Lung Path 3 - Interstitial through Diseases of Vascular Origin (Singh) Flashcards
(150 cards)
List some of the Interstitial lung diseases
UIP: ususal interstitial pneumonia
NSIP: non-specific interstitial pneumonia
COP: Cryptogenic Organizing Pneumonia
Sarcoidosis
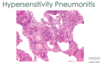
Hypersensitivity Pneumonia
DSIP: Desquamative Interstitial Pneumonia
RB-ILD: Respiratory Bronchiolitis-Interstitial Lung Disease
- *LCH:** Langerhans Cell Histiocytosis
- *PAP:** PulmonaryAlveolarProteinosis
What are the clinical sign/sx’s of chronic interstitial pulmonary diseases?
- Dyspnea and Tachypnea
- End-respiratory crackles “velcro-like”
- Restrictive patters on PFT (decreased DLCO, FVC)
- Basilar infiltrates on CXR
- Cyanosis (late)
- NO wheezing
What is characteristically seen on CXR of someone w/ chronic interstitial pulmonary diseases?
- Bilateral lesions that take form of small nodules, irregular lines, or
- Ground-glass shadows
Grossly, what is the end-stage lung seen in chronic interstitial pulmonary diseases referred to as?
Honeycomb lung

Which 2 chronic interstitial lung diseases are categorized as granulomatous?
- Sarcoidosis
- Hypersensitivity pneumonitis
What are some of the enviornmental and occupational factors which may be associated with Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis?
- Cigarette smoking
- Expsoure to metal fumes and wood dust (industrial)
- Occupations such as: farming, hair-dressing, and stone-polishing
- GERD has also been implicated
Loss-of-function mutations in which 2 genes has been implicated in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis?
- TERT
- TERC
*Encode components of telomerase
What genetic factors have been assoicated with Idiopathyic Pulmonary Fibrosis?
Telomerase mutations
Surfactant mutations
MUC5B variant
Some cases of Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis are associated with a genetic variant leading to ↑ secretion of which mucin?
MUC5B
Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis is a disease most common in which age group?
>50 yo
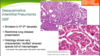
The histologic pattern of fibrosis seen in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis is referred to as what?
What is the imaging modality to diagnosed this condition based on its characteristic appearance?
- Cystic space surrounded by thick excessive fibrosis
- On CT
Usual interstitial pneumonia (UIP)

Microscopically, what is the hallmark of Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis; there is coexistence of what?
Patchy interstitial fibrosis*** (normal mixed with fibroblastic foci)
–> varies in intensity and age
Coexistence of early (fibroblastic foci) and late (collagenous) lesions

In Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis the formation of cystic spaces lined by hyperplastic type II pneumocytes or bronchiolar epithelium is known as what?
Honeycomb fibrosis

The earliest lesions in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis contain exuberant what?
Fibroblastic proliferation (fibroblastic foci)
Diagnosis of Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis requires what?
Classic findings on high-resolution CT or pulmonary biopsy

What are the initial sx’s of Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis and the later sx’s with progression?
- Early —> ↑ dyspnea on exertion and dry cough
- Later –> hypoxemia, cyanosis and clubbing
What is the prognosis and only definitive therapy for Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis?
Median survival 3-5 years after Dx
Lung transplantation
Medication to arrest fibrosis inlcude Tyr kinase inhibitors and TGF-B inhibitors
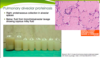
Why is it important to recognize pt’s with Nonspecific Interstitial Pneumonia?
Have much better prognosis than those w/ UIP
What is the histomorphology of the cellular and fibrosing patterns of Nonspecific Interstitial Pneumonia?
Cellular = mild to moderate chronic interstitial inflammation; in UNIFORM parenchyma (can be patchy, but she emphaisized uniform)
Fibrosing = diffuse or patchy fibrotic lesions of roughly the SAME age
Resident cells include lyphocytes and eosinophils surrounding mild to moderate alveolar thickening
–> can be treated at this point.

What is a major morphological difference between the lesions of Nonspecific Interstitial Pneumonia and Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis?
In NSIP the lesions are at roughly SAME stage of development
What 4 morphologial findings are absent in Nonspecific Interstitial Pneumonia?
- NO fibroblastic foci
- NO honeycombing
- NO hyaline membranes
- NO granulomas
Which population is most likely to be affected by Nonspecific Interstitial Pneumonia?
Female NON-smokers in their 6th decade of life
What are the key features of Nonspecific Interstitial Pneumonia seen on high-resolution CT?
Bilateral, SYMMETRIC, predominantly lower lobe reticular opacities

How do patients with Cryprogenic Organizing Pneumonia (formerly BOOP) present and what is seen radiographically?
- Cough and dyspnea
- Patchy SUBpleural or
- peribronchial areas of airspace consolidation