Male and female reproductive tract histology Flashcards
(80 cards)
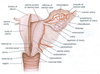
What is the ovary attached to?
What is anchored by?
Posterior face of broad ligament
Anchored by ovarian ligament (to uterus) and suspensory ligament (to pelvic wall)
How is the internal structure of the ovary divided?
Inner medulla (loose connective tissue and blood vessels)
Outer cortex (ovarian follicles)
In which part of the ovary are the follicles found?
Outer cortex
Describe the cortical stroma of the ovary?
Highly cellular connective tissue
Scattered with smooth muscle cells
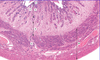
Which organ is this?

Ovary
Describe the surface epithelium of the ovary?
Simple squamous or cuboidal
Continuous with mesothelium
Tunica albuginea beneath it
70% ovarian tumours arise here

Describe the tunica albuginea of the ovary?
Beneath the surface epithelium
Dense connective tissue
Oocytes deep to it
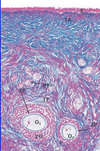
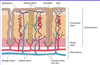
What are primordial oocytes?
Smallest oocytes
Arrested in prophase of meiosis 1
Squamous follicle cells on outside, surrounded by common basal lamina
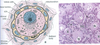
What are primary oocytes?
Oocyte surrounded by zona pellucida (within follicle cell layer)
Enlarged
Follicular cells become cuboidal and multilayered granulosa cells
Stromal cells start to form theca interna and externa
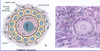
Which cells form the stratum granulosum in the primary oocyte?
Follicular cells
Which cells form the theca interna and externa in the primary oocyte?
Stromal cells
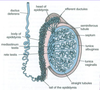
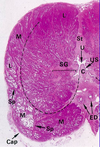
What is a secondary follicle?
Stratum granulosum thickened
Antrum appears
Cumulus oophorus: stalk of granulosa cells that suspend oocyte
Corona radiata formed by granulosa cells around oocyte after release

What is the cumulus oophorus?
Stalk of granulosa cells that suspend oocyte in secondary follicle
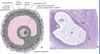
What is the corona radiata?
Granulosa cells around oocyte form corona radiata after release

What is a Graafian follicle?
Mature follicle
When does the oocyte complete its first meiotic division?
Under LH surge
When does the primary oocyte become a secondary oocyte?
When it completes its first meiotic division after the LH surge
What happens after the secondary oocyte is formed?
Follicle ruptures > oocyte released into body cavity > uterine tubes > corpus luteum formed
What is the corpus luteum formed from?
Follicle that has lost its oocyte
Describe the corpus luteum?
Stromal, granulosa and thecal cells invade cavity to differentitate into luteal cells
Contain lipid and become vascularised

What is the function of the corpus luteum?
Produces progesterone and oestrogen to prepare endometrium for implantation
How long does the corpus luteum last for?
14 days without fertilisation
No fertilisation > regresses to form corpus albicans
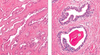
Which important processes occur in the uterine tubes?
Collects released oocytes
Fertilisation and initial development
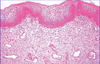
Describe the structure of the uterine tubes?
Serosa: mesothelium plus thin connective tissue
Muscularis: smooth muscle
Mucosa: connective tissue plus epithelium