Cornea Flashcards
Pathogens that can invade through an intact corneal epithelium
Neisseria gonorrhoeae
Neisseria meningitidis
Corynebacterium diphtheriae
Listeria monocytogenes
Shigella
Haemophilus influenzae
Fusarium
Remove a suture from this meridian to decrease post-op astigmatism

90°
Steep axis at 90 and 270, theefore sutures should be removed
start topical abx and re-evaluate in 1 month with repeat corneal topography and manifest refraction
Monitor xeroderma pigmentosum for this
Ocular neoplasms in 11%
SCC, BCC, melanoma on surface and eyelids
Earliest pathologic corneal changes found in keratoconus
Bowman layer
Breaks in Bowman followed by fibrous growth through the break

62 yo M rosacea with blepharitis, marginal keratitis and AFib on warfarin with h/o 2 MI. Tx (oral) for ocular rosacea with least risk for adverse reaction?
Erythromycin
Not doxycycline b/c tetracyclines can potentiate anticoagulant effects, also reduce efficacy of OCP
NOT azithromycin b/c FDA warning that might be hazardous to patients with CV disease
25 yo FBS worse at end of day
Best blood test?

antibodies to La/SS-B antigens (more specific) and
SSA/Ro
rose bengal staining inferior conjunctivae and ropy mucous discharge -> DES
r/o SS
35 yo M blurry vision OD with recurrent episodes of pain and redness. Preferred treatment?
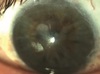
acyclovir 400 mg 2 times daily
(prophylaxis)
HSV stromal keratitis
Treatment for visually significant herpetic interstitial keratitis?
prednisolone 1% drops every 2 hours +
topical trifluridine QID or acyclovir 400 mg BID or valacyclovir 500 mg daily
Taper prednisolone every 1-2 weeks depending on clinical improvement
Cause of this condition?

disruption of descemet membrane
acute corneal hydrops
Diagnosis

limbal stem cell deficiency (LSCD)
whorl-like pattern caused by migration to ocular surface of conjunctival cells. 25%-33% limbus must be intact to ensure normal ocular resurfacing
clear corneal depression with thinning at limbus, adjacent to raised area of conjunctiva. Diagnosis and treatment?
Dellen - occurs due to dehydration of the epithelium and stroma
patching and topical lubrication
Prefered management to treat symptoms

conjunctival resection
(conjunctivochalasis - redundant bulbar conjunctival tissue)
Protein deficiency leading to this condition?

plasminogen deficiency
(ligneous conjunctivitis) Fibrinogen (factor I) needed for platelet aggregation
Cochet-Bonnet esthesiometer
used to evaluate corneal sensation
Hypercalcemia, renal failure, monoclonal spike on SPEP. What ocular finding is a/w this condition?
corneal crystalline deposits
(all layers of the cornea)
hyperviscosity of retinal vasculature, pars plana cysts, proptosis from orbital bony invasion
Diagnosis, genetics and mechanism

Corneal verticillata
Fabry disease
X-linked recessive
deficiency of a-galactosidase
Causes for this and synonyms

Fabry disease or prlonged amiodarone intake
Fleischer vortex
vortex keratopathy
whorl keratopathy
also caused by chloroquine, hydroxychloroquine, indomethacin, phenothiazines
Biopsy of conjunctiva is expected to show..
Consequences of failure to diagnose?

loss of goblet cells
severe case of xerophthalmia due to Vitamin A deficiency
Severe drying of conjunctiva with water beading on surface
Systemic vitamin A deficiency has a mortality rate of 50% if untreated!
eosinophilic extracellular deposits that exhibit birefringence
amyloid deposits
Bitot spots contain this bacteria
Corynebacterium xerosis - foamy appearance
Cause of this condition? Next step in management?

Superior limbic keratoconjunctivitis (SLK)
superior bulbar conjunctival laxity with secondary inflammation from mechanical trauma
a/w thyroid dysfunction
Note: Differentiate from FES by eyelids that can be everted with minimal effort
Expected findings on pathology

superior bulbar conjunctiva with histology showing hyperproliferation (increased C-N ratio), acanthosis, loss of goblet cells, keratinization, nuclear pyknosis with “snake nuclei”
Diagnosis and consequence

Iridocorneal endothelial (ICE) syndrome caused by proliferation of corneal endothelium over the TM eventually causing PAS and secondary angle-closure glaucoma
Glaucoma develop in 50%
















































































