Lecture 1- Introduction to the reproductive system Flashcards
define reproduction
–The action or process of copying something
–The production of offspring by a sexual or asexual process
Two basic modes of repro:
- Asexual
- Sexual reproduction
human repro through
sexual reproduction
- Halving of chromosomes number by meiosis and the restoration via fertilisation
- Two haploid gametes (one male one female)
- Creates genetic diversity
Hormones regulate both male and female reproductive ability
- Puberty
- Menstrual cycle
- Menopause
Hormones are key to regulation of reproductive lifespan
- GnRH
- LH
- FSH
- inhibin
- Follistatin
Gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH)
is the key tropic hormone for regulating gondadotrope cell function and hence reproduction
Luteinising hormone (LH)
gonadotrophic hormone produce and released by cells in the anterior pituitary, crucial in regulating the function of the testes in men and ovaries in women
Follicle stimulating hormones (FSH)
stimulates follicle growth and oestrogen secretion (spermatogenesis in males)
Inhibin and activin
are closely related peptides produced by the ovary, testes, pituitary gland and placenta that influence gonadotrope function
Follistatin
is structurally unrelated to either inhibin or activin. It is a highly glycosylated pituitary peptide that inhibits gonadotrope function but at one-third the potency of inhibin
hypothalamus pituitary gonadal axis

in males FSh
- FSH stimulates Sertoli cells
- Spermatogenesis
- Inhibin released. Negative feedback on anterior pituitary (FSH only) and possibly hypothalamus
in men LH
-
LH stimulates Leydig cells
- Testosterone released.
- Negative feedback on hypothalamus and anterior pituitary
in females FSH
- FSH stimulates granulosa cells
- Follicular development
- Releases inhibin. Specifically inhibits FSH only
- Granulosa cells convert androgens to oestrogen
in females LH
- LH stimulates theca interna cells:
- Releases androgens. Converted to oestrogen by granulosa cells
- LH surge is required for ovulation
- LH maintains corpus luteum after ovulation. Releases progesterone and oestrogen. Lasts 12-14 days unless further stimulated by pregnancy hormone beta- hCG(released after implantation)
male reproductive tract

Spermatic cord
- Formed by the vas deferens (ductus deferens) and surrounding tissue that runs from the deep inguinal ring down to each testicle.
- The cord is present as a pair, with
one cord connecting to either the right or left testicle.
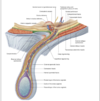
spermatic cord function
- It has multiple physiologic functions in males, including the primary function of facilitating the passage of semen.
testicular torsion
- Spermatic cord is sensitive to torsion. The testicle is prone to rotate within its sac and can kink off its own blood supply. The torsion of spermatic cord may result in irreversible damage to the testicle within hours.
Spermatic cord is also involved in indirect inguinal hernia.
the female reproductive tract

detection when things go wrong with reproductive tract
- General, obstetric and gynaecological examination (anatomy!)
- Urine tests (pregnancy)
- Blood tests (tumour biomarkers)
- Swabs (infections)
- Smears (cervical cancer)
- Imaging
- Cysts of the ovary
- Cancer (male and female) –Infertility to include endometriosis
- Pelvic floor dysfunction
reproductive system imaging
- Ultrasound
- MRI
- Fluoroscopy
- CT
- Fetal or adult anatomy?


