Gene dosage and genomic imprinting Flashcards
What is bi-allelic expression?
Genes are expressed from both gene copies
Majority of genes show bi-allelic expression
What is aneuploidy?
When does it occur?
Unbalanced number of chromosomes
Due to excess or deficiency of individual chromosomes
Most often arises via non-disjunction of two homologous chromosomes or sister chromatids during cell division
Which full term trisomies and monosomies may appear?
Trisomy: 13, 18, 21, XXY, XXXY, XYY
Monosomy: XO, but no autosomal
What is the major cause of intellectual disability and congenital heart disease?
Trisomy 21: Down Syndrome
What is Edwards syndrome?
Trisomy 18
Overlapping fingers, club foot, heart defects, developmental disability

How can phenotypes of various severity arise from a trisomy?
May have full trisomy, partial trisomy, or mosaicism, all producing phenotypes of varying severity
Define haploinsufficiency?
Having only one normal copy of a gene is not sufficient to support normal cell function
(e.g. in autosomal dominant inheritance)
What is mono-allelic expression?
Gene must be expressed from only one copy for normal cell function and development
How does monoallelic gene expression occur?
One of the copies is inactivated
X chromosome inactivation: epigenetic modification
Genomic imprinting: epigenetic and genetic modification
What is epigenetics?
Change in gene expression/repression with no chnage in DNA sequence
Encompasses:
DNA methylation
Histone modifications
RNA mediated gene silencing
Are epigenetic changes passed on through cell division?
Yes
Cellular ‘memory’ encoded in chromatin
Why does X chromosome inactivation occur in females?
Gene dosage mechanism
One X chromosome inactivated to ensure the level of expression of X-linked genes is equal in males and females
When does X-chromosome inactivation occur?
Cells of the early embryo
Somewhere between 8-100 cell stage
Describe how X-chromosome inactivation occurs?
DNA methylation
Hyperchromatin structure
Non-coding RNA acting in cis (expressed by X and acts to create a wave of inactivation on the same X)
Is the same X chromosome inactivated in every cell in females?
No
Females are mosaic (average 50/50)
Is the pattern of X chromosome inactivation hertiable?
Yes
What is the inactive X chromosome referred to as?
Barr body
If X chromosome inactivation occurs, is monosomy X sufficient for normal development?
No
Turner syndrome (45,X)
Short stature
Infertility (absent or immature gonadal development)
Absence of secondary sexual development
Imapired neuro function
Are all genes on the second X chromsome inactivated?
Some genes excape X inactivation
Cluster around pseudo-autosomal regiion, and line up well with Y chromosome

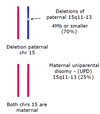
What is genomic imprinting?
The process whereby the parental origin of a particular gene is marked by a reversible epigenetic mechanism
Expression of certain genes depends on whether they are inherited from the maternal or paternal gamete
When does genomic imprinting occur?
Uniform pattern in somatic cells of all individuals >
Imprints erased during gametogenesis >
Imprints re-established in mature gametes, maintained during embryogenesis (depending on the sex of the individual)

Approximately how may imprinted genes exist in the human genome?
Hundreds predicted
1-2% protein coding genes
Define parthenogenetic and androgenetic?
Parthenogenetic: all 46 chromosomes from mother
Androgenetic: all 46 chromosomes from father

Describe the outcome of parthenogenetic and androgenetic embryos?
Parthenogenetic: typically non-viable, ovarian teratomas
Androgenetic: Hydatiform moles > malignant choriocarcinoma