Lecture 2 Flashcards
Connective Tissue Characteristics
Found in every organ except for the CNS
Has few cells
Has an abundant matrix
Connective Tissue Functions
Blood-forming tissue (hematopoietic)
Lymphoid tissue
Connective Tissue Types

Connective Tissue amorphous non-cellular components
Glycosaminoglycans
Glycoproteins
Chondroitin Sulfate
-Cartilage
Hydroxyapatite
-Bone
4 Categories of Glycosaminoglycans (GAGS)
Hyaluronic Acid
Heparin/Heparan Sulfate
Chondroitin/Dermatan Sulfate
Keratan Sulfate
Hyaluronic Acid
Largest of the GAGs
Only GAG that lacks sulfate
Found in synovial fluid and Wharton’s Jelly
Picture of Proteoglycan Aggregates
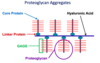
2 Examples of Glycoproteins
Chondronectin
- Promotes adhesion of mature chondrocytes to collagen
Laminin
- Found in basal lamina
- Involved in the attachment of epithelial cells to the lamina
Cartilage Components
(2 Types of cells/ ECM)
Cells
- Chondroblasts- Cartilage forming cells
- Chondrocytes- cartilage maintenance cells
ECM
- Cartilage fibers that are made of type II collagen fibers
Lacunae
Pockets within the matrix where the chondroblasts and chondrocytes are found
Cartilage Structure


Cartilage Structure (E)


3 Types of Bone Tissue

Compact Bone Tissue


3 Types of Cartilage
Hyalin Cartilage
Elastic Cartilage
Fibrocartilage

