Lungs and Pleura Flashcards
What does the right pleural cavity and the left pleural cavity contain?
RPC - Right lung LPC - Left lung
What are the 3 spaces outlined in pink, blue and yellow?

Pink - Right pleural cavity Blue - Mediastinum Yellow - Left pleural cavity
What is the mediastinum and what does it contain?
Space between the 2 pleural cavities
Contains trachea, heart, oesophagus, blood vessels and nerves
What are the 3 spaces outlined in yellow, blue and pink?

Yellow - Right pleural cavity
Blue - Mediastinum
Pink - Left pleural cavity
Complete the diagram of devloping lungs and pleura

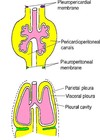
At how many weeks does the respiratory system start to develop?
4-6 weeks
Does the lungs and pleura arise from the ectoderm, mesoderm or endooderm layer?
Endoderm
How does the lungs and pleura develop?
- Endodermal out pouches form lung buds and bronchial buds
- Rapid division of the airways occurs
- Hence the lungs push their way out into the primitive thoracic cavity.
- As they do they take the lining with them (visceral pleura)
Is this the visceral or parietal pleura?
Closely adheres to the lungs including the fissures
Visceral pleura
What is the function of visceral pleura?
Creates a smooth and slippery surface
Which 2 structures does the visceral pleura connect to?
The parietal pleura and the hilum
Complete the diagram


Complete the diagram of the segments of parietal pleura


Is this the visceral or parietal pleura?
Lines the internal aspect of the thoracic wall
Parietal pleura
What are the 4 parts of the paritetal pleura and where do they line?
- Costal (Internal rib cage)
- Mediastinal (Lateral wall of mediastinum)
- Diaphragmatic (Superior diaphragm)
- Cervical (Cervical region)
What is the pleural cavity?
Space between the 2 layers of pleura
What does the pleural cavity contain?
A thin layer of serous fluid
How is the pleural cavity important for breathing?
Surface tension of the serous fluid hold lungs against thoracic wall
Lungs expand as the thoracic cavity expands
Which 2 pathologies cause the surface tension between the pleural layers to be lost?
Pneumothorax
Haemothorax
What is this arrow pointing to?

Pleural cavity
Label the pleural cavity recesses


Why is the pleural cavity not symmetrical?
Because of the heart
When can the pleural cavity recesses be occupied by lung?
During forced inspiration
Name the innervation for the 4 parts of the parietal pleura
Cervical
Costal
Mediastinal
Diaphragmatic
- Cervical – 1st intercostal nerve
- Costal – intercostal nerves
- Mediastinal – phrenic nerve
- Diaphragmatic – lower intercostals and phrenic nerves





















