Histology Flashcards
what is the name of the ring that connects between tracheal cartilage? [1]
trachealis muscle
which part of the male reproductive system is this?
epididymis
tubulus rectus
vas deferens
efferent ductules

which part of the male reproductive system is this?
epididymis
tubulus rectus
vas deferens
efferent ductules: saw toothed !
which of the following is largest in veins?
tunica intima
tunica adventitia
tunica media
which of the following is largest in veins?
tunica intima
tunica adventitia
tunica media

what type of cell is A?
schwann cell
satellite cell
fibroblast
nerve axon
oligodendrocyte

what type of cell is A?
schwann cell
satellite cell
fibroblast
nerve axon
oligodendrocyte
what cells are the arrows pointing to?

osteoclasts !!
which type of gland is this?
Simple tubular
Simple coiled tubular glands
Simple branched tubular glands
Simple acinar glands
Simple branched acinar gland
Compound branched tubular gland
Compound acinar gland
Compound tubulo-acinar gland

which type of gland is this?
Simple tubular
Simple coiled tubular glands
Simple branched tubular glands
Simple acinar glands
Simple branched acinar gland
Compound branched tubular gland
Compound acinar gland
Compound tubulo-acinar gland

how does respiratory and olfactory epithelium differ? / how can you tell the difference? (2)
olfactory epithelium has pseudostrat thicker (but still not stratified)!!
AND
nerve fibres in olfactory lamina propria

what is the cellular layer highlighted called? [1]

periosteum
which type of gland is this?
Simple tubular
Simple coiled tubular glands
Simple branched tubular glands
Simple acinar glands
Simple branched acinar gland
Compound branched tubular gland
Compound acinar gland
Compound tubulo-acinar gland

which type of gland is this?
Simple tubular
Simple coiled tubular glands
Simple branched tubular glands
Simple acinar glands
Simple branched acinar gland
Compound branched tubular gland
Compound acinar gland
Compound tubulo-acinar gland

what is A?

melanocytes
at the end of each seminfierous tubule there is a transition to straight tubules (aka WHAT)? [1]
what is the histological change that occurs here? [1]
what do the tubules empty into? [1]
at the end of each seminfierous tubule there is a transition to straight tubules (aka WHAT)? [1] tubuli recti
what is the histological change that occurs here?
changes to simple cuboidal epi
what do the tubules empty into? [1]
rete testis

what type of cells line the nasal cavity respiratory system - respiratory mucosa?
what are the 3 different types?^
what is role? (2)
respiratory mucosa:
- ciliated, pseudostratified columnar epithelium
a) goblet cells - tall columnar cells producing mucous
b) brush cells - bear short microvilli
c) basal cells - stem cells
role:
warms, moistens and filters the inspired air

what do you find eitherside of the tunica media in muscular arteries? [2]
internal elastic lamina
tunica media
external elastic lamina

label A & B

A: Leydig cells
B: Reinke crystals
label A & B

A: osteoblasts
B: osteocytes
what cell type is this? [1]
brown adipose tissue
white adipose tissue
loose connective tisue
elastin
dense connective tissue

what cell type is this? [1]
brown adipose tissue
white adipose tissue
loose connective tisue
elastin
dense connective tissue
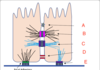
label A-E

A: epiphysis
B: centre of secondary ossification
C: epiphysial growth plate
D: diaphysis
E: cortical bone
what are the 4 layers of the epidermis?
basal layer: stratum basale
stratum spinosum
stratum granulosum
stratum corneum

what is D?
proteoglycans
fibroblasts
elastin
adipocytes
collagen

what is D?
proteoglycans
fibroblasts
elastin
adipocytes
collagen
which of the following allows heart muscle cells to contract more forcefully by synchronising calcium release from the sarcoplasmic reticulum throughout the cell
A
B
C
D
E

which of the following allows heart muscle cells to contract more forcefully by synchronising calcium release from the sarcoplasmic reticulum throughout the cell
A
B
C
D
E
which of the following are contain cadherins?
tight junction
desmosome
hemidesmosome
gap junction
which of the following are contain cadherins?
tight junction
desmosome
hemidesmosome
gap junction

Which histological landmarks of the sarcomere shrink when a muscle contracts? [3]
The I-band and the H-band decrease in size; [2]
the A-band remains the same.
what is this?

adipocytes
what is this highlighted?
basament membrane