Medical Microbiology - Intro Flashcards
True or False: All living organisms use DNA as their genetic material?
True
What are the three major groups of organisms?
Eubacteria
Archaebacteria (Archaea)
Eukarya (Eukaryotes)
True or False: Archaea are closer to Eucaryotes on the Tree of Life than Eubacteria are.
True; Archaea are much closer, evolutionarily, to Eucaryotes than are Eubacteria.
True or False; Viruses are the smalles infectious particles?
True
What is the genetic material of viruses?
Most viruses contain either DNA OR RNA; they typically do not contain both.
What is the exception to the rule that viruses usually contain DNA or RNA?
Mimivirus is the exception. This virus contains DNA and RNA.
It is a virus of amoeba.
It contains genes for nucleotide and amino acid synthesis.
It does not, however, contain genes for ribosomes.
What is a prion?
Prions are small particles that are composed of abnormally-folded proteins.
They cause disease by causing other proteins within the body to misfold and clump together in aggregates (plaques).
What are the characteristics of Eukaryotes?
Membrane-bound organelles
DNA contained within a nucleous
Linear DNA contained within multiple chromosomes
~20,000 genes
No cell wall
Large size as compared to bacteria and viruses
80S ribosome made up of 40S subunit and 60S subunit
What are the characteristics of Eubacteria (Prokaryotes)?
Lack membrane-bound organelles
DNA contained within a nucleopid region
DNA is circular chromosome
May contain circular plasmids (DNA) as well
Usually only one plasmid
1000-6000 genes
Has cytoplasmic inclusions (granuels)
Usually live independently
Small size as compared to Eukaryotes
Contain a cell membrane AND a peptidoglycan cell wall (Most contain cell walls)
70S ribosome made up of 30S subunit and 50S subunit
Do not reproduce sexually
How are bacteria characterized?
Shape
Size
Spatial arrangement
Gram + or -
Pathogenecity
Describe fungi.
Fungi are eukaryotes
Most have a cell wall that is made of chitin
Some are single celled (yeasts) and some are multi-cellular (molds)
Some can switch between being single and multicellular (Dimorphic); this is frequently determined by temperature
Fungi can reproduce both sexually and asexually; fungi are frequently characterized by their mode of reproduction
Describe parasites.
Can be unicellular (protozoans) or multicellular (worms, insects)
Some are obligate parasites
Others may have a free-living stage
What is an obligate parasite?
This is an organism that cannot complete its lifecycle without exploiting a suitable host.
Without the host, the parasite will not reproduce.
What is the size range of most viruses?
0.03 to 0.3 um
What is the size range of most bacteria?
0.1 to 10 um
What is the size range of most protozoa and fungi?
4 - 10 um
What are the mechanisms of host defense?
The immune system.
What are the characteristics of viruses?
Viruses have DNA or RNA as their genetic material (One exception: Mimivirus has both)
Obligate, intracellular parasite
Cannot reproduce outside of the cell
Have no organelles
Have a protein coat (Capsid) that helps to protect them from the environment
How many major shapes of bacteria are there?
Three:
Rods
Spiral
Cocci
True or False; Bacteria usually live independently.
True; bacteria can live in ‘bioflims’ with other bacteria however.
What are the three major parts of the bacterial cell and what are their functions?
Cell membrane: Carries out many biochemical / enzymatic reactions, participates in cell division, involved in ATP production via the electron transport chain, contains the enzymes for cell wall production.
Cell wall: Made up of peptidoglycan
Capsule: Slime layer. Protective layer surrounding bacterial cell.
What is the bacterial cell wall?
The bacterial cell wall is a semi-rigid layer of peptidoglycan that is outside of the cell membrane.
It helps the bacteria maintain shape, protects against lysis, determines Gram staining characteristics, and is a target for some antibiotics.
What do the shapes and arrangements of bacteria result from?
The shapes and arrangements of bacteria result from the cell wall and cell division.
What are the smallest bacterial cell types?
Mycoplasma and spiroplasma
What is the bacterial cell wall made of?
It is made up of a peptidoglycan layer (Murein layer)
This is a polymer of N-acetylglucosamine (NAG, GluNAc) and N-acetylmuramic acid (NAM, MurNAc)
How is the bacterial cell wall held together?
It is held together by beta 1,4 linkages between NAM and NAG
Four amino acids also attach to NAM and these help to provide more stability.
One set of amino acids is cross-linked to another set. This leads some bacteria to have peptide bridges in the peptiodglycan cell layer and this is the target of penicillins.
What form of amino acids do bacteria use?
D form
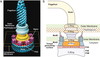
Image of gram + and gram - cell walls.

Second image of gram + and gram - cell walls.

Third image of gram + and gram - cell walls.

What are the characteristics of Gram + bacteria?
- cytoplasmic lipid membrane
- thick peptidoglycan layer
- teichoic acids and lipoids are present, forming lipoteichoic acids, which serve as adherence factors.
- capsule polysaccharides (only in some species)
-
flagellum (only in some species)
- if present, it contains two rings for support as opposed to four in Gram-negative bacteria because Gram-positive bacteria have only one membrane layer.
What are the characteristics of Gram - bacteria?
- Cytoplasmic membrane
- Thin peptidoglycan layer (which is much thicker in gram-positive bacteria)
- Outer membrane containing lipopolysaccharide (LPS, which consists of lipid A, core polysaccharide, and O antigen) in its outer leaflet and phospholipids in the inner leaflet
- Porins exist in the outer membrane, which act like pores for particular molecules
- There is a space between the layers of peptidoglycan and the secondary cell membrane called the periplasmic space
- If present, flagella have four supporting rings instead of two
- No teichoic acids or lipoteichoic acids are present
- Lipoproteins are attached to the polysaccharide backbone.
- Most do not form spores.
What is Lipid A?
Lipid A is found in Gram - bacterial cells
It is in the outtermembrane
It has very potent endotoxin activity