Breast pathology Flashcards
What does the incidence of breast tumour malignancy rise with?
Age

Are breast lesions in young females usually benign or malignant?
Benign
Describe the histology of breast tissue?
Modified sweat gland
Background of adipose and connective tissue
Many ducts (15-25) that lead to nipple - branch repeatedly in stroma > terminal part of duct leads into lobule
Lobule composed of numerous acini

Describe the histology of the acini?
Inner secretory layer
Outer myoepithelial layer

Where do most breast lesions arise from?
Epithelium of terminal duct lobular unit
Describe the possible clinical presentations of a breast lesion?
Lump
General lumpiness
Pain
Nipple changes
Nipple discharge
Change in shape
Skin changes
Describe fibrocystic change of the breast?
Very common, usually in later reproductive years
Bilateral, multifocal
Duct dilation
Cyst formation
Fibrosis
Adenosis
Apocrine metaplasia (epithelial cells become pink and granular)
May be asymptomatic or produce lumps and discomfort

Describe the investigations that should be carried out when a possible breast lesion is present?
Clinical history and examination
Radiology: US and/or mammography
Biopsy
Describe the rationale behind mammography?
Looks at radio density of breast
Pathology will show up differently to normal breast
Look for patterns of calcification

Why are biopsies of breast lesions performed?
To ensure that a lesion is malignant before commencing treatment
How are biopsies of breast lesions performed?
Which method is preferred and why?
Fine needle aspiration or needle core/tru-cut biopsy
Core/tru-cut preferred as it takes out an actual piece of tissue, so we can see the relationship of cells to each other, the stroma and basement membrane

Describe fibroadenoma?
Solitary, well circumscribed, benign mass
Most common in younger women
Neoplastic or hyperplastic stromal tumour (fibroblasts in stroma predominate)
Minimal increased risk of malignancy

Approximately how many women will be diagnosed with breast cancer?
What is the average age of diagnosis?
1 in 8 diagnosed before the age of 85
Avergae age of first diagnosis is 60 years
Describe the predisposing factors to breast cancer?
Age: more time to accumulate mutations
Genetic factors: most are due to sporadic mutations, but there are some familial cases
Increased oestrogen exposure: stimulates proliferation
Environmental and dietary influences: obesity, alcohol
Past history of certain breast diseases
Describe the sporadic mutations that may give rise to breast cancer?
Somatic mutations in p53 (cell cycle arrest, reapir of DNA damage)
Mutations in HER2 (proto-oncogene, epidermal growth factor receptor on cell surface)

Describe the germline mutations that may give rise to breast cancer?
BRCA1
BRCA2
p53
(TSGs, involved in cell cycle arrest and DNA repair)
Inherited in autosomal dominant fashion
Onset at younger age
May also develop other tumours
Describe why postmenopausal obesity may predispose to breast cancer?
Adipose tissue can make oestrogen > oestrogen stimulates proliferation of cells
Describe the effect of breast feeding on breast cancer risk?
Decreases risk
Lactation > ovulation suppressed > decreased oestrogen
Describe hyperplasia of the breast tissue?
Non-neoplastic proliferation of breast epithelium
With or without atypia
Usually an incidental finding when testing for something else
Does not cause symptoms
Predicts risk of future cancer development

What is in situ carcinoma of the breast?
Describe the risks associated with it?
Malignant population of cells confined to ducts and/or acini, no invasion through basement membrane
Associated with increased risk of developing invasive tumour
Usually asymptomatic
Describe the two types of breast carcinoma in situ?
Ductal carcinoma in situ: most common, frequently associated with calcification seen on mammogram
Lobular carcinoma in situ: incidental finding on biopsy

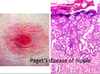
What is Paget’s disease of the nipple?
Malignant cell sof DCIS may extend up ducts to the nipple
Inflammation, erythema and exudate of nipple
What are the two main types of invasive carcinoma of the breast?
Invasive ductal carcinoma: most common
Invasive lobular carcinoma
Describe the characteristics of invasive ductal carcinoma?
50% in upper outer quadrant
Typically firm stellate mass
Desmoplastic stroma
Tumour cells form glandular lumen






