Med-Pscyh Flashcards
What is the CAM score and describe its criteria
CAM score = Diagnosis Delirium and differentiates it from Dementia/Depression
AIDA: Requires A and I, but only either D vs. A
Acute onset and fluctuating
Inattention (spell “world” backwards & forward)
Disorganized thinking (rambling/illogical)
Altered level of consciousness (intermittently not alert?)

S/S of Alcohol Withdrawal -10
these sx PEAK during 2nd day of abstinence and resolve by day 5
PAST NITE
Psychomotor agitation
Anxiety
Seizures
Tremor & DELIRIUM TREMENS
NV
Insomnia & Irritability
Transient Hallcuinations
Excitable autonomics (⬆︎HR, BP)
Describe Delirium Tremens-5 ; when does DT onset?
Further progression of Excitable autnomics =
- ⬆︎ HR
- ⬆︎ BP
- Fever
- Hallucinations
- Tremulousness –> Death
Onsets 2 days post last EtOH (when withdrawal sx peak)
lab w/u for suspected substance abuse-5
- Serum Drug Screen
- Serum AAA (APAP/ASA/Alcohol)
- Urine Drug Screen
- UA
- ABG
Name 5 major Risk Factors of Altered Mental Status
- Dementia
- Age
- Substance Abuse
- Physical issues (Sleep loss/Immobility/Dehydration/Pain)
- ICU
Main cause of Delirium in Hospitalized Elderly
MULTIFACTORIAL
(Urinary Catheters/Restraints/Poor Sleep/Constipation/Malnutrition)
What are Non-Rx ways to ⬇︎Agitation in Delirius pts -5
- DC Delirum-causing meds (Benzo, Benadryl)
- No restraints
- Normalize Sleep
- Reorientation (Write Date on message board)
- Correct Derangements (dehydration, metabolic)
Developmental Milestones for a 1 Year Old
Gross Motor - 3
Fine Motor
Language
Social & Cognition - 2

Developmental Milestones for a 18 Month Old
Gross Motor - 2
Fine Motor - 2
Language - 2
Social & Cognition - 2

Developmental Milestones for a 2 Year Old
Gross Motor - 2
Fine Motor - 2
Language - 2
Social & Cognition - 3

Developmental Milestones for a 3 Year Old
Gross Motor - 2
Fine Motor - 2
Language - 2
Social & Cognition - 2

Developmental Milestones for a 4 Year Old
Gross Motor - 1
Fine Motor - 1
Language - 2
Social & Cognition - 1
Get Audiologic testing in kids with Language Delay!

Developmental Milestones for a 5 Year Old
Gross Motor - 2
Fine Motor - 4
Language - 2
Social & Cognition - 2
Get Audiologic testing in Kids with Language Delay!

Autism usually presents by age ____
What is the CP?-3
EAAARRRLY intervention for Autism is the KEY!
Presents by age 2
- Social Communication deficit (limited language/eye contact, plays alone,poor pickup of social cues)
- Repetitive Behavior (rocking, hand flipping)
- Fixated Interest (insist on same routines, 1-sided convos on fixated topics)
- Autism is +/- language or intellectual impairment*
- Also, consider Fragile X syndrome testing*
How do Older Adults typically present with Depression?
With c/o somatic complaints (i.e. sleeping problems) instead of mood changes
For Bipolar Mania dx, you need at least [__ sx +/- ___] that last for ___ duration. What are the sx? (7)
[3 sx +/- major depression]; 1 week duration;
BIPOLAR
Buying excessively (⬆︎ in pleasurable activity)
Inflated self-esteem
Psychomotor agitation (pacing)
wide awOke - won’t sleep
Lots of talking
ADD like distractability
Racing thoughts
Tx for Delirium in Elderly - 3
Haloperidol vs Risperidone vs Quetiapine
Note: Do NOT use Haloperidol in DLB (Dementia with Lewy Bodies)
What is the diagnositic criteria for Major Depression DO? - 3
- At least 5 out of 9 of SIG E CAPS for
- ≥2 weeks
- At least 1 must be Sadness or Interest loss anhedonia

The diagnositic criteria for Major Depression DO assess for 9 major sx
What are they?
SIG E CAPS
Sadness most of day/everyday
Interest loss anhedonia most of day/everyday
Guilt & worthlessness
Energy deprived & fatigued
Concentration loss
Appetite ⬇︎
Psychomotor agitation/retardation observable by others
Sleep ∆ (insomnia vs Hypersomnia)
Suicidal ideation (thinking about it but haven’t acted yet)
What is CAGE and how is it interpreted?
CAGE = Determines EtOH abuse; ≥ 2 positive answers = EtOH abuse/dependence and 1 positive answer warrants further eval
- ever tried to Cut back on drinking?
- Angry when someone criticizes ur drinking?
- Guilty about how much you drink?
- need an Eye opener in morning to prevent withdrawal/calm nerves?
Clinical criteria for diagnosing PMS (PreMenstrualSyndrome)
At least 5 sx TOTAL (from Group A and B) beginning 1 week before menses but resolving during follicular phase of menses
If sx occur irregularly or throughout menses = mood or personality DO
Clinical criteria for diagnosing PMS (PreMenstrualSyndrome) relies on sx from Group A and Group B
Describe sx for Group A - 6
At least 5 sx (from Group A and B) began 1 week before menses, improve during menses and resolve during week after menses
A: (at least one)
- Mood lability
- irritability
- depression
- hopelessness
- anxiety
- ⬇︎libido
Clinical criteria for diagnosing PMS (PreMenstrualSyndrome) relies on sx from Group A and Group B
Describe Group B sx - 6
At least 5 sx (from Group A and B) began 1 week before menses, improve during menses and resolve during week after menses
B: (at least one)
- Food cravings
- sleep change
- feeling “out of control”
- ⬇︎energy
- Anhedonia
- Physical sx (constipation/diarrhea/breast TTP/HA)
Tx for Premenstrual syndrome - 4
- Menstrual Diary (determines relationship of sx to menses)
- Exercise
- Stress Reduction
- SSRIs **if severe**
Why should Haloperidol be CAUTIOUSLY given to Alcoholics
Haloperidol ⬇︎Seizure threshold and alcoholics going thru withdrawal may already be at risk for seizures!
Describe the clinical features of OCD - 2
- Obsessions (w/symmetry, contamination, taboo urges like killing, fear of arm)
- Compulsions (rituals-that may be used to help combat obsessions)
tx = high dose SSRIs + exposure CBT
OCD tx - 2
[High Dose SSRIs] + [exposure CBT]
Indication for Deep Brain stimulation ; what part of the brain is targeted
[SEVERE, tx-refractory OCD]; nucleus accumbens
Ebstein’s anomaly etx
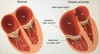
Maternal lithium use during [1st trimester pregnancy] –> malformation and displacement of tricuspid valve into R Vt –> Tricuspid Regurgitation –> R Atrial Enlargement and R Axis deviation –> HEART FAILURE
What kinds of teratogenic effects are you concerned about if Lithium is taken during 2nd and 3rd trimester pregnancy? -2
- Goiter formation
- Transient Neonatal Neuromuscular dysfunction
Ebsteins anomaly is concern for 1st trimester only
Diagnostic criteria for Nightmare Disorder - 3
- Recurrent episodes of waking from sleep with ability to reMember dream
- Child is fully alert on awakening
- Child can be consoled
NightMares occur during REM and is developmentally normal for kids
What is the difference between Sleep Terrors and Nightmare Disorder? - 4
Sleep terrors are :
- NON-REM disorder
- with incomplete awakenings
- and can NOT be consoled
- and pt Seems to forget the dream
What is REM sleep behavior disorder?
Complex motor behaviors or vocalization during REM
Diagnostic criteria for Schizoaffective Disorder - 4
SchizoAffective is weird so
Do Not Miss Diagnosis!
- Depressive or Manic “moody” episodes concurrent with schizophrenia criteria A sx
- NOT 2/2 substances or med condition
- Mood episodes are present most of the time
- ****Delusions or Hallucinations lasting ≥ 2 weeks in the absence of Mood episodes****
“I’m not feeling depressed for the first time in years, but the voices just won’t go away”

Key features for Schizoid personality disorder - 3
SchiZOID are DULL
- Detached
- Unemotional
- LLONERS that are content with being alone!!!!
Key features for SchizoTypal personality disorder
SchizoTypal have magical Thinking
magial Thinking / eccentric / odd behavior
Difference between Avoidant disorder and SchizoiD disorder
Avoidant DO = PERVASIVELY avoids people only due to fears of REJECTION or scrutiny (pts don’t want or like this = egoDystonic)
vs.
SchizoiD DO = avoidance that these pts are perfectly content with = egoSyntonic
In psychiatry, what is splitting? Which demographic is commonly seen in
Splitting people into either all good, or all bad; Borderline PD (PESSP)
Key features for Borderline personality disorder - 5
PESSP
- Pervasive Instability
- Emptiness & fears of abandonment –> ⬆︎suicide
- Self-defeating behavior
- Splitting is common (people are either good or bad)
- Paranoid when stressed
these pts usually have hx of child abuse, will react to stressors with rage and manipulative behavior and tx = DBT only
Delusional PD involves ≥ __ delusion for ≥ ___ months, with no other sx
Describe the subtype Erotomaniac delusional PD
≥1 delusion for ≥1 month
Erotomaniac = pt attempts to contact the object of delusion (usually –> legal problems)
What is the Function and Dz associated with the [MesocorticalLimbic dopaminergic system]
Regulates Behavior ; Schizophrenia
What is the Function and Dz associated with the [Nigrostriatal dopaminergic system]
Voluntary mvmnt coordination ; Parkinsonism
What is the Function of the [Tuberoinfundibular dopaminergic system]? ; What disease occurs when it is blocked by antipsychotics?
INHIBITS Prolactin Secretion ; Hyperprolactinemia–> infertility
This occurs mostly with FIRST generation antipsychotics
Psych pts who’ve taken [D2 R Blockers] chronically may develop EPS
Why would abrupt discontinue of [D2 R Blockers] –> worsening of EPS sx?
Chornic blockade of D2 Receptors –> ⬆︎D2 receptors and sensitivity. With abrupt [D2 R blocker] d/c, these receptors are over stimulated even with low dopamine levels –> Exaggerated EPS
EPS = TADD sx
Serotonin Syndrome Clinical Presentation (8)
“Serotonin gave me the SHIVERS!”
Shivering
[Hyperreflexia & Myoclonus]
INC Temp
[Vital sign instability] (tachycardia vs. tachypnea vs. HTN)
Encephalopathy (Confusion vs. Agitation)
Restlessness
Sweating
Italicized = Triad Sx
How do you treat Refractory Serotonin Syndrome
Cyproheptadine
(antihistamine with anti-serotonergic properties)
Describe Neuroleptic Malignant Syndrome
RARE SE of Any Dopamine Blocker (Antipsychotics vs. GI meds) that –> FEVER
- [Fever > 40C]
- Encephalopathy (Confusion)
- Vitals unstable (INC HR / RR / BP from autonomic dysfunction)
- Enzymes CreaTine and WBC ⬆︎
- Rigitidy ⬆︎ (Tremor)
Tx = supportive, dantrolene, [dopamine agonist if refractory]
What’s the best way to approach treatment for [Neuroleptic Malignant Syndrome] - 3
Treat Rigiditiy with Dantrolene (inhibits Ca+ release from sk. muscle sarcoplasmic reticulum)
+
supportive care
followed by [Bromocriptine or Amantadine] dopamine agonist if refractory
What is the diagnostic criteria for ADHD? - 3
- Sx present for at least 6 mo. AND inappropriate for dvpmental age
- Sx start between 6-12 yo and not after 12 yo
- Evident in 2 or more settings (school/work/home)
And Obvi, ALL psych disorders MUST be functionally impairing, NOT 2/2 medical condition and/or cause significant distress
Diagnostic criteria for Cyclothymic disorder - 3
- Chronic flutuating mood (depression vs bipolar) disturbance
- lasting ≥ 2 years
- and does not meet full criteria for hypomanic or depressive episodes
What is the clinical criteria for hypomanic episodes
- Elevated or irritable mood 4< x <7 days PLUS
- ≥3 Classic BIPOLAR sx

Diagnostic criteria for Bipolar II ? - 3
- Major Depressive Episodes +
- hypomanic episode +
- NOT functionally impairing
What is the clinical criteria for Manic episodes
- Elevated or irritable mood ≥ 7 days PLUS
- ≥3 Classic BIPOLAR sx

Diagnostic criteria for Bipolar I ? - 3
- Major Depressive Episodes +
- Manic episode +
- Functionally impairing
What is the difference between Acute Stress Disorder and PTSD?
ASD is ACUTE! which = [3 days ≤ sx ≤ 1 month] post exposure
vs
PTSD = sx > 1 month
Diagnostic criteria for Panic disorder - 2
- Panic attacks +
- Persistent concern about additional attacks and +/- attempts to avoid them
Be sure to r/u medical conditions that mimic them
Describe Advanced sleep phase syndrome
This is a Circadian rhythm disorder
circadian rhythm DO in which you can not stay awake past 7 pm –> early morning insomnia
Diagnostic criteria for Delayed sleep phase syndrome - 4
This is a Circadian rhythm disorder
AKA “The Night Owls”
- inability to fall asleep at “normal” bedtimes
- Difficulty waking in morning
- Excessive early daytime sleepiness
- Normal sleep ONLY WHEN ALLOWED TO SET OWN UR SLEEP SCHEDULE with later bedtimes
Diagnostic criteria for Persistent Depressive Dysthymia disorder - 3
- at least 2 / 6 of sigeca
- CONSTANT for ≥ 2 years (or 1 year in kids)
- No relief > 2 mo

Major Depressive Episodes may also occur with this
Clozapine’s SE is agranulocytosis
Name the Granulocytes - 3
BEN
Basophils
Eosinophils
Neutrophils
Clozapine also causes Metabolic Syndrome X, Seizures and Myocarditis
Which test are routinely (q3-6 mo) done in Lithium patients?-2 why?
Thyroid function test: monitor for hypothyroidism
Creatinine: monitor renal function
Diagnostic criteria for Adjustment disorder with depressed mood - 4
- [≤ 4 SIGeCAPSS s/s] within 3 mo. of acute stressor that –>
- functionally impairing
- and resolves within 6 mo. after stressor ends
- NOT 2/2 an other more specific disorder

Tx = CBT
Postpartum depression affects women during what time periods? What 2 methods are used to screen for this?
within 1st year > first 3 mo ;
- [PHQ2 –(if both +)–> PHQ9]
- Edinburgh Postnatal Depression Scale
Screen prenatal, postnatal and well child
Give brief descriptions that differentiate Postpartum
Blues vs Depression vs Psychosis
- Blues = onsets right after birth, peaking at postpartum day 5 and subsiding PPD14, worst w/lactation
- Depression = onset right after birth - 12 months later. Traditional s/s. Previous Depression hx is RF
- Psychosis = RARE but onsets IMMEDIATELY after birth

Tx for Delirium
Short course of PO haloperidol
alternatives: Aripiprazole/Olanzapine/Risperidone
What would you expect diagnostic appearance of a Major Depression pt to be - 3
- ⬇︎Body wt
- poor grooming
- poor hygiene
What would you expect diagnostic appearance of an Anorexia Nervosa pt to be - 3
- ⬇︎Body wt
- baggy clothes
- Lanugo -image

What is echopraxia
repetitive imitation of mvmnts of another person
EchoLALIA = repetitve imitation of verbiage of another person
What is sterotyping
isolated purposeless mvmnt performed reptitively
What is alexithymia
Pt can NOT describe their mood
What is pressured speech? ; Which pt mental illness exhibit this?
ABC (S)TAMP LICKER
rapid and difficult to interrupt (verbally runs you over!) ; Mania
Describe referential delusions
random events are of some special significance
“the Cubs won, so that’s a signal the alien invasion is coming!”
What is the diagnostic clinical criteria for Panic Disorder/Specificier? - 3
DSM5 no longer considers this its own DO but now as a Specifier for other conditions
- Recurrent Panic Attacks
- Unexpected Panic Attacks
- At least 1 attack is followed by ≥1 mo. of 1 or both of below:
- persistent worry of having another panic attack
- huge behavior changes to try and avoid future panic attacks
4. ≥ 4 of Panic Specifier symptoms - image - And obvs can’t be 2/2 drugs or other condition*

What is formication
feeling bugs crawling under skin
common in Cocaine and Meth users!! lol
What is hallucinosis
pt knows their hallucinations aren’t real
Common in Alcoholics
What is the diagnostic clinical criteria for Agoraphobia? - 3
- Fear & Avoidance OOP of ≥ 2 / 5 agora situations - image
- Fear & Avoidance OOP are > 6 months
- Fear & Avoidance OOP –> distress and functional impairment

OOP = Out Of Proportion
What is the diagnostic clinical criteria for Generalized Anxiety Disorder? - 2
- Excessive anxiety includes ≥ 3 / 6 of anxiety sx - WATCHERS
- Sx ≥ 6 months

- Excessive anxiety –> distress and functional impairment*
- OOP = Out Of Proportion*
What is the diagnostic clinical criteria for PTSD? - 3
Lifetime prevalence = 8% and more common in Women
- All 4 sx categorymet - image
- sx > 1 month
- Exposure done via Direct (single or repeated), Witnessed, occurred to close fam/friend

What is the diagnostic clinical criteria for Acute Stress Disorder? - 3
image

Risk factors for developing PTSD? - 7
Lifetime prevalence = 8% and more common in Women
- Substance abuse
- Violence, Mood or Anxiety med hx (self or family)
- Suicidal Ideation/attempts
- Work or Marriage problems
- Homelessness
- Prior trauma
- Female

Demographic for Panic Disorder - 2 ; What is this group at risk for?
Women in the late teens/early 20s ; Death from Stroke vs MI
Usually Occurs with MDD/GAD/OCD
Tx for Panic Disorder - 6
CBT (can be used alone)(breathing technique, exposure therapy) +/-
- SSRI (1st line rx)
- SNRIs
- [Benzo or BBlocker for situational]
- TCA
- MAOi
* Similar to Social Phobic Anxiety Disorder tx*
Diagnostic clinical criteria for Specific Phobia - 2 ; Tx?
- Specific things (objects/locations/events) provoke IMMEDIATE fear/anxiety OOP –> active avoidance
- sx ≥ 6 mo
Tx = CBT Exposure Therapy (ONLY USE BENZOS IF CBT IS UNAVAILABLE)







