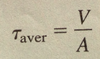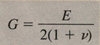Mechanics; Chapter 1 Flashcards
(63 cards)
Define the Term “Free Body Diagram”
A sketch of the structure, removed from it’s supports, showing all dimensions, applied forces, and reactions.
Chapter 1
Define a “brittle material”-
A material that fractures w/o significant strain such that there is no noticeable deflection before fracture occurs.
Chapter 1
Define the term “stiffness”-
Stiffness is the force required to cause a unit displacement in a linear elastic member. (K=P/δ)
Chapter 1
Define the term “Flexibilty”-
Flexibility is the amount of deformation caused by a unit force in a linear elastic member.
Chapter 1
Define a “determinate” structure-
A Determinate Structure is one that has the same number of unknown reactions as the number of applicable equations of static equilibrium.
Chapter 1
Greek Alphabet

Chapter 1
Define Prismatic Bar
A straight structural member having the same cross section throughout its length.
Chapter 1
Define Axial Force
A load directed along the axis of a member, resulting in either tension or compression in the member.
Chapter 1
Define Cross Section
A section taken perpendicular to the longitudinal axis of a member.
Chapter 1
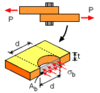
Define Stress (Mechanics of Material)
Intensity of a force (Force per unit Area); Denoted by the greek letter Sigma (σ)
Mechanics of Materials
Define Normal Stress
Stress that act in a direction perpendicular to the cut surface.
σ=P/A
σ= Normal Stress;
P= Axial force;
A= cross-sectional area

Chapter 1
Mechanics of Material; Because normal strain is a ratio of 2 lengths, it is a _____ ______.
Dimensionless quantity
Chapter 1
Sign Convention for Tensile Stress & Compressive Stress
Tensile Stress= Positive Compressive Stress= Negative
Chapter 1
Normal Strain equation-
Elongation per unit length-
ε= δ/L; Epsilon=Delta/Original Length
ε = ΔL/L
Chapter 1
The elongation of the bar is assumed normal, or perpendicular, to the cross section.
Normal Strain (Continued)
Chapter 1
A _____ is a device that is used to measure changes in lengths of an object. Is is useful for the stress/strain measurements & tensile test.
Extensometer

Mechanics
The ASTM standard tension specimen has a diameter of ___ in. and a gage length of ___ in. between the gage Marks, which are the points where the extensometer arms are attached to the specimen.
.505 inch
2 inch.

Chapter 1
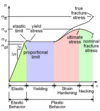
The ______ ______ is the point where the material changes from linear to non-linear on the stress/strain diagram.
proportional limit
Chapter 1
Explain Stress Strain Diagram
Elastic Range; Yielding; Strain Hardening; Necking
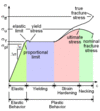
Chapter 1
Explain how the Equation of a line is used in Mechanics of Material
y = mx + b ;
y = how far up;
x = how far along;
m=Slope (Rise/Run);
b = the Y Intercept (where the line crosses the Y axis).
This equation can be substituted into the stress/strain diagram to solve problems. σ = E * ε + B
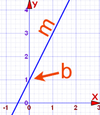
Chapter 1
Define a Ductile Material
Metals such as structural steel that undergo large permanent strains before failure.
Chapter 1
Structural Steel is also know as-
Mild Steel Low-Carbon Steel
Chapter 1
When a material such as aluminum does not have an obvious yield point and yet undergoes large strains after the proportion limit is exceeded, and arbitrary yield stress may be determined by the _____ _____.
offset method

Chapter 1
For the offset method, a straight line is drawn on the stress-strain diagram parallel to the initial linear part of the curve, but offset by some standard strain, such as _____ of (___%)
.002 2%