Lecture 6: Cardiac Rhythm Disturbances (Atrial, Junctional, Ventricular) Flashcards
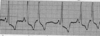
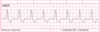
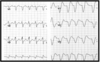
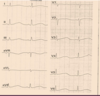
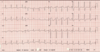
What is your interpretation?

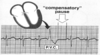
Sinus Arrhythmia
What is Sinus Arrythmia due to?
Normal, but minimal, increase in HR during inspiration and decrease in HR during exhalation

Bile salt accumulation in obstructive jaundice can have an affect on the SA node and lead to what type of HR?
Bradycardia
What is the effect of hyperkalemia on HR?
Bradycardia
List some drugs that can cause bradycardia?
- Quinidine
- Digitalis
- HTN drugs –> clonidine, methyldop, and reserpine
- Beta-blockers —> propranolol and metoprolol
Sinus bradycardia is a common finding with what type of MI?
Acute inferior MI (increased vagal tone, N/V)
Sick sinus syndrome has what effect on HR?
Bradycardia
Which HR is considered bradycardia?
HR < 60/min
What are characteristic ECG findings of someone with Sick Sinus Syndrome?
- Periods of inappropriate, and often, severe bradycardia
- Sinus pauses, arrest, and sinoatrial (SA) exit block with, and often without, appropriate atrial and junctional escape rhythms
- Alternating bradycardia and atrial tachyarrhythmias
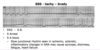
For each of these parameters, pO2, pCO2, pH, and BP, use (↑↓) to describe which is associated with bradycardia
- ↓pO2
- ↑pCO2
- ↓pH
- ↑BP
What is the most common cause of unexplained pause on an EKG tracing?
Nonconducted PAC

What is the tx of choice for pt with sinus bradycardia, if HR <45-50 with hemodynamic compromise/unstable acute situations?
Use caution in which pt’s?
- Atropine
- Use caution in glaucoma –> can ↑ IOP
If atropine is given to someone with hemodynamically unstable sinus bradycardia and fails to work, what are the next 3 options for tx?
- Epinephrine
- Isoproterenol
- Pacemaker
Define automaticity in regards to cardiac cells
Property of cardiac cells to depolarize spontaneously during phase 4 of AP/leads to generation of an impulse
What characteristics are used to determine if a PAB is present and to help differentiate it from something more serious?
- Appears early in the cycle
- Morphologically distinct from the previous P waves

What is the characteristic finding on an EKG of a PAB with aberrant ventricular conduction?
Wide QRS following PAB

What is this known as?

Atrial Bigeminy

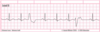
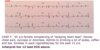
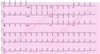
Interpret the tracing in A and B

- A) 1st degree AV block w/ non-conducted PAC
- B) 1st degree AV block w/ non-conducted PAC occurring in trigeminal rhythm

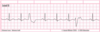
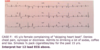
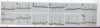
Interpret this EKG

Non-conducted PAC in Bigeminal rhythm
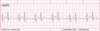
What is the tx for PAC’s if symptomatic?
- Reverse causes (i.e., coffee, alcohol, other contributors)
- Beta-blocker —> Metoprolol
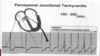
Paroxysmal atrial tachycardia has a sudden onset and what is the HR?
Rate = 150-250/min
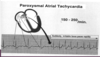
What are the criteria for paroxysmal atrial tachycardia with AV block?
What should you suspect as underlying cause?
- Greater than one P’ wave per QRS complex; 2 P’ waves for each QRS
- Rapid rate with spike P’ waves
- Suspect digitalis toxicitiy

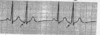
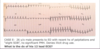
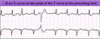
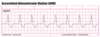
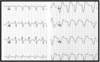
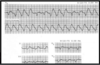
Interpret this EKG

Atrial Tachycardia with 2:1 AV block

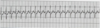
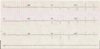
Interpret this EKG

Atrial Tachycardia w/ 2:1 AV block