Lecture 2: Cardiovascular Review Flashcards
(28 cards)
Phase 0 of the myocardial AP is dominated by opening of what channels?
Voltage-gated Na<strong>+</strong> channels

What is occurring during phase 1 of the myocardial AP?
- Initial repolarization
- Inactivation of Na+ channels
- Voltage-gated K+ channels begin to open; K+ flows out

What is occurring during phase 2 (plateau) of the myocardial AP?
Ca2+ influx balances K+ efflux

What is occurring during phase 3 of the myocardial AP?
- Rapid repolarization
- Massive K+ efflux due to opening of votage-gated slow K+ channels and closure of Ca2+ channels

What is occurring during phase 4 of the myocardial AP?
High K+ permeability = high K+ conductance

What are the 3 phases of the pacemaker AP and the events of each?
- Phase 0 = upstroke - opening of Ca2+ channels and closing of K+
- Phase 3 = repolarization - closing of Ca2+ channels and opening of K+ channels –> ↑ K+ efflux
- Phase 4 = slow spontaneous diastolic depolarization due to opening of funny voltage-gated Na+ channels (If )

The slope of which phase of the pacemaker AP in the SA node determines HR?
Phase 4

At the top of the graph of the cardiac cycle what are the 3 events occurring in order during systole?
1) Isovolumetric contraction
2) Rapid ejection
3) Reduced ejection
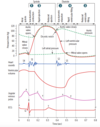
At the top of the graph of the cardiac cycle what are the 3 events occurring in order during diastole?
1) Isovolumetric relaxation
2) Rapid ventricular filling
3) Reduced ventricular filling

Which valves are associted with the S1 and S2 heart sounds?
- S1 = mitral valve closes
- S2 = aortic valve closes

Which phase of cardiac cycle is represented by #1?

Isovolumetric contraction

Which phase of the cardiac cycle is represented by #2?

Systolic ejection

Which phase of the cardiac cycle is represented by #3?
Isovolumetric relaxation

Which phase of the cardiac cycle is represented by #4 and #5?

- # 4 = rapid ventricular filling
- # 5 = reduced ventricular filling

The QRS complex represents which phase of the AP spreading throughout the ventricles?
Phase 0

The T wave represents which phase of the ventricular myocyte AP?
Phase 3 = repolarization

The dicrotic notch represents what?
Aortic valve closure

The P wave represent which phase of the atrial myocyte AP?
Phase 0

At which point is the voltage differences between regions of the ventricles the greatest?
Point 8

The start of isovolumetric contractin correlates with what waves on the ECG?
Peak of R wave thru the S wave

Afterload is the pressure the heart must overcome to do what?
Open the aortic valve for ejection of blood
Which term is used to describe the amount of stretch on the myocardium at the end of diastole (i.e., the volume in the ventricle)?
Preload

Point 7

The reduced ejection phase of systole is represented by what wave on the ECG?
T wave







