Lecture 06. CNS Flashcards
Central Nervous System
- Information Transfer
- Basic Pattern
- Spinal Cord
- Brain
Information Transfer
Information can pass through the CNS via Long Neural Pathways Multsynaptic Pathways
Basic Pattern of CNS

CNS - Spinal Cord

Reflexes
A reflex is a rapid, predictable motor response to a stimulus.
Reflexes may:
- Be inborn or learned (acquired)
- Involved only in peripheral nerves and the spinal cord
- Involve high brain centers as well
Reflex Arc

Reflex Classification
- Classified Functionally
- Somatic Reflexes
- Autonomic Reflexes
Reflexes in Adult Humas
- Accommodation reflex
- Achilles reflex
- Biceps stretch reflex
- Brachioradialis reflex
- Corneal reflex (also known as the blink reflex)
- Crossed extensor reflex
- Gag reflex
- Mammalian diving reflex
- Patellar reflex (knee-jerk reflex)
- Photic sneeze reflex
- Plantar reflex (Babinski reflex)
- Pupillary reflex
- Quadriceps reflex
- Salivation
- Scratch reflex
- Sneeze
- Tendon reflex
- Triceps stretch reflex
- Vestibulo-ocular reflex
- Withdrawal reflex
- Yawn
Crossed Extensor Reflex

Mammalian Diving Reflex
Submerging the face into water causes the mammalian diving reflex
Includes three factors:
- Bradycardia
- Peripheral vasoconstriction
- Blood shift
When the face is submerged, receptors that are sensitive to water within the nasal cavity and other areas of the face supplied by cranial nerve V (trigeminal) relays the information to the brain and then innervates cranial nerve X (vagus).
Photic Sneeze Reflex
A medical condition by which people exposed to bright light sneeze.
- Occurs in 17% to 25% of humans
- The probable cause is a congenital malfunction in nerve signals in the trigeminal nerve nucleus.
- Overstimulation of the optic nerve triggers the trigeminal nerve, and this causes the photic sneeze reflex.
Yawn
A reflex of deep inhalation and exhalation associated with being tired, with a need to sleep, or from lack of stimulation. Pandiculation.
- It is claimed to help increase the state of alertness of a person. It could possibly be from lack of oxygen.
- The exact causes of yawning are still unknown.
Spinal Cord Trauma: Transection
- Cross sectioning of the spinal cord at any level results in total motor and sensory loss in regions inferior to the cut
- Paraplegia – transection between T1 and L1
- Quadriplegia – transection in the cervical region
Poliomyelitis
- Destruction of the anterior horn motor neurons by the poliovirus
- Early symptoms – fever, headache, muscle pain and weakness, and loss of somatic reflexes
The Brain
- Composed of wrinkled, pinkish gray tissue
- Surface anatomy includes cerebral hemispheres, cerebellum, and brain stem
Adult Neural Canal Regions


Ventricles of The Brain

Protection of the Brain
- The brain is protected by bone, meninges, and cerebrospinal fluid
- Harmful substances are shielded from the brain by the blood-brain barrier
Meninges
- Three connective tissue membranes that lie external to the CNS – dura mater, arachnoid mater, and pia mater
- Functions of the meninges include:
- Cover
- Protect
- Contain
- Form

Dura Mater

Arachnoid Mater

Pia Mater

Cerebrospinal Fluid (CSF)

Choroid Plexuses

Blood-Brain Barrier
- Protective mechanism that helps maintain a stable environment for the brain
- Bloodborne substances are separated from neurons by:
- Continuous endothelium of capillary walls
- Relatively thick basal lamina
- Bulbous feet of astrocytes
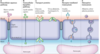
Blood-Brain Barrier: Functions
- Reduce the immune systems access to the brain
- Comprised of the cells that make up the smallest blood vessels of the brain
- Anatomical structures
- Physiological transport systems
- Accounts for some drug actions
- Morphine vs. heroin
- Accounts for some drug actions
- Many substances are not lipid soluble
- Glucose and other important brain substrates
Brain

- Brainstem
- Midbrain
- Pons
- Medulla Oblongata
- Cerebellum
- Forebrain
- Diencephalon
- Cerebrum
- Limbic System

Midbrain
- Located between the diencephalon and the pons
- Midbrain structures include:
- Corpora quadrigemina
- Superior Colliculi
- Inferior Colliculi
- Corpora quadrigemina
- Sustantia nigra
- Cerebral Aqueduct
Midbrain Nuclei

Pons

Medulla Oblongata

Cerebellum

Forebrain
- Two Regions
- Cerebrum
- Diencephalon
Cerebrum

Functional Areas: Left Cerebral Cortex

Primary Motor Cortex

Sensorymotor Cortex
- Premotor cortex
- Supplementary motor cortex
- Parietal-lobe association cortex
Somatosensory Cortex

Diencephalon

Limbic System

Cerebrovascular Accidents

Brain Atrophy in Advanced Alzheimer’s Disease

Huntingtons Disease
- Genetic disorder
- HD gene located on chromosome 4
- Extra CAG repeat on the end of the gene
- Caused by degeneration of neuronal cells
- Frontal lobes
- Basal ganglia
- Caudate nucleus
- Symptoms
- Jerky uncoordinated movements which become progressively worse
- Excecutive function, abstract thinking, speech and perceptual and spatial function are all affected
Blood Supply



