Anatomy SBAs Flashcards
Which of these is INCORRECT?
A.The glenohumeral joint is proximal to the elbow
B.The descending aorta is posterior to the pancreas
C.The heart is posterior to the body of the sternum
D.The parietal pleura is superficial to the thoracic cage
E.The splenic flexure is distal to the hepatic flexure
Which of these is INCORRECT?
A.The glenohumeral joint is proximal to the elbow
B.The descending aorta is posterior to the pancreas
C.The heart is posterior to the body of the sternum
D.The parietal pleura is superficial to the thoracic cage
E.The splenic flexure is distal to the hepatic flexure
A – Right Tibia
B – Left Tibia
C – Right Ulna
D – Left Ulna
E – Right Radius

A – Right Tibia
B – Left Tibia
C – Right Ulna
D – Left Ulna
E – Right Radius
medial malleolus:

A – Manubrium
B – Frontal bone
C – Sternum
D – Scapula
E - Tarsal
A – Manubrium
B – Frontal bone
C – Sternum
D – Scapula
E - Tarsal

What compartment is this and what are the actions of these muscles?
A – Anterior compartment, flexes hip, flexes
knee
B – Anterior compartment, flexes hip, extends knee
C – Posterior compartment, flexes hip, flexes knee
D – Posterior compartment, extends hip, flexes knee
E – Posterior compartments, extends hip, extends knee

What compartment is this and what are the actions of these muscles?
A – Anterior compartment, flexes hip, flexes
knee
B – Anterior compartment, flexes hip, extends knee
C – Posterior compartment, flexes hip, flexes knee
D – Posterior compartment, extends hip, flexes knee
E – Posterior compartments, extends hip, extends knee

What type of imaging of the brain can be seen here?
a) X-ray
b) MRI T/2
c) Ultrasound
d) CT Scan
e) PET scan

What type of imaging of the brain can be seen here?
a) X-ray
b) MRI T/2
c) Ultrasound
d) CT Scan
e) PET scan

What is A? (T7 section)
A.Right inferior lobe
B.Right posterior lobe
C.Right middle lobe
D.Left inferior lobe
E.Left middle lobe
F.Left superior lobe
G.Left anterior lobe

What is A? (T7 section)
A.Right inferior lobe
B.Right posterior lobe
C.Right middle lobe
D.Left inferior lobe
E.Left middle lobe
F.Left superior lobe
G.Left anterior lobe
What bone is this?
A.C1
B.C2
C.C4
D.C7
E.T2
F.T10
G.L1
H.L3
I.Sacrum
J.Coccyx

What bone is this?
A.C1
B.C2
C.C4
D.C7
E.T2
F.T10
G.L1
H.L3
I.Sacrum
J.Coccyx

What is segment number three?
A.Left Lumbar
B.Left Hypochondriac
C.Left Iliac
D.Left Inguinal
E.Left Lateral

What is segment number three?
A.Left Lumbar
B.Left Hypochondriac
C.Left Iliac
D.Left Inguinal
E.Left Lateral

Red arrow: visceral peritoneum,
yellow arrow: parietal peritoneum

A.Aorta
B.Oesophagus
C.Right atrium
D.Left ventricle
E.Left lung


uterus

popliteal artery

hepatic portal vein

A.Common iliac a.
B.Abdominal aorta
C.Internal iliac a.
D.Branch of internal iliac a.
E.Femoral a.


ovary
During thoracotomy, after the thymic remnants have been reflected, a structure can be noted crossing the midline from the left and emptying into the superior vena cava. What is this structure?
A.Left external jugular vein
B.Inferior vena cava
C.Left subclavian vein
D.Left brachiocephalic vein
e Left internal jugular vein
During thoracotomy, after the thymic remnants have been reflected, a structure can be noted crossing the midline from the left and emptying into the superior vena cava. What is this structure?
A.Left external jugular vein
B.Inferior vena cava
C.Left subclavian vein
D.Left brachiocephalic vein
Left internal jugular vein
What type of nerve fibres are in A?
A.Somatic
B.Parasympathetic
C.Sympathetic
D.Autonomic

What type of nerve fibres are in A?
A.Somatic
B.Parasympathetic
C.Sympathetic
D.Autonomic

A.Radial a.
B.Ulnar a.
C Palmar arch (deep

Identify A
A.Right atrium
B.Right ventricle
C.Left atrium
D.Left ventricle
E.Interventricular septum
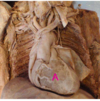
Identify A
A.Right atrium
B.Right ventricle
C.Left atrium
D.Left ventricle
E.Interventricular septum

what anatomical position does the pancreas have the stomach?
a) anterior
b) inferior
c) superior
d) posterior
what anatomical position does the pancreas have the stomach?
a) anterior
b) inferior
c) superior
d) posterior
What anatomical relationship does the greater omentum have to the stomach?
a) anterior
b) inferior
c) superior
d) posterior
What anatomical relationship does the greater omentum have to the stomach?
a) anterior
b) inferior
c) superior
d) posterior



