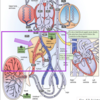
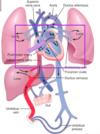
Lecture 16: Fetal and Neonatal Physiology Flashcards
(50 cards)
What week do nucleated RBC’s form in the yolk sac and mesothelium of placenta?
3rd week

When do the spleen and lymphoid tissue begin forming RBC’s?
9-12 weeks (3rd month)
When does renal function mature rapidly in the neonate; when does functional development of the kidney complete?
- Renal function matures rapidly in 3rd Trimester
- Kidneys are immature at birth
- Functional development complete around 1 month of life
What is the major hemoglobin of fetal life and how does it compare to that of an adult?
- Hb F (α2γ2)
- Oxygen binding affinity: fetal Hb > maternal Hb
Fetal urine accounts for what % of the amniotic fluid?
70-80%
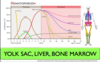
What is the order of the 3 structures which begin hematopoiesis from earliest to latest?
1) Yolk sac
2) Liver
3) Bone Marrow
What is the ability of the fetal liver like in conjugation, protein/coagulation factor formation, and utilizing glucose; what does the infant use for metabolism until feeding from mother?
- Poor conjugation of bilirubin (hence neonatal jaundice)
- Deficiency in forming plasma proteins and coagulation factors
- Deficient blood glucose (levels the 1st day could be as low as 30-40 mg/dL of plasma)
- Infant uses its stored fats and proteins for metabolism until mother’s milk can be provided
What are the Ca2+ and Vit D needs like in a neonate; why is vitamin D so important for calcium?
- In stage of rapid ossification of their bones at birth, so need ready supply of calcium
- Can normally get adequate amount from diet of milk
- Absorption of calcium by the GI tract is poor in the absence of vitamin D —> can lead to rickets!
Where is iron stored in the infant and how much is typically stored in healthy infant?
Infants liver has stored enough iron to keep forming blood for about 6 months
If a mother does not have adequate iron in her diet during pregnancy what can this lead to?
Severe anemia is likely to occur in the infant
What are the nutritional needs of Vit C like in an infant; where do they get their Vit C from?
- Not stored in significant quantities in the fetal tissues
- Adequate amounts can usually be provided by the mother’s breast milk
- In some instances infants w/ Vit C deficiency need prescribed supplements
What is the immunitity of the neonate like at birth, at the end of the first month, and when do they start building up their immune system?
- Inherits great degree of immunity from the mother; not forming Ab’s of its own yet at birth
- By end of 1st month, there is a decrease in the baby’s gamma globulin (contains the Ab’s)
- Own immune system begins to form Ab’s and gamma globulin concentrations return to normal by age 12-20 months
Ab’s inherited from the mother protect the infant for how long?
6 months against major diseases
Ab’s inherited against what disease are normally insufficient in the neonate?
Whooping cough; require immunization within the 1st month or so of life
What secretes surfactant, what is its role, when is it formed?
- Secreted by type II alveolar epithelial cells
- Decreases surface tension
- Synthesis begins in the last trimester
How quick is breathing initiated at birth and what are the stimuli?
- Within seconds of birth
Stimuli:
- Asphyxiation during birth
- Sudden drop in ambient temperature and cooling of skin
What can cause delayed breathing at birth?
- Use of general anesthesia during delivery
- Prolonged labor
- Head trauma of infant during birth
What are 4 causes of hypoxia during delivery?
1) Compression of umbilical cord
2) Premature separation of placenta
3) Excessive uterine contractions
4) Excessive anesthesia of the mother (depressed maternal breathing)
What is the tolerance for hypoxia like in a neonate vs. an adult?
- Neonates have higher tolerance for hypoxia
- Adults: 4 min
- Neonates: 8-10 min
At birth, the alveoli are collapsed due to surface tension of amniotic fluid, how much pressure is needed to open them for first time and how much negative pressure is created and air brought in during the first breath?
- More than 25 mmHg negative inspiratory pressure is needed to overcome surface tension and to open the alveoli for the 1st time
- 1st inspiration capable of creating as much as 60 mmHg negative pressure in the intrapleural space
- 1st inspiratory movements bring in nearly 40 mL air

Why does deflation of the lung also require strong positive pressure?
To overcome the viscous resistance of fluid in bronchioles
What happens to the ease of breathing after first breath and when does it normalize?
- Less effort needed after 1st breath, and so on..
- Becomes normal about 40 min after birth

Respiratory distress syndrome is commonly seen when? What does failure to secrete adequate amounts of surfactant result in?
- Commonly seen in premature infants and infants born to diabetic mothers
- Failure to secrete adequate amounts of surfactant resulting in collapsed alveoli and development of pulmonary edema
What is the fetuses initial heart beat like and how does the bpm change up until birth?
- Initially contracting at 65 bmp
- Rate increases steadily to 140 bpm immediately before birth