMC - contraction occurs (also Na)
Approximately 95% of people with celiac disease carry one particular MHC molecule. What is this?
HLA-DQ2
which nerve innervates the muscle that elevates the pharnyx during swallowing ?
a) trigeminal nerve
b) facial nerve
c) glossopharnyngeal
d) vagus nerve
e) hypoglossal
which nerve innervates the muscle that elevates the pharnyx during swallowing ?
a) trigeminal nerve
b) facial nerve
* *c) glossopharnyngeal - stylopharnygeus muscle**
d) vagus nerve
e) hypoglossal
What are the 3 divisions of the small intestine, and name a molecule that is commonly absorbed here? [3]
- Duodenum: iron
- Jejunum: main site of absorption
- Ileum: terminal ileum site of vitamin B12 absorption


This patient has a congenital absence of a muscle. Which action at the shoulder would be significantly weakened?
a) flexion
b) extension
c) abduction
d) external rotation
This patient has a congenital absence of a muscle. Which action at the shoulder would be significantly weakened?
- *a) flexion**
b) extension
c) abduction
d) external rotation
blunt trauma to peritoneum can be tear away from the which artery and cause internal bleeding?
- left gastric artery
- right gastric artery
- splenic artery
- common hepatic artery
- gastroduodenal artery
blunt trauma to peritoneum can be tear away from the which artery and cause internal bleeding?
- left gastric artery
- right gastric artery
- *- splenic artery - cuz spleen is intraperitoneal so moves lots**
- common hepatic artery
- gastroduodenal artery
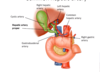
A 45-year-old woman was referred to gastroenterology to investigate unresolved dyspepsia. She has been receiving NSAID treatment to manage a flare-up of rheumatoid arthritis. Endoscopy reveals the presence of a gastric ulcer.
What has contributed to the endoscopy findings?
what is the correct label for this strucutre?
a) rotundudm foramen
b) manibular foramen
c) mental foramen
d) ovale foramen
e) hypoglossal foramen

what is the correct label for this strucutre?
a) rotundudm foramen
b) manibular foramen
* *c) mental foramen**
d) ovale foramen
e) hypoglossal foramen
An 8-year-old girl is brought to the physician due to developmental delay and seizure attacks since the age of 6. She presented with abnormal behaviour, ataxia, unusual laughing, intellectual disability, and mandibular prognathism. Genomic testing revealed a deletion in the 15q11-q13 chromosome. She was diagnosed with Angelman syndrome (AS). AS originates from the dysfunctional expression of the ubiquitin-protein ligase E3A gene on chromosome 15.
Which of the following cellular activities is most likely to be impaired?
Aerobic respiration
Catabolism of very long chain fatty acids and AAs
Folding of new proteins
Proteasomal degradation of proteins
Translation of RNA into proteins
An 8-year-old girl is brought to the physician due to developmental delay and seizure attacks since the age of 6. She presented with abnormal behaviour, ataxia, unusual laughing, intellectual disability, and mandibular prognathism. Genomic testing revealed a deletion in the 15q11-q13 chromosome. She was diagnosed with Angelman syndrome (AS). AS originates from the dysfunctional expression of the ubiquitin-protein ligase E3A gene on chromosome 15.
Which of the following cellular activities is most likely to be impaired?
Aerobic respiration
Catabolism of very long chain fatty acids and AAs
Folding of new proteins
Proteasomal degradation of proteins - Ubiquitin tagging destines proteins to proteasome for degradation
Translation of RNA into proteins
Which one of the peritoneal ligaments contains the tail of the pancreas?
Splenorenal ligament
Gastrosplenic ligament
Hepatoduodenal ligament
Hepatogastric ligament
Gastrocolic ligament
Falciform ligament
Which one of the peritoneal ligaments contains the tail of the pancreas?
Splenorenal ligament
Gastrosplenic ligament
Hepatoduodenal ligament
Hepatogastric ligament
Gastrocolic ligament
Falciform ligament
Which one of the following actions is directly caused by glucagon?
Vasoconstriction of vascular smooth muscle
Decreases osteoclastic activity
Inhibits insulin secretion
Decreases plasma phosphate
Increases glycogenolysis
Decreases renal reabsorption of phosphate
Which one of the following actions is directly caused by glucagon?
Vasoconstriction of vascular smooth muscle
Decreases osteoclastic activity
Inhibits insulin secretion
Decreases plasma phosphate
Increases glycogenolysis
Decreases renal reabsorption of phosphate
which of the following vitamins are antioxidants?
- vitamin A & C
- vitamin C only
- vitamin A & E
- vitamin A & C
- vitamin A, C & E
which of the following vitamins are antioxidants?
- vitamin A & C
- vitamin C only
- vitamin A & E
- vitamin A & C
- *- vitamin A, C & E**
A 12-year-old boy is being investigated for coeliac disease and has recently had biopsies of both the small and large intestinal linings.
In a normal biopsy, which of the following can be found in the lining of the small intestine but not in that of the large intestine?
Muscularis mucosae
Myenteric nerve plexus
Villi
Columnar epithelium
Goblet cells
A 12-year-old boy is being investigated for coeliac disease and has recently had biopsies of both the small and large intestinal linings.
In a normal biopsy, which of the following can be found in the lining of the small intestine but not in that of the large intestine?
Muscularis mucosae
Myenteric nerve plexus
Villi
Columnar epithelium
Goblet cells
the dorsal mesogastrium forms connections between which structures? [2]
dorsal mesogastrium forms connections between:
stomach & spleen [1]
spleen and posterior ab. wall [1]
which 3 regulatory systems regulate body fluid? [3]
hormonal (RAAS)
CNS (osmorecptors)
kindeys
name two source of endogenous free radicals [2]
mitochondria [1]
ER [1]
peroxisome [1]
An 18-year-old man is referred to the acute medical team with nausea and vomiting. He is a type 1 diabetic and has recently been unwell. Blood tests confirm diabetic ketoacidosis, and he is started on an insulin infusion.
What type of receptor does this treatment bind to?
Beta-1 receptors
GPRC
Guanylate cylase receptors
Ligand-gated ion channel receptors
Tyrosine kinase receptors
An 18-year-old man is referred to the acute medical team with nausea and vomiting. He is a type 1 diabetic and has recently been unwell. Blood tests confirm diabetic ketoacidosis, and he is started on an insulin infusion.
What type of receptor does this treatment bind to?
Beta-1 receptors
GPRC
Guanylate cylase receptors
Ligand-gated ion channel receptors
Tyrosine kinase receptors
Which of the following is not a catabolic pathway?
Glycolysis
TCA cycle
Glycogenolysis
Gluconeogenesis
Glycogenesis
Which of the following is not a catabolic pathway?
Glycolysis
TCA cycle
Glycogenolysis
Gluconeogenesis
Glycogenesis
Anabolic pathways build complex molecules from simpler ones and typically need an input of energy.
Catabolic pathways involve the degradation (or breakdown) of complex molecules into simpler ones. Molecular energy stored in the bonds of complex molecules is released in catabolic pathways and harvested in such a way that it can be used to produce ATP.
What is the cause of PKU, its genetic inheritance and how would you describe the condition to a patient (3 marks)
PKU is a condition which is caused a mutation on the enzyme phenylalanine hydroxylase (or insufficiency of tetrahydrobiopterin) [1]
therefore prevents conversion of phenylalanine into tyrosine. [1]
The condition is normally autosomal recessive, which means that two individuals need to be carriers in order to for their offspring to have PKU. [1]
what type of cells line stomach?
a. Squamous cell
b. Pseudostratified cell
c. Columnar cell
d. Cuboidal call
what type of cells line stomach?
a. Squamous cell
b. Pseudostratified cell
c.Columnar cell - simple columnar cells
d.Cuboidal call
which part of the manible serves as the muscle attachment point and moves the mandible?
a) coronoid process
b) neck
c) head
d) ramus
e) body
which part of the manible serves as the muscle attachment point and moves the mandible?
- *a) coronoid process**
b) neck
c) head
d) ramus
e) body
What is the rate controlling step of glycolysis? What factors decrease the activity? [1] increase the activity [1] of this step? [1]
Fructose-6-phosphate to Fructose-1,6-bisphosphate via the enzyme Phosphofructokinase-1.
Is regulated by:
- ATP:AMP ratio
- Citrate (decreases activity)
- Fructose-2,6-bisphosphate (increased activity)
A 56-year-old lady is due to undergo a left hemicolectomy for carcinoma of the splenic flexure. The surgeons decide to perform a high ligation of the inferior mesenteric vein. Into which of the following does this structure usually drain
Portal vein
IVC
Left renal vein
Left iliac vein
Splenic vein
A 56-year-old lady is due to undergo a left hemicolectomy for carcinoma of the splenic flexure. The surgeons decide to perform a high ligation of the inferior mesenteric vein. Into which of the following does this structure usually drain
Portal vein
IVC
Left renal vein
Left iliac vein
Splenic vein
which of the following is found in the stomach body?
a) parietal and chief cells
b) parietal and D cells & chief cells
c) mucous cells, D cells & chief cells
d) mucous cells and D cells & G cells
e) parietal cells, G cells & chief cells
which of the following is found in the stomach body?
a) parietal and chief cells
* *b) parietal and D cells & chief cells**
c) mucous cells, D cells & chief cells
d) mucous cells and D cells & G cells
e) parietal cells, G cells & chief cells
which antibody activates basophils and mast cells to make antimicrobrial factors
a) IgG
b) IgM
c) IgA
d) IgE
e) IgD
which antibody activates basophils and mast cells to make antimicrobrial factors
a) IgG
b) IgM
c) IgA
d) IgE
e) IgD
during ox. phosph H+ are pumped across the inner mitochondrial matrix at which complexes?
- complexes 1, 2 & 3
- complexes 1, 2 & 4
- complexes 1, 3, & 4
- complexes 2, 3 & 4
during ox. phosph H+ are pumped across the inner mitochondrial matrix at which complexes?
- complexes 1, 2 & 3
- complexes 1, 2 & 4
- *- complexes 1, 3, & 4**
- complexes 2, 3 & 4
what two things does HIF-1 cause to occur within cell [2]
expression of VEGF - induces angiogenesis
reduces expression of mitochondria
Where in the body is most angiotensin-converting-enzyme located?
Adrenal cortex
Liver
Lungs
Kidneyss
Pancreas
Where in the body is most angiotensin-converting-enzyme located?
Adrenal cortex
Liver
Lungs
Kidneyss
Pancreas
this indicates weakenss of which muscle?
a) serratus anterior
b) deltoid
c) trapezuis
d) latissimus dorsi

this indicates weakenss of which muscle?
a) serratus anterior
b) deltoid
c) trapezuis
d) latissimus dorsi
insulin is present as what form when it is not used / stored?
a) monomer
b) dimer
c) pentameter
d) hexamer
insulin is present as what form when it is not used / stored?
a) monomer
b) dimer
c) pentameter
* *d) hexamer**
when active: monomer


what do u find in the centre of villi? [4]
Each villus has a central core composed of:
one artery
one vein,
a strand of muscle
centrally located lymphatic capillary (lacteal)
Which one of the following types of epithelium lines the lumenal surface of the normal oesophagus?
Non keratinsed stratified squamous epithelium
Ciliated columnar epithelium
Keratinsed stratified squamous epithelium
Non ciliated columnar epithelium
None of the above
Which one of the following types of epithelium lines the lumenal surface of the normal oesophagus?
Non keratinsed stratified squamous epithelium
Ciliated columnar epithelium
Keratinsed stratified squamous epithelium
Non ciliated columnar epithelium
None of the above
Explain why the pH of a sprinter will be lower than that of the marathon runner after a race, with reference to the Cori cycle. [5]
- The sprinter uses anaerobic respiration to produce the required amount of ATP for his race.
- This involves the break down of glucose to pyruvate to produce a net of 2 ATP.
- This is converted into lactic acid to prevent entry into the TCA cycle, which ultimately requires oxygen.
- The lactic acid is sent to the liver via the blood, and hence, as an acid, lowers the pH.
- The lactic acid is converted back into glucose, at the cost of 6 ATP and is delivered back to the muscle.
which molecule coming into B langerhan cells in pancreas causes the secretion of insulin?
a) Na+
b) K+
c) ACh
d) Ca2+
e) Cl-
which molecule coming into B langerhan cells in pancreas causes the secretion of insulin?
a) Na+
b) K+
c) ACh
d) Ca2+
e) Cl-
which condition renders the body in a positive nitrogen balance?
endurance exercise
starvation
a car accident
pregnancy
which condition renders the body in a positive nitrogen balance?
endurance exercise
starvation
a car accident
pregnancy
the liver excretes excess cholesterol esters in which form? (1)
bile
Which one of the following structures will lie posterior to the epiploic foramen ?
hepatic artery
cystic duct
hepatic portal vein
greater omentum
SMA
IVC
Which one of the following structures will lie posterior to the epiploic foramen at this level?
hepatic artery
cystic duct
hepatic portal vein
greater omentum
SMA
IVC
The epiploic foramen has the following boundaries:
Anteriorly (in the free edge of the lesser omentum): Bile duct to the right, portal vein behind and hepatic artery to the left.
PosteriorlyInferior vena cava
Inferiorly1st part of the duodenum
SuperiorlyCaudate process of the liver
which of the following is found in the stomach antrum?
a) D cells and G cells
b) G cells and mucous cells
c) mucous cells, D cells & chief cells
d) mucous cells and D cells & G cells
e) D cells & G cells & chief cells
which of the following is found in the stomach antrum?
a) D cells and G cells
b) G cells and mucous cells
c) mucous cells, D cells & chief cells
* *d) mucous cells and D cells & G cells**
e) D cells & G cells & chief cells
which two hormones cause glycogen breakdown at the muscles?
- insulin and adrenaline
- adrenaline and glucagon
- adrenaline and calcium
- calcium and glucagon
- glucagon and insulin
which two hormones cause glycogen breakdown at the muscles?
- insulin and adrenaline
- adrenaline and glucagon
- *- adrenaline and calcium**
- calcium and glucagon
- glucagon and insulin
glucagon only works in liver !!
muscles of mastication are supplied by which nerve?
a) hypoglossal
b) glossopharyngeal
c) facial nerve
d) trigeminal nerve
e) vagus nerve
muscles of mastication are supplied by which nerve?
a) hypoglossal
b) glossopharyngeal
c) facial nerve
* *d) trigeminal nerve - V3 mandibular branch**
e) vagus nerve
where in GI tract most likely to find payers patches?
a) stomach
b) duodenum
c) jejunum
d) ileum
e) colon
where in GI tract most likely to find payers patches?
a) stomach
b) duodenum
c) jejunum
* *d) ileum**
e) colon
what divides the peritoneum into the supracolic and infracolic regions? [1]
the transverse mesocolon

which of the following would a clinical deficiency cause peripheral neuropathy?
vitamin A
vitamin D
vitamin E
vitamin K
which of the following would a clinical deficiency cause peripheral neuropathy?
vitamin A
vitamin D
vitamin E
vitamin K
which nerve is most as risk from this fracture
a) median
b) ulnar
c) radius
d) axillary

which nerve is most as risk from this fracture
- *a) median**
b) ulnar
c) radius
d) axillary
Which one of the following actions is directly caused by angiotensin II?
Promotes water reabsorption in the collecting ducts of the kidneys by the insertion of aquaporin-2 channels
Increases Na+ reabsorption in the renal distal tubule
Increases gut absorption of calcium
Increases gluconeogenesis
Vasoconstriction of vascular smooth muscle
Converts angiotensinogen to angiotensin I
Which one of the following actions is directly caused by angiotensin II?
Promotes water reabsorption in the collecting ducts of the kidneys by the insertion of aquaporin-2 channels
Increases Na+ reabsorption in the renal distal tubule
Increases gut absorption of calcium
Increases gluconeogenesis
Vasoconstriction of vascular smooth muscle
Converts angiotensinogen to angiotensin I
the adaptive reflex in the proximal part of the stomach causes what to be released?
a) Ach
b) CCK
c) NO
d) Ca2+
e) cAMP
the adaptive reflex in the proximal part of the stomach causes what to be released?
a) Ach
b) CCK
* *c) NO - causes relaxation of the stomach via ENS**
d) Ca2+
e) cAMP
A 73-year-old lady is admitted for a laparoscopic cholecystectomy. During her pre-operative assessment it is noted that she is receiving furosemide for the treatment of hypertension. Where is the site of action of this diuretic?
PCT
Descenidng loop of Henle
Ascending loop of Henle
DCT
CD
A 73-year-old lady is admitted for a laparoscopic cholecystectomy. During her pre-operative assessment it is noted that she is receiving furosemide for the treatment of hypertension. Where is the site of action of this diuretic?
PCT
Descending loop of Henle
Ascending loop of Henle
DCT
CD
MoA of urea cycle:
a) what is the rate determining step?
b) what are the two amino groups required? for it
c) what is the key regulating enzyme?
Rate controlling step:
o HCO3- + NH4+ –> carbamoyl phosphate (via enzyme carbamoyl phosphate synthase 1)
o Requires 2 ATP.
o Controlled allosterically by glutamate metabolite: N-acetyl glutamate - this is formed in an excess of glutamate, so drives urea cycle.
b) the two amino groups required from: aspartate (1) & ammonia (1)
essentially is a shuttle reaction of NH4 into from aspartate and ammonia into urea
hard palatine is made of which two bones?
a) maxilla and palatine
b) vomer and ethmoid
c) palatine and ethmoid
d) vomer and palatine
e) palatine and mandible
hard palatine is made of which two bones?
- *a) maxilla and palatine**
b) vomer and ethmoid
c) palatine and ethmoid
d) vomer and palatine
e) palatine and mandible
which of the following is not a primary retroperitoneal structure?
- aorta
- kidneys
- pancreas
- ureter
- anal canal
which of the following is not a primary retroperitoneal structure?
- aorta
- kidneys
- *- pancreas**
- ureter
- anal canal
which apoprotein, added by HDL to a chylomicron, means the chylomicron remnant can be taken up by the liver to deliver FA & cholesterol?
- Apo B48
- Apo B100
- Apo C2
- Apo E
- Apo B10
which apoprotein, added by HDL to a chylomicron, means the chylomicron remnant can be taken up by the liver to deliver FA & cholesterol?
- Apo B48
- Apo B100
- Apo C2
- *- Apo E**
- Apo B10
Which one of the following inhibits the secretion of insulin?
Adrenaline
Lipids
Gastrin
Arginine
Vagal cholinergic activty
Which one of the following inhibits the secretion of insulin?
Adrenaline
Lipids
Gastrin
Arginine
Vagal cholinergic activty
A 54-year-old woman is admitted with symptoms of a stroke, including difficulty speaking and vision changes. She was in a hair salon at the time and got a headache after having her hair washed.
Investigation shows a vertebral arterial dissection, which is thought to be caused by hyperextending her neck.
How does this blood vessel enter the cranial cavity?
carotid canal
foramen magnum
foramen ovale
foramane spinosum
jugular foramen
A 54-year-old woman is admitted with symptoms of a stroke, including difficulty speaking and vision changes. She was in a hair salon at the time and got a headache after having her hair washed.
Investigation shows a vertebral arterial dissection, which is thought to be caused by hyperextending her neck.
How does this blood vessel enter the cranial cavity?
carotid canal
foramen magnum
foramen ovale
foramane spinosum
jugular foramen
what effect does high levels of circulating T3 have on TSH? [1]
T3 inhibits pituitary release of TSH
which of the following is not a pancreatic enzyme?
- Pepsin
- Trypsinogen
- Chymotripsinogen
- Amylase
- Lipase
which of the following is not a pancreatic enzyme?
- *-Pepsin**
- Trypsinogen
- Chymotripsinogen
- Amylase
- Lipase
A 24-year-old woman presents to her general practitioner with a 7-month history of fatigue, abdominal cramping, and abdominal bloating. It is suspected that she may have coeliac disease and the following blood test result is obtained:
Tissue transglutaminase IgA+ve
Which of the following immune cells is responsible for the production of this result?
Eosinophils
Macrophages
Memory cells
Plasma cells
T cells
A 24-year-old woman presents to her general practitioner with a 7-month history of fatigue, abdominal cramping, and abdominal bloating. It is suspected that she may have coeliac disease and the following blood test result is obtained:
Tissue transglutaminase IgA+ve
Which of the following immune cells is responsible for the production of this result?
Eosinophils
Macrophages
Memory cells
Plasma cells
T cells
adaptations of endocrine organs? (3)
- high vasculature (bc secrete into blood)
- cells in the gland are very close to capillaries
- interact with own organ first e.g. in adrenal gland: hormones from cortex can see tissues in the medulla first -> to influence own response of organ
which cells in the stomach secrete pepsinogen?
a) mucous secreting cells
b) chief cells
c) parietal cells
d) D cell
e) G cells
which cells in the stomach secrete pepsinogen?
a) mucous secreting cells
b) chief cells
c) parietal cells
d) D cell
e) G cells
once food has passed into the duodenum, which three hormones are secreted by duodenum to inhibit gastric acid secretion? [3]
CCK
GIP - (gastric inhibitory protein)
Secretin
The soft palatine is supplied by which nerve?
a) facial nerve
b) trigeminal nerve
c) glossopharyngeal nerve
d) hypoglossal nerve
e) vagus nerve
The soft palatine is supplied by which nerve?
a) facial nerve
b) trigeminal nerve
c) glossopharyngeal nerve
d) hypoglossal nerve
* *e) vagus nerve**
which of the following have subnuclear granules?
- goblet cells
- paneth cells
- enteroendocrine cells
- m cells
which of the following have subnuclear granules?
- goblet cells
- paneth cells
- *- enteroendocrine cells**
- m cells
Explain the gene expression changes in HIF1a and VEGF seen after altitude training. Why is the baseline EPO expression higher in a marathon runner compared to sprint trainer, with reference to the TCA cycle. [3]
- HIF1: Hypoxia induced factor down regulates mitochondria, which require oxygen to produce ATP via the TCA cycle and are therefore less useful in hypoxic conditions. Promotes VEGF expression.
- VEGF: Increased vasculature and therefore oxygen supply, countering hypoxic conditions.
- EPO increases the number erythrocytes produced, causing a higher haematocrit and therefore higher oxygen binding capacity. This is necessary for the marathon runner who primarily uses the TCA cycle to produce ATP in aerobic conditions, which requires large amounts of oxygen.
•A patient is diagnosed with pernicious anemia. How will the vitamin B12 be administered to the patient and why? (2)
•Intramuscular injections of hydroxocobalamin because patient cannot release IF.
Explain how coeliac disease leads to diarrhoea?
•Chyme sits in intestinal lumen- has an osmotic effect and water is drawn out of epithelial cells into lumen à diarrhoea
A 61-year-old man undergoes a carotid endarterectomy after carotid artery stenosis was found in investigations following a TIA. When he wakes he has a hoarse voice, which is still present and has not improved after 72 hours. He has also been refusing food. On examination, his gag reflex is not present. A CT head is performed which shows no abnormalities.
What is the most likely cause of his symptoms?
- Facial nerve injury
- glossopharnygeal nerve injury
- hypoglossal nerve injury
- vagus nerve injury
- stroke
A 61-year-old man undergoes a carotid endarterectomy after carotid artery stenosis was found in investigations following a TIA. When he wakes he has a hoarse voice, which is still present and has not improved after 72 hours. He has also been refusing food. On examination, his gag reflex is not present. A CT head is performed which shows no abnormalities.
What is the most likely cause of his symptoms?
- Facial nerve injury
- glossopharnygeal nerve injury
- hypoglossal nerve injury
- vagus nerve injury
- stroke
All innervation for speech originates from the vagus (X) nerve so injuries to the vagus will cause speech problems
what are the origins for the following?
superior epigastric artery [1]
inferior epigastric artery [1]
- *internal thoracic artery** –> superior epigastric artery
- *external iliac artery** –> inferior epigastric artery
A 13-year-old female presents with painful muscle cramp associated with early fatigue and ‘red urine’ with strenuous exercise. Blood glucose and lactate levels are normal. She is diagnosed with glycogen storage disease type V (McArdle disease).
Which of the following enzymes is deficient in this patient?
Glucose-6-phosphatase
Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase
debranching enzyme
glycogen phosphorylase
GLucocerebroisdae
A 13-year-old female presents with painful muscle cramp associated with early fatigue and ‘red urine’ with strenuous exercise. Blood glucose and lactate levels are normal. She is diagnosed with glycogen storage disease type V (McArdle disease).
Which of the following enzymes is deficient in this patient?
Glucose-6-phosphatase
Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase
debranching enzyme
glycogen phosphorylase aka myophosphatase
GLucocerebroisdae
which is the active form of thyroid hormone?
- T1
- T2
- T3
- T4
- T5
which is the active form of thyroid hormone?
- T1
- T2
- T3 - T4
- T5
T4 = inactive T3 = active
A 35-year-old woman goes to her general practitioner complaining of epigastric pain which is worse after eating a takeaway or drinking alcohol. Upon further questioning, a nocturnal cough is also reported. A diagnosis of gastro-oesophageal reflux disorder (GORD) is made. Symptoms of this disorder are due to irritation caused by stomach acid (H+), released from cells under gastrin stimulation.
Which cell type is stimulated by this hormone?
G cells
Gastric chief cells
Gastric mucousal cells
Gastric parietal cells
Intinsic cells
A 35-year-old woman goes to her general practitioner complaining of epigastric pain which is worse after eating a takeaway or drinking alcohol. Upon further questioning, a nocturnal cough is also reported. A diagnosis of gastro-oesophageal reflux disorder (GORD) is made. Symptoms of this disorder are due to irritation caused by stomach acid (H+), released from cells under gastrin stimulation.
Which cell type is stimulated by this hormone?
G cells
Gastric chief cells
Gastric mucousal cells
Gastric parietal cells
Intinsic cells
With respect to the phosphorylation of glucose, which one of the following is most associated with glucokinase?
Not affected by insulin
Low capacity (low Vmax)
High affinity for glucose (low Km)
Inhibited by glucose-6-phosphate
When glucose levels are low helps sequester glucose in the tissues
When glucose levels are high helps store excessive glucose in the liver
With respect to the phosphorylation of glucose, which one of the following is most associated with glucokinase?
Not affected by insulin
Low capacity (low Vmax)
High affinity for glucose (low Km)
Inhibited by glucose-6-phosphate
When glucose levels are low helps sequester glucose in the tissues
When glucose levels are high helps store excessive glucose in the liver
GLUT4 is located in which 3 locations? [3]
GLUT4 is located in which 3 locations? [3]
- **adipose tissues
- liver**
- skeletal muscle
the motor supply to all of muscles of the tongue except the pataoglossus are innervated by?
a) glossopharnygeal
b) trigeminal
c) vagus nerve
d) hypoglossal
e) facial nerve
the motor supply to all of muscles of the tongue except the pataoglossus are innervated by?
a) glossopharnygeal
b) trigeminal
c) vagus nerve
* *d) hypoglossal**
e) facial nerve
where do u find paneth cells in the intestinal crpyts?

cytochrome C transfers electrons to oxygen at which complex in oxidative phosphorlyation?
a) complex 1
b) complex 2
c) complex 3
d) complex 4
cytochrome C transfers electrons to oxygen at which complex in oxidative phosphorlyation?
a) complex 1
b) complex 2
c) complex 3
* *d) complex 4**
the presence of which immune cell would signify significant oesphagitus?
macrophage
lymphocyte
plasma cell
neutrophil
eiosonophil
the presence of which immune cell would signify significant oesphagitus?
macrophage
lymphocyte
plasma cell
neutrophil
eiosonophil

which cells cause depolarisation to initiate stomach muscle contraction? [1]
interstitial cells of cajal
pepsinogen is activated by secretions from which cell?
mucous lining
stem
parietal
D cell
G cell
pepsinogen is activated by secretions from which cell?
mucous lining
stem
parietal: pepsinogen –> pepsin by HCl of parietal
D cell
G cell
IgA anti-gliadin, anti-tTG and anti-endomysial* (EMAs) are produced by which immune cell? [1]
B cells
which inflammatory cytokines are associated with CD?
IFN-γ
TNF-a
IL-1
IL-6
which inflammatory cytokines are associated with CD?
IFN-γ
TNF-a
IL-1
IL-6
what is the effect of increased citrate levels on the rate determing step of glycolysis? [1]
what is the effect of increased ADP / AMP levels on the rate determing step of glycolysis? [1]
what is the effect of increased citrate levels on the rate determing step of glycolysis? [1]
inhibits
what is the effect of increased ADP / AMP levels on the rate determing step of glycolysis? [1]
increases it


which of the following is the linear alba?
A
B
C
D
E
F

which of the following is the linear alba?
A
B
C
D
E
F
which of the following is the inguinal ligmanet?
A
B
C
D
E
F

which of the following is the inguinal ligmanet?
A
B
C
D
E
F
which of the following is the external oblique?
A
B
C
D
E
F

which of the following is the external oblique?
A
B
C
D
E
F
which of the following is the rectus abdominus?
A
B
C
D
E
F

which of the following is the rectus abdominus?
A
B
C
D
E
F
which of the following is the tendinous intersections?
A
B
C
D
E
F

which of the following is the tendinous intersections?
A
B
C
D
E
F
which artery becomes the inferior epigastric artery?
internal iliac artery
SMA
IMA
external iliac artery
lower intercosal arteries
which artery becomes the inferior epigastric artery?
internal iliac artery
SMA
IMA
external iliac artery
lower intercosal arteries
inability for cells to produce Acetyl CoA is produced by a deficiency in
vitamin B1
vitamin K
vitamin C
vitamin B2
vitamin B6
inability for cells to produce Acetyl CoA is produced by a deficiency in
vitamin B1
vitamin K
vitamin C
vitamin B2
vitamin B6
which muscle makes the UOS? [1]
cricopharyngeus
what are the two oesophageal sphincters? which one is an anatomical sphincter, which one is a physiological sphincter?
how do they make sure they are sphincters/
upper oesophageal sphincter: produced by skeletal muscle cricopharyngeus. anatomical sphincter
- *lower oesophageal sphincter:** looks the same as oesophagus. physiological sphincter. aided by:
a) acute angle of stomach enter
b) right curs of the diaphragm: pinch-cock effect

which part of small intestine is this? why? (2)


which part of small intestine is this? why? (2)


ID A-E

A = **rectus abdominis** B = **linea alba** C = **ASIS** D = **inguinal ligament** E = **tendinous intersection**

what is this muscle? [1]

geniohyoid
which of the following is foramen cecum of tongue?
A
B
C
D
E

which of the following is foramen cecum of tongue?
A
B
C
D
E
which of the following is foliate papillae?
A
B
C
D
E

which of the following is foliate papillae?
A
B
C
D
E
which of the following is lingual tonsil?
A
B
C
D
E

which of the following is lingual tonsil?
A
B
C
D
E
which of the following is vallate papillae?
A
B
C
D
E

which of the following is vallate papillae?
A
B
C
D
E
which of the following is the foramen cecum ?
A
B
C
D
E

which of the following is the foramen cecum ?
A
B
C
D
E
which hormone acts to counter hypocalcemia?
LH
T3
TSH
GnRH
PTH
which hormone acts to counter hypocalcemia?
LH
T3
TSH
GnRH
PTH (parathyroid hormone)
what is the overall net / gain or loss of ATP during glycolysis?
2 ATP gain
2 ATP loss
4 ATP gain
4 ATP loss
38 Gain
what is the overall net / gain or loss of ATP during glycolysis?
2 ATP gain
2 ATP loss
4 ATP gain
4 ATP loss
38 Gain
what is the overall net / gain or loss of ATP during cori cycle?
2 ATP gain
2 ATP loss
4 ATP gain
4 ATP loss
38 Gain
what is the overall net / gain or loss of ATP during cori cycle?
2 ATP gain
2 ATP loss
4 ATP gain
4 ATP loss
38 Gain
what is this bit?

ligamentum teres: inferior aspect of the falciform ligament

why are the peritoneal recesses of clinical importance?
- sites of collection of inflammatory fluid (may go undiagnose). inflammatory fluid can spread via epiploic foramen: peritonitis
which of the following is not a suprahyoid muscle?
Stylohyoid
Digastric
Sternohyoid
Geniohyoid
Mylohyoid
which of the following is not a suprahyoid muscle?
Stylohyoid
Digastric
Sternohyoid
Geniohyoid
Mylohyoid
which of the following is not an infrahyoid muscle?
Geniohyoid
Sternohyoid
Omohyoid
Sternothyroid
Thyrohyoid
which of the following is not an infrahyoid muscle?
Geniohyoid
Sternohyoid
Omohyoid
Sternothyroid
Thyrohyoid








label a-e


during ox. phosph H+ are pumped across the inner mitochondrial matrix at which complexes?
- complexes 1, 2 & 3
- complexes 1, 2 & 4
- complexes 1, 3, & 4
- complexes 2, 3 & 4
during ox. phosph H+ are pumped across the inner mitochondrial matrix at which complexes?
- complexes 1, 2 & 3
- complexes 1, 2 & 4
- *- complexes 1, 3, & 4**
- complexes 2, 3 & 4
The arterial branches from the superior mesenteric artery that supply the small intestine form arcades and have vasa recta (straight vessels) emanating from those arcades to the intestine itself.
The appearance of the arcades and vasa recta differs as the intestine progresses from jejunum to ileum. How?
jejunum: long vasa recta and fewer loops - A
ileum: larger arcades and vasa recta are shorter - B

The arterial branches from the superior mesenteric artery that supply the small intestine form arcades and have vasa recta (straight vessels) emanating from those arcades to the intestine itself.
The appearance of the arcades and vasa recta differs as the intestine progresses from jejunum to ileum. How?
jejunum: long vasa recta and fewer loops - A
ileum: larger arcades and vasa recta are shorter - B

which part of the gut is the appendix in?
foregut
midgut
hindgut
which part of the gut is the appendix in?
foregut
midgut
hindgut
Which nerve provides parasympathetic innervation to the hindgut?
Vagus nerve
pelvic splachnic nerves
pudendal nerve
phrenic nerce
Which nerve provides parasympathetic innervation to the hindgut?
Vagus nerve
pelvic splachnic nerves
pudendal nerve
phrenic nerce
identify the peritoeal folds indicated by the markers !

- falicform ligament
- greater omentum
what is the name of the artery outlined in green?

cysteic artery
what is the name of the artery outlined in green?

cysteic artery
which nerve provides sympathetic innervation to hindgut? [1]
lumbar splachnic nerve
absorption of amino acids through apical surface of intestinal cells occurs via?
faciliated diffusion
Na-linked secondary active transport
Ca-linked secondary active transport
Simple diffusion
Paracellular diffusion
absorption of amino acids through apical surface of intestinal cells occurs via?
faciliated diffusion
Na-linked secondary active transport
Ca-linked secondary active transport
Simple diffusion
Paracellular diffusion
absorption of amino acids through basolateral surface of intestinal cells occurs via?
faciliated diffusion
Na-linked secondary active transport
Ca-linked secondary active transport
Simple diffusion
Paracellular diffusion
absorption of amino acids through basolateral surface of intestinal cells occurs via?
faciliated diffusion
Na-linked secondary active transport
Ca-linked secondary active transport
Simple diffusion
Paracellular diffusion
which enzyme acts a sensor initiating production of insulin?
glucokinase
glycogen synthase
glycogen phosphorylase
PFK-1
PDH
which enzyme acts a sensor initiating production of insulin?
glucokinase
glycogen synthase
glycogen phosphorylase
PFK-1
PDH
Ach binds to which receptor on parietal cell to stimulate HCl production?
M1
M2
M3
H2
CCK2
Ach binds to which receptor on parietal cell to stimulate HCl production?
M1
M2
M3
H2
CCK2
what does Ca2+ binding to calmodulin in smooth muslce allow to occur? [2]
Ca2+ binding to calmodulin in smooth muscle allows it to interact with and activate myosin light chain kinase which catalyzes the phosphorylation of myosin.


