Let 1 Genomic Regulations Flashcards
How much volume does the nucleus take up
6%
Roles of the Nucleus
Cell regulation proliferation DNA transcription
What is the central Dogma
1.DNA to RNA to Protein 2.DNA replication 3. transfer of genetic info from parent to offspring 4. transcription vrsus tranlsation 5. mRNA exclusive carrier of info DNA to protein 6. RNA can go to DNA (RNA virus)
DNA is both ______ and _______
double stranded and anti- parallel
how many bonds between A and T
2 hydrogen bonds
how many bonds between G and C
3 hydrogen bonds
What are the grooves of DNA

What needs to happen to allow DNA to fit all 3.2 billion Base pairs?
An incredible amount of condensation is needed throughout cell cycle (condensed 500 times) compared with interphase chromosomes
What is DNA wound around?
Histone Proteins
There are 142 H bonds between DNA and what?
histone octamer in each nuclesomes
T/F histone protein are highly conserved across species?
T
What makes up 20% of histone protein?
Lysine(Lys) or K Arginine(Arg) or R
Do histones have a charge?
Positive charges which attracts them to negatively charged DNA backbone
Two types of proteins that bind DNA
- Histone proteins
- non-histone chromosomal proteins (TFs) transcription factors
Nucleosome core particle consists of a complex of ______?
eight histone proteins (octomer)
DNA+protein=________
chromatin
What is Euchromatin?
LIGHTLY PACK FORM OF chromatin.
most active portion of genome
What is Heterochromatin
very condensed chromatin (stains dark)
late replicating and genetically inactive
Near centromeres and telomeres
What happened in Feb, 2001
sequence of human genome was announced
(90%)
Percentage of DNA sequence in exons?
1.5% (this is low)
what are CGH arrays?
comparative genome hybridization
Probe human genome CHIP with DNA from one person and with DNA from a normal reference ( detecs copy number variation.)
what is RNAi
bio process in which RNA miRNA molecules inhibit gene expression or translation
Neutralize targeted mRNA molecules
What are Long Terminal Repeats?

What do 99% of introns begin and end with?
begin with […GT] and end with [AG…]
What deacetylates Histones?
Histone Deacetylase (HDAC)
What acetylates histones?
Histone Acetyl Transferase (HAT)
what does acetylation and deacetylation do?
Deacetylation keeps beads wound tight on string wich represses gene expression
Acetylation actively promotes gene expression. ( beads are wound loosely)
Where do post-translational modifications (PTM) occur in histones?
on the histone tails
Types of PTM to histones

what is DNA Methylation
MEthyl groups added to DNA molecule (Cytosine and Adenine). This changes activity (represses gene transcription when at gene promoter)
(Genomic imprinting, x-chrom inact, aging, carcinogens)
What does DNA polymerase require in a primer ?
a free 3’ -OH to begin processing
DNA polymerase moves in what direction
5’ to 3’
What does semi-conservative mean with DNA

What part of DNA continuous vs. discontinuous?
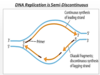
What unwinds DNA
DNA helicase ATP used
What do Single stranded DNA binding proteins do (SSBP)
binds cooperatively to exposed ssDNA
(stabilizes unwound DNA)no haripins
(Bases remain exposed)
Topoisomerase role and name in bacteria?
relieves overwound supercoils (DNA Gyrase in bacteria)
by breaking phosphodiester bond.
What is the pharmaceutical significance of DNA topoisomerase?
Used as anti-cancer agents (topoisomerase inhibitors)
- block the cell cycle
- generate single and double stranded breaks
- harms integrity of genome
- leads to apoptosis and cancer cell death
What synthesizes RNA-DNA primer?
DNA polymerase alpha
What synthesizes DNA and what direction
DNA polymerase delta and epsilon 5’ to 3’
What fills in gaps in DNA
DNA polymerase delta
What seals nicks in DNA
DNA ligase
how are errors mainly corrected in DNA synthesis
proofreading (DNA polymerase) and repair
Types of DNA damages
- Ionizing radiation
- non-iodizing radiation
- spontaneous DNA damage (depurination/deamination)
- chem agents
- methylated cytosine resudes in CpG sites/ islands
ionizing radiation

Non-ionizing radiation

Spontaneous (depurination)

spontaneous-deamination

Spontaneous DNA damage possible outcomes
Either a base deletion or substitution
What happens to a methylated CpG island?
stable silences genes (cancer/DNA repair genes)
How does methylated cytosine cause problems
deamination of Mehyl-C produces a Thymine which is now mismatched with G
Cross-linking and its agents
cross links between bases in the same DNA stand or between two complementary DNA strands
Nitrogen mustard
cisplatin
mitomycin C
CArmustine
Alkylating Agents
induce a wide variety of methylated base changes and alkylation of phosphodiesters into triesters
Dimethyl sulfate (DMS)
Methyl methanesulfonate (MMS)
what are intercalating agents plus ex.?
insert between stacked bases of DNA double helix causing some unwinding of the helix and seperation of base pairs
Thalidomide
how metab can produce carcinogens

Double strand break repair (Recombination repair)
Nonhomologous vs Homologous
N-accidental break►loss of nucleotides from ends ►
end joining ► deletion of DNA sequence
H-accidental break► loss of nucleotides from ends ►
end processing and homologous recombination ► damage repaired accurately using info from sister chromatid
Homologous or non-homologous break repair more common?
Non. generally okay as so little of genome is protein coding
can see scarring
Epigenetics
a mechanism for regulating gene activity independent of DNA sequence that determines which genes are turned on or off
ubiquination
lysine side chain residues. lysine attach to lysine ubiqinated chain signals problems. signals proteosome for degredation
cycle repeats with reuse of ubiquitin
SUMOylation cycle
precursor with glycines which is activated to mature SUMO which attaches substrate
Ubiquitination of SUMOylated protein
Poly SUMOnation which then gets ubiquitinated which then gets degraded (post translational modifications will work together)
CpG islands and sites modification
Hypermethylation can cause stably silence these CpG islands which are in 70% of promoter regions so it will silence the gene.
Start Codon
ATG (in DNA) AUG (in RNA) Methionine
What is Direct repair
pyrimidine (or thymine) dimer by UV light can be separated by photolyase which is activated by light.
O6 methylguanine pairs with T rather than C. MGMT transfers methyl group from guanine to a to a cysteine on itself directly reversing damage
What is base excision repair (BER)
single base mismatches or non distorting alterations
The single base can be removed and then replaced
What is Nucleotide excision repair (NER)
repair adducts that distort the DNA like pyrimidine dimers. DNA unwound a nick on both sides of mistake made template guides for replacement of missing section
Mismatch Excision Repair (MER)
MER finds a wrongly places nucleotide in the daughter strand. nicks the affected area and then replaces the daughter strand bases (not known how daughter stand known)
Recombination repair
Homologous and non homologous end joining (double strand break repair)
transcription coupled repair (TCR)
RNA polymerase stalls at a lesion during transcription which recruits ERCC 6 and 8 to recruit other repair items
Translesion synthesis
incorporate A opposite T dimers uses a DNA polymerase that doesnt proofread.
Nucleoside analogue inhibitors of DNA synthesis
DNA synthesis formation of 3’ to 5’ phosphodiester bonds nucleoside analogues that lack the 3’ OH group act as drugs that inhibit DNA replication (acyclovir) acts as chain terminators


