Living Anatomy and Ultrasound Flashcards
How does ultrasound work?
By transmitting high-frequency soundwaves through tissue from a transducer. Changes in tissue density are detected by transducer.
Does fluid and air appear hyperechoic or hypoechoic?
Hypoechoic - black
Does bone appear hyperechoic or hypoechoic?
Hyperechoic - white
What colour is muscle and viscera on ultrasound?
Mid grey
Should you point the marker on the probe to the left or right side of the patient?
Right
For cardiac ultrasound should you point the marker on the probe to the left or right side of the patient
Left
Which pathologies is point of care ultrasound used to assess?
Pulmonary oedema Pleural effusion Pneumothorax
Name the type of transducer


Complete the diagram

Figure 1: AL = apex lung;
DpG = deltopectoral groove;
HoF = horizontal fissure;
OF = oblique fissure;
ScJ = sternoclavicular joint;
4CsJ = fourth costosternal joint;
6CsJ = sixth costosternal joint;
7MiCL = seventh rib in midclavicular line;
8CC = eighth costal cartilage in the midline;
10MAL = tenth rib midaxillary line.
Complete the diagram

Figure 2: AL = apex lung;
HoF = horizontal fissure;
SpinPT1 = spinous process of T1;
SpinPT10, = spinous process of T10;
SpinPT12 = spinous process of T12.
Where is the tricuspid valve?
Tricuspid valve lies just above the level of the 5th costal cartilage to the right lateral edge of the sternum.
Where is the mitral valve?
Mitral valve lies just left of the midline adjacent to the left 4th costal cartilage and 4th intercostal space.
Where is the aortic valve?
Aortic valve lies adjacent to the 3rd intercostal space roughly in the midline of the sternum.
Where is the pulmonary valve?
Pulmonary valve lies in the plane of the 3rd costal cartilage to the left lateral edge of the sternum.
Complete the diagram


Complete the diagram

RA- right atrium,
LV- left ventricle,
RV- right ventricle,
AH- apex of heart,
SVC- superior vena cava,
RBV- right brachiocephalic vein,
LBV- left brachiocephalic vein,
AA- arch of aorta,
DA- descending aorta,
BT- brachiocephalic trunk,
RSA - right subclavian artery,
RCCA- right common carotid artery,
LCCA- left common carotid artery,
LSA- left subclavian artery,
PTr- pulmonary trunk
What does this ultrasound show and what is the clinical significance of this?


Complete the diagram


Which part shows lung sliding?


What imaging technique is this?
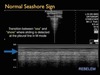
M-Mode
What is the pathology shown in this image?

Pneumothorax
Complete the diagram


Where is the safe triangle and what are the 4 edges?
Under armpit
BA = base of axilla
LPMA = lateral border Pectoralis Major
LLD = lateral border Latissimus Dorsi
5IS = 5th Intercostal Space

What view of the heart is this?

Apical view







