ECG: Bundle Branch Blocks/Hemiblocks (Johnston) Flashcards
Define intrinsic deflection (ID)
Time lapse from beginning of the QRS to the peak of the R wave

During ventricular depolarization the septum is activated in which direction?
From L –> R

Which feature of the QRS complex is characteristic of bundle branch blocks?
Wide QRS (>0.12 sec) = >3 small squares
List 6 causes of rsR’ variants in V1-V2
- Normal
- Pectus or straight back
- RV diastolic volume overload
- WPW syndrome
- RVH
- Duchenne dystrophy
What are 4 underlying etiologies where LBBB is more likely to occur?
- HTN
- Ischemia
- Aortic stenosis
- Cardiomyopathy
LBBB with RAD is usually due to what?
Congestive Cardiomyopathy
In LBBB which 2 leads share similar features with V6?
Lead I and AVL (point in similar direction)
If T wave polarity is in the same direction of the QRS complex, it is called what type of T wave change?
Usually due to what?
- Primary T wave change
- Due to ischemia
What type of block is this?

Left Anterior Hemiblock

What type of axis deviation is associated with a left anterior hemiblock and a left posterior hemiblock?
- LAH is associated with LAD
- LPH is associated with RAD
What is the morphology of the Q and R waves associated with a left anterior hemiblock and in which leads?
- Small Q in leads I and aVL
- Small R in leads II, III, and aVF

What is the morphology of the Q and R waves associated with a left posterior hemiblock and in which leads?
- Small R in leads I and aVL
- Small Q in leads II, III, and aVF

What is the typical etiology of left anterior hemiblocks?
- Disease in conduction system
- Often associated w/ MI (LAD - occlusion)

Interpret this EKG

Left Anteior Hemiblock

Interpret this EKG
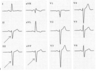
Left Anterior Hemiblock

Interpret this EKG

Bifascicular block: RBBB + Left Anterior Hemiblock
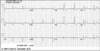
Interpret this EKG

Left Posteior Hemiblock

The consideration for left posterior hemiblock requires that there be no evidence of what?
Right ventricular hypertrophy
Interpret this ECG (i.e., axis and rhythm)

RAD w/ left posterior hemiblock and RBBB


