Lens & Cataract Flashcards
eye with extreme increased axial length susceptible to this issue
lens-iris diaphragm repulsion syndrome (LIDRS)
reverse pupillary block and AC deepens
Where is the germative zone of the lens epithelium located?
immediately anterior to the lens equator
oily rings of debris aroudn the lashes “collarettes” are hallmark for this and RF for surgery
blepharitis and meibomianitis
endophthalmitis
Reduces PCO formation in acrylic foldable IOL
truncated or square-edge optic design
best describes viscosity of an OVD
resistance to flow; thickness or thinness of a fluid
Cohesive OVD
long-chain, high MW, high viscosity
maintain space well at no or low shear rate, displaced at high shear rates
easier to remove from eye because they stick together (spaghetti)
minimal coating (less protection)
Optical characteristics of human lens with age
increasing anterior and posterior curvature
decrease index of refraction
(increased index of refraction in NSC)
Type of cataract characteristic of ischemic ocular conditions eg Takayasu arteritis, Buerger disease, anterior segment necrosis
posterior subcapsular
lens with higher rates of capsular opacification
round edge
Lens has higher level of what compared to surrounding aqeous and vitreous
K+
amino acids
This patient c/o glare and vague shadow (double) image. Cause of this problem?

Capsular rupture
Association explains patient’s disorder for abnormality shown

anterior subcapsular cataract a/w atopic dermatitis
cataract formation in 25% (2nd and 3rd decade) resemble shield like plaques
type of IOL most likely to cause negative dysphotopsia
square-edge posterior chamber IOL in the capsular bag
Decentered PC IOLs of all types cause this
positive dysphotopsias
Thickness at each portion

A - 14 um
B - 21 um
C - 17 um
D - 23 um
E - 4 um
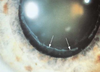
88 yo F p/w pain and redness, VA HM
Diagnosis

phacolytic glaucoma
often large white particles seen in AC
(note: not phacoantigenic
Medication that caused this complication

Afluzosin (alpha 1 adrenergic antagonist)
(floppy iris syndrome RF for intraoperative iridodialysis)
Changes occur to lens epithelial cells during terminal differentiation
increase in cell protein content and loss of organelles
MC cataract in RP
PSC
RF a/w intraoperative choroidal hemorrhage
Glaucoma
HTN
tachycardia
obesity
high myopia
anticoagulation
advanced age
chronic ocular inflammation
(Note: younger age reduces risk)
What percentage of lens glucose passes through the citric acid cycle?
3%
Change in lens and zonule when ciliary muscle contracts?
the equatorial diameter of the lens decreases
diameter of muscle ring reduced
zonular tension decreases
axial thickness of lens increases
dioptric power increases
OVD that maintains volume and expels easily
cohesive
Management intraop for patient with numerous corneal guttae
increase use of dispersive OVD during phacoemulsification